
The Andes or Andean Mountains are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. This range is about 7,000 km (4,300 mi) long, about 200 to 700 km wide, and of an average height of about 4,000 m (13,000 ft). The Andes extend from north to south through seven South American countries: Venezuela, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, Bolivia, Chile and Argentina.

La Paz, officially known as Nuestra Señora de La Paz, also named Chuqi Yapu (Chuquiago) in Aymara, is the seat of government and the de facto national capital of the Plurinational State of Bolivia. With an estimated 789,541 residents as of 2015, La Paz is the third-most populous city in Bolivia. Its metropolitan area, which is formed by La Paz, El Alto and Viacha, makes up the most populous urban area in Bolivia, with a population of 2.3 million. It is also the capital of the La Paz Department.

Sucre is the constitutional capital of Bolivia, the capital of the Chuquisaca Department and the 6th most populated city in Bolivia. Located in the south-central part of the country, Sucre lies at an elevation of 2,810 meters. This relatively high altitude gives the city a cool temperate climate year-round.

The Chaco War was fought between Bolivia and Paraguay over control of the northern part of the Gran Chaco region of South America, which was thought to be rich in oil. It is also referred to as La Guerra de la Sed in literary circles, for being fought in the semi-arid Chaco. It was the bloodiest military conflict fought in South America during the 20th century, between two of its poorest countries, both having previously lost territory to neighbors in 19th-century wars.

The President of Bolivia officially known as the President of the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is head of state and head of government of Bolivia. According to the current Constitution, the president is elected by popular vote to a five-year term, renewable once. In 2016, in a referendum the country voted to maintain term limits. Since 2009, if no candidate wins a majority, the top two candidates advance to a runoff election. Prior to 2009, if no candidate won half the popular vote, the president was chosen by a vote in a joint legislative session from among the top two candidates.
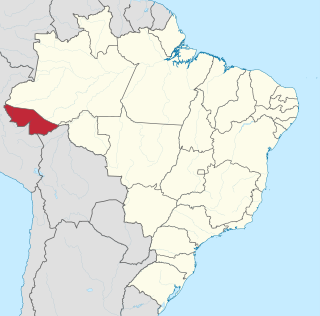
Acre is a state located in the northern region of Brazil. Located in the westernmost part of the country with a two hours time difference from Brasília, Acre is bordered clockwise by Amazonas to the north and northeast, Rondônia to the east, the Bolivian department of Pando to the southeast, and the Peruvian regions of Madre de Dios, Ucayali and Loreto to the south and west. It occupies an area of 152,581.4 km2, being slightly smaller than Tunisia.
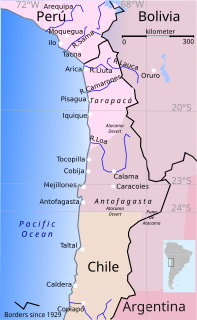
The War of the Pacific, also known as the Saltpeter War and by multiple other names was a war between Chile and a Bolivian-Peruvian alliance. It lasted from 1879 to 1884, and was fought over Chilean claims on coastal Bolivian territory in the Atacama Desert. The war ended with victory for Chile, which gained a significant amount of resource-rich territory from Peru and Bolivia. Chile's army took Bolivia's nitrate rich coastal region and Peru was defeated by Chile's navy.

Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine departments. Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the federal Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each state in proportion to their total population.

Potosí is a department in southwestern Bolivia. It comprises 118,218 km² with 823,517 inhabitants. The capital is the city of Potosí. It is mostly a barren, mountainous region with one large plateau to the west, where the largest salt flat in the world, Salar de Uyuni, is located.

Cochabamba is a city and municipality in central Bolivia in a valley in the Andes mountain range. It is the capital of the Cochabamba Department and the fourth largest city in Bolivia, with a population of 630,587 according to the 2012 Bolivian census. Its name is from a compound of the Quechua words qucha "lake" and pampa, "open plain." Residents of the city and the surrounding areas are commonly referred to as cochalas or, more formally, cochabambinos.

The Bolivia national football team, also known as La Verde or Los Sin Mar, has represented Bolivia in international football since 1926. Organized by the Bolivian Football Federation (FBF), it is one of the 10 members of FIFA's South American Football Confederation (CONMEBOL).

A province is the second largest administrative division in Bolivia, after a department. Each department is divided into provinces. There are 112 provinces.

The Bolivian Football Federation is the governing body of football in Bolivia. It was founded in 1925, making it the eighth oldest South American federation. It affiliated to CONMEBOL and FIFA in 1926 and is in charge of Bolivia national football team.

The Vice President of the Plurinational State of Bolivia or Vice President of Bolivia, is the second highest political position in Bolivia. The Vice President replaces the President in his definitive absence or others impediment and is the President of the Legislative Assembly.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Bolivia:

Bolivia–Russia relations is the relationship between the two countries, Bolivia and Russia. Russia has an embassy in La Paz, and Bolivia has an embassy in Moscow.

Chearoco, Chiaraco or Chiaroco is a mountain in the Cordillera Real in the Andes of Bolivia. It has a height of about 6,127 m (20,102 ft). It is situated in the La Paz Department, Larecaja Province, Guanay Municipality, southeast of the peak of Aman Pata. Chearoco lies between Qalsata in the northwest and Chachakumani in the southeast.

Bolivian cuisine stems from the combination of Spanish cuisine with indigenous ingredients and Aymara traditions, among others, with later influences from Germans, Italians, French, and Arabs due to the arrival of immigrants from those countries. The traditional staples of Bolivian cuisine are corn, potatoes, quinoa and beans. These ingredients have been combined with a number of staples brought by the Spanish, such as rice, wheat, and meat, including beef, pork, and chicken.
The history of the Jews in Bolivia stretches from the colonial period of Bolivia in the 16th century to the end of the 19th century. In the 19th century, Jewish merchants came to Bolivia, most of them taking local women as wives and founding families that merged into the mainstream Catholic society. This was often the case in the eastern regions of Santa Cruz, Tarija, Beni and Pando, where these merchants came either from Brazil or Argentina.















