| Look up elbe or Elbe in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Elbe is a river in the Czech Republic and Germany.
Contents
Elbe may also refer to:
| Look up elbe or Elbe in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
Elbe is a river in the Czech Republic and Germany.
Elbe may also refer to:

The Elbe, historically in English also Elve, is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia, then Germany and flowing into the North Sea at Cuxhaven, 110 kilometres northwest of Hamburg. Its total length is 1,094 km (680 mi).

The Elbe–Lübeck Canal is an artificial waterway in eastern Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It connects the rivers Elbe and Trave, creating an inland water route across the drainage divide from the North Sea to the Baltic Sea. The canal includes seven locks and runs for a length of 64 kilometres (40 mi) between the cities of Lübeck in the north and Lauenburg in the south by way of the Mölln lakes. The modern canal was built in the 1890s to replace the Stecknitz Canal, a medieval watercourse linking the same two rivers.

The Havel is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and 325 kilometres (202 mi) long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mouth is only 94 kilometres (58 mi). For much of its length, the Havel is navigable; it provides an important link in the waterway connections between the east and west of Germany, as well as beyond.

A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary between maritime shipping routes and waterways used by inland water craft. Maritime shipping routes cross oceans and seas, and some lakes, where navigability is assumed, and no engineering is required, except to provide the draft for deep-sea shipping to approach seaports (channels), or to provide a short cut across an isthmus; this is the function of ship canals. Dredged channels in the sea are not usually described as waterways. There is an exception to this initial distinction, essentially for legal purposes, see under international waters.

A replenishment oiler or replenishment tanker is a naval auxiliary ship with fuel tanks and dry cargo holds which can supply both fuel and dry stores during underway replenishment (UNREP) at sea. Many countries have used replenishment oilers.

The Port of Hamburg is a seaport on the river Elbe in Hamburg, Germany, 110 kilometres (68 mi) from its mouth on the North Sea.

The Type 404 Elbe-class replenishment ships of the German Navy were built to support its squadrons of Fast Attack Craft, submarines and minesweeper/hunters, as such they are usually referred to as tenders.

The Eisvogel class icebreakers was a two ship class built for the German Navy by the Hitzler Werft shipyard of Lauenburg/Elbe.

SS Elbe was a transatlantic ocean liner built in the Govan Shipyard of John Elder & Company, Ltd, Glasgow, in 1881 for the Norddeutscher Lloyd of Bremen. She foundered on the night of 30 January 1895 following a collision in the North Sea with the loss of 334 lives.

The MV Greenpeace was a Greenpeace ship built in 1959 as an oceangoing tug/salvage vessel. She was purchased by Greenpeace in 1985 from the Maryland Pilotage Company, the vessel then being named MV Maryland, and transferred back to the Netherlands to be refitted with modern equipment before being recommissioned. She took over from the first Rainbow Warrior, which had been sunk in 1985 by French commandos. In 2001 she was replaced by the MV Esperanza.

AIDAluna is a Sphinx class cruise ship, owned by US based Carnival Corp and operated by AIDA Cruises. Built by Meyer Werft shipyards in Papenburg, Germany, she is the third ship of the class, preceded by AIDAdiva and AIDAbella, and is followed by AIDAblu, AIDAsol, and AIDAmar. The ship has a capacity of 2,100 passengers and has a gross tonnage of 69,203. AIDAluna was initially deployed in the Baltic Sea for the 2009 Summer season. In Winter 2009, she was redeployed in Canary Islands. AIDAluna has an 8 × 4.5-m poolside theater, which is a first for AIDA Cruises.
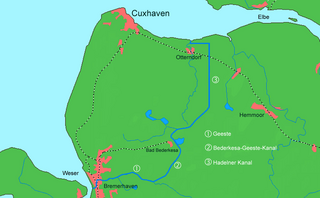
The Elbe–Weser waterway or Elbe–Weser shipping channel is a short-cut between the rivers Elbe and Weser in North Germany which is part-canal and part-river. It has a length of 54.7 kilometres (34.0 mi) and is designed for smaller coastal vessels. It includes some 60 kilometres (37 mi) of canal dykes and 45 kilometres (28 mi) of canal paths. The channel starts in Otterndorf with the Hadeln Canal, then becomes the Bederkesa-Geeste Canal from the town of Bad Bederkesa to the River Geeste, the final leg of the shipping channel, which flows into the Weser at Bremerhaven. It is owned by the state of Lower Saxony, maintained by the NLWKN from its Stade office. Today they just look after maintenance of the drainage system, because the economic element of the canal – commercial shipping which was particularly thriving in the late 1960s – declined increasingly from 1973 onwards and today hardly exists at all. Nevertheless the waterway is still used by smaller yachts as a short cut between Elbe and Weser.
Amazon most often refers to:

HMS Piercer was a Royal Navy Archer-class gun-brig launched in 1804. She served against the French, Danes and Dutch in the Napoleonic Wars and was assigned to the Downs station. She participated in a number of operations in the Bay of Biscay, the English Channel, and the North Sea. In 1814 the British government transferred Piercer to the Kingdom of Hanover for use as a guard ship. Hanover decommissioned her in 1850.

Steinwerder is a quarter of Hamburg, Germany in the borough Hamburg-Mitte on the southern bank of the river Elbe. It is a primarily maritime industrial location, with a resident population in 2017 of only 39.

Roald Amundsen, originally named Vilm, is a German steel-ship built on the Elbe River in 1952. Having worked in different areas, she was refitted in 1992 to 1993 as a brig and now serves as a sail training ship. During summer, she usually operates in the Baltic Sea, and usually embarks for journeys to farther destinations for winter, including several trans-Atlantic crossings.

CSCL Indian Ocean is a container ship, operated by China Shipping Container Lines. She was built in Ulsan, Korea, by Hyundai Heavy Industries, and launched on November 15, 2014. At the time of her construction she, and her four sister ships, CSCL Globe, CSCL Pacific Ocean, CSCL Atlantic Ocean and CSCL Arctic Ocean, were the largest container ships afloat, each carrying 19,100 twenty-foot equivalent unit containers. Chinese officials said the vessels cost $136 million each to build.

SMS Cyclop was a Camäleon-class gunboat of the Prussian Navy that was launched in 1860. A small vessel, armed with only three light guns, Cyclop served during the three wars of German unification; during the first, the Second Schleswig War on 1864, she guarded the Prussian coastline but saw no action. She supported the army's campaign against the Kingdom of Hanover during the Austro-Prussian War of 1866, and she defended the Elbe for the duration of the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871, but again took part in no battles. Badly deteriorated by 1872, she was stricken from the naval register in March that year and reconstructed into an iron-hulled gunboat. Recommissioned in 1875, she thereafter served abroad in the German colonial empire before being stricken again in 1888. She was thereafter used as a storage hulk before ultimately being broken up for scrap after 1914.

Elbe (A511) is the lead ship of the Elbe-class replenishment ships of the German Navy.

Mosel (A512) is the second ship of the Elbe-class replenishment ships of the German Navy.