Biostatistics is a branch of statistics that applies statistical methods to a wide range of topics in biology. It encompasses the design of biological experiments, the collection and analysis of data from those experiments and the interpretation of the results.
Dysgeusia, also known as parageusia, is a distortion of the sense of taste. Dysgeusia is also often associated with ageusia, which is the complete lack of taste, and hypogeusia, which is a decrease in taste sensitivity. An alteration in taste or smell may be a secondary process in various disease states, or it may be the primary symptom. The distortion in the sense of taste is the only symptom, and diagnosis is usually complicated since the sense of taste is tied together with other sensory systems. Common causes of dysgeusia include chemotherapy, asthma treatment with albuterol, and zinc deficiency. Liver disease, hypothyroidism, and rarely, certain types of seizures can also lead to dysgeusia. Different drugs can also be responsible for altering taste and resulting in dysgeusia. Due to the variety of causes of dysgeusia, there are many possible treatments that are effective in alleviating or terminating the symptoms. These include artificial saliva, pilocarpine, zinc supplementation, alterations in drug therapy, and alpha lipoic acid.
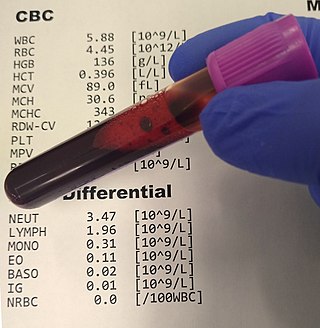
A complete blood count (CBC), also known as a full blood count (FBC), is a set of medical laboratory tests that provide information about the cells in a person's blood. The CBC indicates the counts of white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, the concentration of hemoglobin, and the hematocrit. The red blood cell indices, which indicate the average size and hemoglobin content of red blood cells, are also reported, and a white blood cell differential, which counts the different types of white blood cells, may be included.

Electronic test equipment is used to create signals and capture responses from electronic devices under test (DUTs). In this way, the proper operation of the DUT can be proven or faults in the device can be traced. Use of electronic test equipment is essential to any serious work on electronics systems.

A sphygmomanometer, a.k.a. a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury or aneroid manometer to measure the pressure. Manual sphygmomanometers are used with a stethoscope when using the auscultatory technique.

A scientific control is an experiment or observation designed to minimize the effects of variables other than the independent variable. This increases the reliability of the results, often through a comparison between control measurements and the other measurements. Scientific controls are a part of the scientific method.
In neuroscience and psychophysics, an absolute threshold was originally defined as the lowest level of a stimulus – light, sound, touch, etc. – that an organism could detect. Under the influence of signal detection theory, absolute threshold has been redefined as the level at which a stimulus will be detected a specified percentage of the time. The absolute threshold can be influenced by several different factors, such as the subject's motivations and expectations, cognitive processes, and whether the subject is adapted to the stimulus.
The absolute threshold can be compared to the difference threshold, which is the measure of how different two stimuli must be for the subject to notice that they are not the same.

Somnology is the scientific study of sleep. It includes clinical study and treatment of sleep disorders and irregularities. Sleep medicine is a subset of somnology.

Antibiotic sensitivity testing or antibiotic susceptibility testing is the measurement of the susceptibility of bacteria to antibiotics. It is used because bacteria may have resistance to some antibiotics. Sensitivity testing results can allow a clinician to change the choice of antibiotics from empiric therapy, which is when an antibiotic is selected based on clinical suspicion about the site of an infection and common causative bacteria, to directed therapy, in which the choice of antibiotic is based on knowledge of the organism and its sensitivities.
In statistical hypothesis testing, a type I error is the mistaken rejection of a null hypothesis that is actually true. A type I error is also known as a "false positive" finding or conclusion; example: "an innocent person is convicted". A type II error is the failure to reject a null hypothesis that is actually false. A type II error is also known as a "false negative" finding or conclusion; example: "a guilty person is not convicted". Much of statistical theory revolves around the minimization of one or both of these errors, though the complete elimination of either is a statistical impossibility if the outcome is not determined by a known, observable causal process. By selecting a low threshold (cut-off) value and modifying the alpha (α) level, the quality of the hypothesis test can be increased. The knowledge of type I errors and type II errors is widely used in medical science, biometrics and computer science.

Microarray analysis techniques are used in interpreting the data generated from experiments on DNA, RNA, and protein microarrays, which allow researchers to investigate the expression state of a large number of genes – in many cases, an organism's entire genome – in a single experiment. Such experiments can generate very large amounts of data, allowing researchers to assess the overall state of a cell or organism. Data in such large quantities is difficult – if not impossible – to analyze without the help of computer programs.
Medical statistics deals with applications of statistics to medicine and the health sciences, including epidemiology, public health, forensic medicine, and clinical research. Medical statistics has been a recognized branch of statistics in the United Kingdom for more than 40 years but the term has not come into general use in North America, where the wider term 'biostatistics' is more commonly used. However, "biostatistics" more commonly connotes all applications of statistics to biology. Medical statistics is a subdiscipline of statistics. "It is the science of summarizing, collecting, presenting and interpreting data in medical practice, and using them to estimate the magnitude of associations and test hypotheses. It has a central role in medical investigations. It not only provides a way of organizing information on a wider and more formal basis than relying on the exchange of anecdotes and personal experience, but also takes into account the intrinsic variation inherent in most biological processes."
The Canadian Advanced Nanospace eXperiment (CanX) program is a Canadian CubeSat nanosatellite program operated by the University of Toronto Institute for Aerospace Studies, Space Flight Laboratory (UTIAS/SFL). The program's objectives are to involve graduate students in the process of spaceflight development, and to provide low-cost access to space for scientific research and the testing of nanoscale devices. The CanX projects include CanX-1, CanX-2, the BRIght Target Explorer (BRITE), and CanX-4&5.
Julian B. Rotter was an American psychologist known for developing social learning theory and research into locus of control. He was a faculty member at Ohio State University and then the University of Connecticut. A Review of General Psychology survey, published in 2002, ranked Rotter as the 64th most eminent and 18th most widely cited psychologist of the 20th century. A 2014 study published in 2014 placed at #54 among psychologists whose careers spanned the post-World War II era.

Two-point discrimination (2PD) is the ability to discern that two nearby objects touching the skin are truly two distinct points, not one. It is often tested with two sharp points during a neurological examination and is assumed to reflect how finely innervated an area of skin is.

An olfactometer is an instrument used to detect and measure odor dilution. Olfactometers are used in conjunction with human subjects in laboratory settings, most often in market research, to quantify and qualify human olfaction. Olfactometers are used to gauge the odor detection threshold of substances. To measure intensity, olfactometers introduce an odorous gas as a baseline against which other odors are compared.

Esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document reflux disease, assess the severity of the disease and monitor the response of the disease to medical or surgical treatment. It can also be used in diagnosing laryngopharyngeal reflux.

In the design of experiments, a between-group design is an experiment that has two or more groups of subjects each being tested by a different testing factor simultaneously. This design is usually used in place of, or in some cases in conjunction with, the within-subject design, which applies the same variations of conditions to each subject to observe the reactions. The simplest between-group design occurs with two groups; one is generally regarded as the treatment group, which receives the ‘special’ treatment, and the control group, which receives no variable treatment and is used as a reference. The between-group design is widely used in psychological, economic, and sociological experiments, as well as in several other fields in the natural or social sciences.

In medicine, monitoring is the observation of a disease, condition or one or several medical parameters over time.
Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve Explorer and Tester (ROCCET) is an open-access web server for performing biomarker analysis using ROC curve analyses on metabolomic data sets. ROCCET is designed specifically for performing and assessing a standard binary classification test. ROCCET accepts metabolite data tables, with or without clinical/observational variables, as input and performs extensive biomarker analysis and biomarker identification using these input data. It operates through a menu-based navigation system that allows users to identify or assess those clinical variables and/or metabolites that contain the maximal diagnostic or class-predictive information. ROCCET supports both manual and semi-automated feature selection and is able to automatically generate a variety of mathematical models that maximize the sensitivity and specificity of the biomarker(s) while minimizing the number of biomarkers used in the biomarker model. ROCCET also supports the rigorous assessment of the quality and robustness of newly discovered biomarkers using permutation testing, hold-out testing and cross-validation.











