
An electromagnetic coil is an electrical conductor such as a wire in the shape of a coil. Electromagnetic coils are used in electrical engineering, in applications where electric currents interact with magnetic fields, in devices such as electric motors, generators, inductors, electromagnets, transformers, and sensor coils. Either an electric current is passed through the wire of the coil to generate a magnetic field, or conversely, an external time-varying magnetic field through the interior of the coil generates an EMF (voltage) in the conductor.

An inductor, also called a coil, choke, or reactor, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that stores energy in a magnetic field when electric current flows through it. An inductor typically consists of an insulated wire wound into a coil.
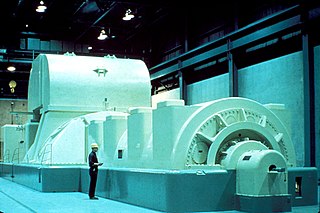
In electricity generation, a generator is a device that converts motion-based power or fuel-based power into electric power for use in an external circuit. Sources of mechanical energy include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. Generators provide nearly all the power for electrical grids.
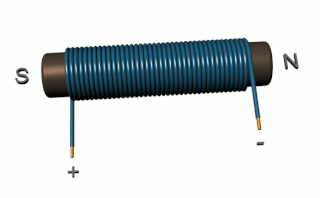
An electromagnet is a type of magnet in which the magnetic field is produced by an electric current. Electromagnets usually consist of wire wound into a coil. A current through the wire creates a magnetic field which is concentrated in the hole in the center of the coil. The magnetic field disappears when the current is turned off. The wire turns are often wound around a magnetic core made from a ferromagnetic or ferrimagnetic material such as iron; the magnetic core concentrates the magnetic flux and makes a more powerful magnet.
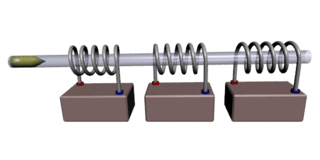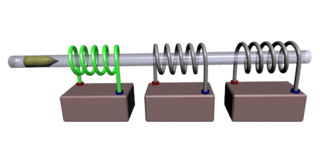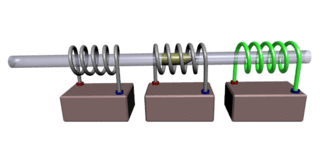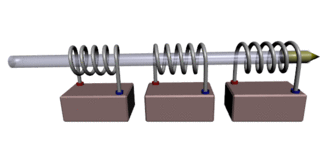
A coilgun is a type of mass driver consisting of one or more coils used as electromagnets in the configuration of a linear motor that accelerate a ferromagnetic or conducting projectile to high velocity. In almost all coilgun configurations, the coils and the gun barrel are arranged on a common axis. A coilgun is not a rifle as the barrel is smoothbore.

A DC motor is any of a class of rotary electrical motors that converts direct current (DC) electrical energy into mechanical energy. The most common types rely on the forces produced by induced magnetic fields due to flowing current in the coil. Nearly all types of DC motors have some internal mechanism, either electromechanical or electronic, to periodically change the direction of current in part of the motor.

A contactor is an electrically-controlled switch used for switching an electrical power circuit. A contactor is typically controlled by a circuit which has a much lower power level than the switched circuit, such as a 24-volt coil electromagnet controlling a 230-volt motor switch.
Eddy-current testing is one of many electromagnetic testing methods used in nondestructive testing (NDT) making use of electromagnetic induction to detect and characterize surface and sub-surface flaws in conductive materials.

The arc converter, sometimes called the arc transmitter, or Poulsen arc after Danish engineer Valdemar Poulsen who invented it in 1903, was a variety of spark transmitter used in early wireless telegraphy. The arc converter used an electric arc to convert direct current electricity into radio frequency alternating current. It was used as a radio transmitter from 1903 until the 1920s when it was replaced by vacuum tube transmitters. One of the first transmitters that could generate continuous sinusoidal waves, it was one of the first technologies used to transmit sound by radio. It is on the list of IEEE Milestones as a historic achievement in electrical engineering.

A string galvanometer is a sensitive fast-responding measuring instrument that uses a single fine filament of wire suspended in a strong magnetic field to measure small currents. In use, a strong light source is used to illuminate the fine filament, and the optical system magnifies the movement of the filament allowing it to be observed or recorded by photography. The principle of the string galvanometer remained in use for electrocardiograms until the advent of electronic vacuum-tube amplifiers in the 1920s.

William Du Bois Duddell was an English physicist and electrical engineer. His inventions include the moving coil oscillograph, as well as the thermo-ammeter and thermo-galvanometer.
An inductive sensor is a device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to detect or measure objects. An inductor develops a magnetic field when an electric current flows through it; alternatively, a current will flow through a circuit containing an inductor when the magnetic field through it changes. This effect can be used to detect metallic objects that interact with a magnetic field. Non-metallic substances, such as liquids or some kinds of dirt, do not interact with the magnetic field, so an inductive sensor can operate in wet or dirty conditions.

A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundation upon which many other later electric-power conversion devices were based, including the electric motor, the alternating-current alternator, and the rotary converter.
The Dennis Gabor Medal and Prize is a prize awarded biannually by the Institute of Physics for distinguished contributions to the application of physics in an industrial, commercial or business context. The medal is made of silver and is accompanied by a prize and a certificate.

A magnetic starter is an electromagnetically operated switch which provides a safe method for starting an electric motor with a large load. Magnetic starters also provide under-voltage and overload protection and an automatic cutoff in the event of a power failure.

André-Eugène Blondel was a French engineer and physicist. He is the inventor of the electromechanical oscillograph and a system of photometric units of measurement.
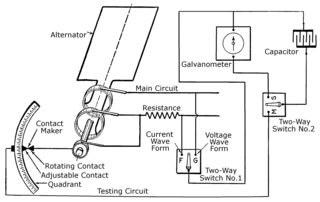
The history of the oscilloscope was fundamental to science because an oscilloscope is a device for viewing waveform oscillations, as of electrical voltage or current, in order to measure frequency and other wave characteristics. This was important in developing electromagnetic theory. The first recordings of waveforms were with a galvanometer coupled to a mechanical drawing system dating from the second decade of the 19th century. The modern day digital oscilloscope is a consequence of multiple generations of development of the oscillograph, cathode-ray tubes, analog oscilloscopes, and digital electronics.

The thermo-galvanometer is an instrument for measuring small electric currents. It was invented by William Duddell about 1900. The following is a description of the instrument taken from a trade catalog of Cambridge Scientific Instrument Company dated 1905:
For a long time the need of an instrument capable of accurately measuring small alternating currents has been keenly felt. The high resistance and self-induction of the coils of instruments of the electro-magnetic type frequently prevent their use. Electro-static instruments as at present constructed are not altogether suitable for measuring very small currents, unless a sufficient potential difference is available.
The thermo-galvanometer designed by Mr W. Duddell can be used for the measurement of extremely small currents to a high degree of accuracy. It has practically no self-induction or capacity and can therefore be used on a circuit of any frequency and currents as small as twenty micro-amperes can be readily measured by it. It is equally correct on continuous and alternating currents. It can therefore be accurately standardized by continuous current and used without error on circuits of any frequency or wave-form.
The principle of the thermo-galvanometer is simple. The instrument consists of a resistance which is heated by the current to be measured, the heat from the resistance falling on the thermo-junction of a Boys radio-micrometer. The rise in temperature of the lower junction of the thermo-couple produces a current in the loop which is deflected by the magnetic field against the torsion of the quartz fibre.

Electromagnetic articulography (EMA) is a method of measuring the position of parts of the mouth. EMA uses sensor coils placed on the tongue and other parts of the mouth to measure their position and movement over time during speech and swallowing. Induction coils around the head produce an electromagnetic field that creates, or induces, a current in the sensors in the mouth. Because the current induced is inversely proportional to the cube of the distance, a computer is able to analyse the current produced and determine the sensor coil's location in space.
Electromagnetically induced acoustic noise (and vibration), electromagnetically excited acoustic noise, or more commonly known as coil whine, is audible sound directly produced by materials vibrating under the excitation of electromagnetic forces. Some examples of this noise include the mains hum, hum of transformers, the whine of some rotating electric machines, or the buzz of fluorescent lamps. The hissing of high voltage transmission lines is due to corona discharge, not magnetism.
















