
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the second-most-populous city in Brazil and the sixth-most-populous city in the Americas.

Petrópolis, also known as the Imperial City, is a municipality in the Southeast Region of Brazil. It is located in the state of Rio de Janeiro, 68 kilometres (42 mi) northeast of the city of Rio de Janeiro. According to the 2022 Brazilian census, Petrópolis municipality had a population of 278,881 inhabitants. Besides being the largest and most populous city in the Fluminense Mountain Region, the city also has the largest GDP and HDI in the region.

The Federal University of Rio de Janeiro (UFRJ), alternatively known as University of Brazil, is a public research university in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is the largest federal university in the country and is one of the Brazilian centers of excellence in teaching and research.

Angra Nuclear Power Plant is Brazil's only nuclear power plant. It is located at the Central Nuclear Almirante Álvaro Alberto (CNAAA) on the Itaorna Beach in Angra dos Reis, Rio de Janeiro. It consists of two pressurized water reactors (PWR), Angra I, with a net output of 609 MWe, first connected to the power grid in 1985 and Angra II, with a net output of 1,275 MWe, connected in 2000.

Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A. is a major Brazilian electric utilities company. The company's headquarters are located in Rio de Janeiro.

Luiz Pinguelli Rosa was a Brazilian scientist.

CPFL Energia (former name: Companhia Paulista de Força e Luz) is the second largest non state-owned group of electric energy generation and distribution in Brazil and the third biggest Brazilian electric utility company, after Eletrobras and Energisa. The corporation is composed by CPFL Brasil, CPFL Piratininga, CPFL Paulista, CPFL Geração, CPFL Renováveis, Rio Grande Energia (RGE) and SEMESA. Each of these companies operates as a holding company that owns dozens of other companies. Its headquarters are located in Campinas, the third-largest city in state of São Paulo. In 2017, it was purchased by the Chinese utility State Grid Corporation of China, a state-owned enterprise under State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council.
GE Aerospace Research, formerly GE Research, is the research and development division of GE Aerospace. Before 2024, it was a division of the General Electric Company, which split three ways between 2023 and 2024 and pivoted to aviation.

Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in workshops dating from the beginning of the 19th century. Most of the country's industrial establishments appeared in the Brazilian southeast, and, according to the Commerce, Agriculture, Factories and Navigation Joint, 77 establishments registered between 1808 and 1840 were classified as "factories" or "manufacturers". However, most, about 56 establishments, would be considered workshops by today's standards, directed toward the production of soap and tallow candles, snuff, spinning and weaving, foods, melting of iron and metals, wool and silk, amongst others. They used both slaves and free laborers.

Rio de Janeiro State University is a public research university in the state of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is one of the largest and most prestigious universities in the country. The university's law and medical schools are among the best in the nation. Its Biology, Social Science, Nursing and Philosophy courses are also highly praised, as stated by Guia do Estudante.

Brazil is the 7th largest energy consumer in the world and the largest in South America. At the same time, it is an important oil and gas producer in the region and the world's second largest ethanol fuel producer. The government agencies responsible for energy policy are the Ministry of Mines and Energy (MME), the National Council for Energy Policy (CNPE), the National Agency of Petroleum, Natural Gas and Biofuels (ANP) and the National Agency of Electricity (ANEEL). State-owned companies Petrobras and Eletrobras are the major players in Brazil's energy sector, as well as Latin America's.

Greater Rio de Janeiro, officially the Rio de Janeiro Metropolitan Region is a large metropolitan area located in Rio de Janeiro state in Brazil, the second largest in Brazil and third largest in South America. It consists of 22 municipalities, including the state capital, Rio de Janeiro.

The Tucuruí Dam is a concrete gravity dam on the Tocantins River located on the Tucuruí County in the State of Pará, Brazil. The main purpose of the dam is hydroelectric power production and navigation. It is the first large-scale hydroelectric project in the Brazilian Amazon rainforest. The installed capacity of the 25-unit plant is 8,370 megawatts (11,220,000 hp). Phase I construction began in 1980 and ended in 1984 while Phase II began in 1998 and ended in 2010. The dam was featured in the 1985 film The Emerald Forest.

Centro is a neighborhood in the Central Region of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It represents the financial heart of the city, and the crux of the Central Region.
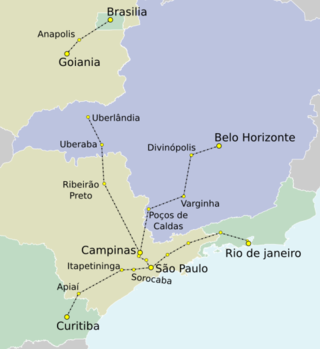
The TAV is Brazil's first planned high-speed rail service. The first line is proposed to run between Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo. It will travel 403 kilometres (250 mi) between Barão de Mauá station and Campo de Marte Airport. The journey will take 85 minutes, reaching a maximum speed of 350 kilometres per hour (220 mph).

Eletrobras Furnas is a regional power utility and a major subsidiary of Eletrobras. The company generates or transmits electricity to 51% of households in Brazil and more than 40% of the nation's electricity passes through their grid. The company has a generating capacity of 10,050 MW which corresponds to 10% of Brazil's electrical production.

Fundação Getulio Vargas is a Brazilian higher education institution and think tank founded on December 20, 1944.

The Polytechnic School of Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, also called "Poli", founded in 1792, is the third oldest engineering school in the world and oldest in the Americas, with the Military Institute of Engineering being one of the first institutions of higher education in Brazil. It is considered one of the best institutions of Latin America in engineering education. It is located in the UFRJ Center of Technology (CT), in the Cidade Universitária, Rio de Janeiro.

The Garabí Dam, is a planned dam and generating station on the Uruguay River between Argentina and Brazil. Part of the Garabí-Panambi Hydroelectric Complex. There is some controversy over the environmental impact on the fast-flowing river.
Mario Veiga Ferraz Pereira is a Brazilian scientist and engineer known as Mario Veiga in Brazil and Mario Pereira outside Brazil. He founded PSR, a consulting and software development company in the energy sector. He is best known for his work in electrical engineering and operations research. Mario Pereira is also known for developing the Stochastic Dual Dynamic Programming algorithm, used to solve multistage stochastic programming problems, in particular in the context of power system operation and planning.

















