This article needs editing to comply with Wikipedia's Manual of Style.(February 2018) |
Eli A. Friedman (born in Brooklyn, New York, April 9, 1933) is an American nephrologist.
This article needs editing to comply with Wikipedia's Manual of Style.(February 2018) |
Eli A. Friedman (born in Brooklyn, New York, April 9, 1933) is an American nephrologist.
Friedman attended New Utrecht High School, Brooklyn College, and the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center where he received an M.D. degree in 1957. In 1957, Friedman married Mildred Barrett-Lennard with whom he fathered three daughters: Amy Louise, Rebecca Alica, and Sara Jo. He served as Intern, Nephrology Fellow, and Senior Medical Resident at Harvard Medical School's Peter Bent Brigham Hospital from 1957 to 1961. After two years as an Epidemic Intelligence Officer for the United States Public Health Service's Communicable Disease Center, from 1961 to 1963, Friedman returned to SUNY Downstate in Brooklyn, New York, where he is currently a Distinguished Teaching Professor of Medicine. Dr. Friedman was Chief of the Division of Nephrology in SUNY Downstate's Department of Medicine until 2009.
In 1976, Friedman invented the "Suitcase Kidney," a portable dialysis machine scaled to fit a metal attache case that permits dialysis patients to be mobile performing their hemodialysis off site in hotel rooms or on ships. By being able to dialyze themselves, patients gained a large degree of freedom from large, centralized treatment centers enhancing their life quality. Exceptionally high liability insurance rates restricted the broad utilization of the device which still is limited in application.
Mildred died in 1997. Following his wife's death, Friedman's research focused on kidney failure. Friedman has performed clinical studies in the course of diabetes and high blood pressure. His work has been recognized by the American College of Physicians which conferred the distinction of terming him a "Master." He received two honorary degrees (University of Madras, India and Long Island University, New York) and has been made a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians in the United Kingdom. Having edited nine books and published over 520 peer reviewed papers, Friedman is a recognized authority in nephrology, serving as president of several scientific societies, including the American and International Societies for Artificial Organs and The International Society for Geriatric Nephrology and Urology. Friedman has been consistently listed as a "Best Doctor" in New York and the National and International Who's Who. Both the International Society for Hemodialysis and the Alumni Association of Downstate Medical Center awarded Lifetime Achievement Awards to Friedman who celebrated his 79th Birthday in 2011.
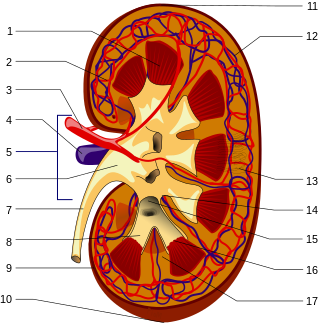
Nephrology is a specialty for both adult internal medicine and pediatric medicine that concerns the study of the kidneys, specifically normal kidney function and kidney disease, the preservation of kidney health, and the treatment of kidney disease, from diet and medication to renal replacement therapy. The word "renal" is an adjective meaning "relating to the kidneys", and its roots are French or late Latin. Whereas according to some opinions, "renal" and "nephro" should be replaced with "kidney" in scientific writings such as "kidney medicine" or "kidney replacement therapy", other experts have advocated preserving the use of renal and nephro as appropriate including in "nephrology" and "renal replacement therapy", respectively.

Kidney dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. This is referred to as renal replacement therapy. The first successful dialysis was performed in 1943.

Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapies. An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis.

New York Medical College is a private medical school in Valhalla, New York. Founded in 1860, it is a member of the Touro University System.

SUNY Downstate Medical Center is a public medical school and hospital in Brooklyn, New York. It is the southernmost member of the State University of New York (SUNY) system and the only academic medical center for health education, research, and patient care serving Brooklyn's 2.5 million residents. As of Fall 2018, it had a total student body of 1,846 and approximately 8,000 faculty and staff.
Nils Alwall was a Swedish professor at Lund University, Sweden. He was a pioneer in hemodialysis and the inventor of one of the first practical dialysis machines. Alwall pioneered the technique of ultrafiltration and introduced the principle of hemofiltration. Alwall is referred to as the "father of extracorporeal blood treatment."

Joseph Wetherill Eschbach was an American doctor and kidney specialist whose twenty years of research starting in the 1960s led to an improvement in the treatment of anemia.

Northwest Kidney Centers is a regional, not-for-profit community-based provider of kidney dialysis, public health education, and research into the causes and treatments of chronic kidney disease. Established in Seattle in 1962, it was the world's first out-of-hospital dialysis provider. It offers dialysis throughout the greater Seattle area in 20 free-standing clinics, eight hospitals and its home dialysis program. It opened its first clinic in Everett in 2020, the organization's first in Snohomish county.
Dr. T. K. Sreepada Rao is a well known nephrologist of Indian origin in the U.S. His biggest scientific achievement is discovering two new renal diseases namely Nephropathy associated with Intravenous heroin addiction in early 1970s, and Nephropathy associated with HIV infection in early 80's. His professional achievement was to transport two cadaver donor kidneys from New York to Bombay, and participate in the renal transplantation when such concept was unknown in India. He has more than 130 scientific publications to his credit. He is one of the few International Medical Graduates who has a Tenured Professorship in a Medical School in the United States.

Robert Provenzano is an American nephrologist. He is also an Associate Clinical Professor of Medicine at Wayne State University School of Medicine.
The Rogosin Institute is an independent, not-for-profit treatment and research center with facilities throughout New York City that treat patients with kidney disease, including dialysis and kidney transplantation; lipid disorders; and hypertension. It is affiliated with NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medical College and is a leader in research programs for cancer and diabetes.
Dialysis Clinic, Inc. is a nonprofit medical corporation founded in 1971 and chartered as a 501(c)(3) tax-exempt organization under IRS regulations.
Nathan W. Levin is an American physician and founder of the Renal Research Institute, LLC., a research institute dedicated to improving the outcomes of patients with kidney disease, particularly those requiring dialysis. Levin is one of the most prominent and renowned figures in clinical nephrology as well as nephrology research. He has authored multiple book chapters and over 350 peer-reviewed publications, including articles in leading journals such as Nature, the New England Journal of Medicine, and The Lancet.
Andrew Peter Lundin III (1944–2001) was a nephrologist. He was Assistant Professor of Medicine at SUNY Downstate Medical Center.
Samuel Lee Kountz Jr. was an African-American kidney transplantation surgeon from Lexa, Arkansas. He was most distinguished for his pioneering work in the field of kidney transplantations, and in research, discoveries, and inventions in Renal Science. In 1961, while working at the Stanford University Medical Center, he performed the first successful Kidney transplant between humans who were not identical twins. Six years later, he and a team of researchers at the University of California, San Francisco, developed the prototype for the Belzer kidney perfusion machine, a device that can preserve kidneys for up to 50 hours from the time they are taken from a donor's body. It is now standard equipment in hospitals and research laboratories around the world.
Mohamed Hussain Rezvi Sheriff, FRCP (Lon), FRCPE (Edin), FRACP, FCCP, FSLCGP, FNASSL is a Sri Lankan academic, nephrologist and physician. He served as the director of the Postgraduate Institute of Medicine; senior professor of medicine; head of the Department of Clinical Medicine at the Faculty of Medicine, University of Colombo. He is currently serving as the Senior Professor of Medicine at General Sir John Kotelawala Defence University. He is also a consultant physician and nephrologist at National Hospital of Sri Lanka. He is also the founder and owner of Western Hospital.
Kamyar Kalantar-Zadeh is a US American physician doing research in nephrology, kidney dialysis, nutrition, and epidemiology. He is best known as a specialist in kidney disease nutrition and chronic kidney disease and for his hypothesis about the longevity of individuals with chronic disease states, also known as reverse epidemiology including obesity paradox. According to this hypothesis, obesity or hypercholesterolemia may counterintuitively be protective and associated with greater survival in certain groups of people, such as elderly individuals, dialysis patients, or those with chronic disease states and wasting syndrome (cachexia), whereas normal to low body mass index or normal values of serum cholesterol may be detrimental and associated with worse mortality. Kalantar-Zadeh is also known for his expertise in kidney dialysis therapy, including incremental dialysis, as well as renal nutrition. He is the brother of Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh, who is an Australian scientist involved in research in the fields of materials sciences, nanotechnology, and transducers.

The SUNY Downstate Health Sciences University is a public medical school in Brooklyn, New York City. The university includes the College of Medicine, College of Nursing, School of Health Professions, School of Graduate Studies and School of Public Health.
Sree Bhushan Raju M.D., D.M., Diplomate of National Board, is a nephrologist from Telangana, India. He is currently Senior professor and Unit head, Dept of Nephrology, Nizam's Institute of Medical Sciences Panjagutta, Hyderabad. Which is one of the largest Nephrology teaching Department in India having ten DM seats. He is one of the principal investigators of CKD task force by Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) to evaluate the prevalence of CKD in adult urban population in India. He is currently an associate editor of Indian Journal of Nephrology, Indian Journal of Organ Transplantation and Frontiers in Medicine. He is a popular advocator of Public Health and early detection of non-communicable disease. He frequency writes editorials in various Regional and National News papers about quality of care, public health, health care systems
Indu Bhushan Sinha was an Indian nephrologist and medical academic from the Indian state of Bihar. He is a former professor and head of the department of nephrology at Patna Medical College and Hospital. He has served as the editor of The Patna Journal of Medicine of the Indian Medical Association (1986–89) and is a life member of the Indian Society of Nephrology. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2008, for his contributions to medical science.