
The American Civil War was a civil war in the United States between the Union and the Confederacy, which was formed in 1861 by states that had seceded from the Union. The central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction.

The Battle of Gettysburg was a three-day battle in the American Civil War fought between Union and Confederate forces between July 1 and July 3, 1863, in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The battle, which was won by the Union, is widely considered the Civil War's turning point, ending the Confederacy's aspirations to establish an independent nation. It was the Civil War's bloodiest battle, claiming over 50,000 combined casualties over three days.

James Longstreet was an American military officer who served as a Confederate general during the American Civil War and was the principal subordinate to General Robert E. Lee, who called him his "Old War Horse". He served under Lee as a corps commander for most of the battles fought by the Army of Northern Virginia in the Eastern Theater, and briefly with Braxton Bragg in the Army of Tennessee in the Western Theater.

George Edward Pickett was a career United States Army officer who became a major general in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. He is best remembered for being one of the commanders at Pickett's Charge, the futile and bloody Confederate offensive on the third day of the Battle of Gettysburg that bears his name.

Elizabeth Van Lew was an American abolitionist and philanthropist who built and operated an extensive spy ring for the Union Army during the American Civil War. Many false claims continue to be made about her life. The single most reliable source is a 2002 biography by University of Virginia professor Elizabeth R. Varon.
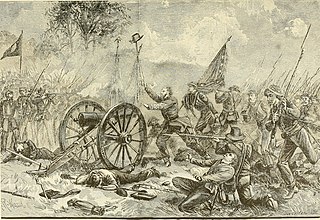
Pickett's Charge, was an infantry assault on the last day of the Battle of Gettysburg in Pennsylvania during the Civil War. Ordered by Confederate General Robert E. Lee against Major General George G. Meade's Union positions on Cemetery Hill, the attack was a costly mistake that decisively ended Lee's invasion of the north and forced a retreat back to Virginia.

The Appomattox Court House National Historical Park is the preserved 19th-century village named Appomattox Court House in Appomattox County, Virginia. The village was named for the presence nearby of what is now preserved as the Old Appomattox Court House. The village is the site of the Battle of Appomattox Court House, and contains the McLean House, where the surrender of the Army of Northern Virginia under Robert E. Lee to Union commander Ulysses S. Grant took place on April 9, 1865, an event widely symbolic of the end of the American Civil War. The village itself began as the community of Clover Hill, which was made the county seat of Appomattox County in the 1840s. The village of Appomattox Court House entered a stage of decline after it was bypassed by a railroad in 1854. In 1930, the United States War Department was authorized to erect a monument at the site, and in 1933 the War Department's holdings there was transferred to the National Park Service. The site was greatly enlarged in 1935, and a restoration of the McLean House was planned but was delayed by World War II. In 1949, the restored McLean House was reopened to the public. Several restored buildings, as well as a number of original 19th-century structures are situated at the site.

Augustus Baldwin Longstreet was an American lawyer, minister, journalist, educator, and humorist, known for his book Georgia Scenes. He held strong pro-slavery and pro-secessionist views which he publicly advocated for in his various positions. He personally owned dozens of slaves throughout his life. He held the presidency of several southern universities, including the University of Mississippi (twice), South Carolina College, and Emory College.

The Lost Cause of the Confederacy is an American pseudohistorical and historical negationist myth that claims the cause of the Confederate States during the American Civil War was just, heroic, and not centered on slavery. First enunciated in 1866, it has continued to influence racism, gender roles, and religious attitudes in the Southern United States into the 21st century. Historians have dismantled many parts of the Lost Cause mythos.

The Battle of Appomattox Court House, fought in Appomattox County, Virginia, on the morning of April 9, 1865, was one of the last battles of the American Civil War (1861–1865). It was the final engagement of Confederate General in Chief Robert E. Lee and his Army of Northern Virginia before they surrendered to the Union Army of the Potomac under the Commanding General of the United States Army, Ulysses S. Grant.

Bushrod Rust Johnson was a Confederate general in the American Civil War and an officer in the United States Army. As a university professor he had been active in the state militias of Kentucky and Tennessee and on the outbreak of hostilities he sided with the South, despite having been born in the North in a family of abolitionist Quakers. As a divisional commander he managed to evade capture at the Battle of Fort Donelson, but was wounded at the Battle of Shiloh. He served under Robert E. Lee throughout the 10-month Siege of Petersburg, and surrendered with him at Appomattox.

James Henry Lane was a university professor and Confederate general in the American Civil War.

The Battle of Sailor's Creek was fought on April 6, 1865, near Farmville, Virginia, as part of the Appomattox Campaign, near the end of the American Civil War. It was the last major engagement between the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, commanded by General Robert E. Lee, and the Army of the Potomac, under the overall direction of Union General-in-Chief Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant.

The Battle of Cumberland Church was fought on April 7, 1865, between the Union Army's II Corps of the Army of the Potomac and the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia during the Appomattox Campaign of the American Civil War.
The Battle of Appomattox Station was fought between a Union Army cavalry division under the command of Brigadier General George Armstrong Custer and Confederate Army of Northern Virginia artillery units commanded by Brigadier General Lindsay Walker with support from some dismounted cavalrymen, artillerymen armed with muskets and some stragglers on April 8, 1865, at Appomattox Station, Virginia during the Appomattox Campaign of the American Civil War.

The Battle of Rice's Station was a minor engagement in Appomattox Campaign of the American Civil War that was fought at the same time as the Battle of Sailor's Creek on April 6, 1865. In the early morning of April 6, Confederate Lieutenant General James Longstreet's command reached Rice's Station, Virginia on the South Side Railroad. As Longstreet's corps was the first to reach Rice's Station after Lee moved his army west from Amelia Springs, Virginia, they awaited the remainder of the army, most of which ended up being delayed at the Battle of Sailor's Creek.

The Peers House is a structure within the Appomattox Court House National Historical Park. It was registered in the National Park Service's database of Official Structures on June 26, 1989.
William Wilhartz Freehling is an American historian, and Singletary Professor of the Humanities Emeritus at the University of Kentucky.
In Lee's Last Retreat: The Flight to Appomattox, historian William Marvel identified Private Pleasant Riggs Crump, of Talladega County, Alabama, who died December 31, 1951, as the last confirmed surviving veteran of the Confederate States Army. Citing English professor and biographical researcher Dr. Jay S. Hoar, Marvel states that after Crump's death a dozen other men claimed to have been Confederate soldiers, but military, pension, and especially census records prove they were impostors. Marvel further wrote that the names of two other supposed Confederate survivors alive in April 1950, according to Hoar, are not on the Appomattox parole lists and one, perhaps both, of their Confederate service claims were faked. An extensively researched book by Frank L. Gryzb, The Last Civil War Veterans: The Lives of the Final Survivors State by State, published March 29, 2016, supports the conclusion by Hoar, Marvel, Serrano and others that Pleasant Crump was the last confirmed and verified surviving veteran of the Confederate States Army.
Longstreet: The Confederate General Who Defied the South is a non-fiction book by Elizabeth R. Varon, published in 2023 by Simon & Schuster. It is about James Longstreet.















