Related Research Articles

A mangrove is a shrub or tree that grows mainly in coastal saline or brackish water. Mangroves grow in an equatorial climate, typically along coastlines and tidal rivers. They have special adaptations to take in extra oxygen and to remove salt, which allow them to tolerate conditions that would kill most plants. The term is also used for tropical coastal vegetation consisting of such species. Mangroves are taxonomically diverse, as a result of convergent evolution in several plant families. They occur worldwide in the tropics and subtropics and even some temperate coastal areas, mainly between latitudes 30° N and 30° S, with the greatest mangrove area within 5° of the equator. Mangrove plant families first appeared during the Late Cretaceous to Paleocene epochs, and became widely distributed in part due to the movement of tectonic plates. The oldest known fossils of mangrove palm date to 75 million years ago.

Hydrobiology is the science of life and life processes in water. Much of modern hydrobiology can be viewed as a sub-discipline of ecology but the sphere of hydrobiology includes taxonomy, economic and industrial biology, morphology, and physiology. The one distinguishing aspect is that all fields relate to aquatic organisms. Most work is related to limnology and can be divided into lotic system ecology and lentic system ecology.

Sergei Nikolaevich Winogradsky (Russian: Сергей Николаевич Виноградский; Ukrainian: Сергій Миколайович Виноградський; 13 September [O.S. 1 September] 1856, Kyiv – 24 February 1953, Brie-Comte-Robert), also published under the name Sergius Winogradsky, was a Russian microbiologist, ecologist and soil scientist who pioneered the cycle-of-life concept. Winogradsky discovered the first known form of lithotrophy during his research with Beggiatoa in 1887. He reported that Beggiatoa oxidized hydrogen sulfide (H2S) as an energy source and formed intracellular sulfur droplets. This research provided the first example of lithotrophy, but not autotrophy. Born in the capital of present-day Ukraine, his legacy is also celebrated by this nation.
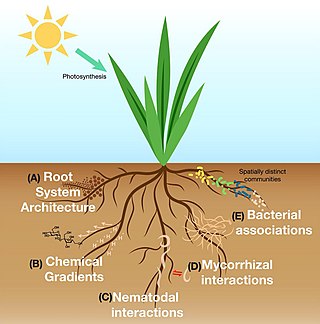
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed rhizodeposition, and the proteins and sugars released by roots, termed root exudates. This symbiosis leads to more complex interactions, influencing plant growth and competition for resources. Much of the nutrient cycling and disease suppression by antibiotics required by plants occurs immediately adjacent to roots due to root exudates and metabolic products of symbiotic and pathogenic communities of microorganisms. The rhizosphere also provides space to produce allelochemicals to control neighbours and relatives.

Rhizobacteria are root-associated bacteria that can have a detrimental, neutral or beneficial effect on plant growth. The name comes from the Greek rhiza, meaning root. The term usually refers to bacteria that form symbiotic relationships with many plants (mutualism). Rhizobacteria are often referred to as plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, or PGPRs. The term PGPRs was first used by Joseph W. Kloepper in the late 1970s and has become commonly used in scientific literature.
Microbial inoculants also known as soil inoculants or bioinoculants are agricultural amendments that use beneficial rhizosphericic or endophytic microbes to promote plant health. Many of the microbes involved form symbiotic relationships with the target crops where both parties benefit (mutualism). While microbial inoculants are applied to improve plant nutrition, they can also be used to promote plant growth by stimulating plant hormone production. Although bacterial and fungal inoculants are common, inoculation with archaea to promote plant growth is being increasingly studied.

Phospholipid-derived fatty acids (PLFAs) are widely used in microbial ecology as chemotaxonomic markers of bacteria and other organisms. Phospholipids are the primary lipids composing cellular membranes. Phospholipids can be saponified, which releases the fatty acids contained in their diglyceride tail. Once the phospholipids of an unknown sample are saponified, the composition of the resulting PLFA can be compared to the PLFA of known organisms to determine the identity of the sample organism. PLFA analysis may be combined with other techniques, such as stable isotope probing to determine which microbes are metabolically active in a sample. PLFA analysis was pioneered by D.C. White at the University of Tennessee, in the early to mid 1980s.
A chronosequence describes a set of ecological sites that share similar attributes but represent different ages.
A bioeffector is a viable microorganism or active natural compound which directly or indirectly affects plant performance (biofertilizer), and thus has the potential to reduce fertilizer and pesticide use in crop production.

The root microbiome is the dynamic community of microorganisms associated with plant roots. Because they are rich in a variety of carbon compounds, plant roots provide unique environments for a diverse assemblage of soil microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and archaea. The microbial communities inside the root and in the rhizosphere are distinct from each other, and from the microbial communities of bulk soil, although there is some overlap in species composition.

Guenter Neumann is an agricultural scientist at the University of Hohenheim. He is a plant physiologist specialising in rhizosphere research and scientific coordinator of the EU Research Project Biofector.
Gabriele Berg is a biologist, biotechnologist and university lecturer in Environmental and Ecological Technology at the Technical University of Graz. Her research emphasis is on the development of sustainable methods of plant vitalisation with Bioeffectors and molecular analysis of microbial processes in the soil, particularly in the Rhizosphere.
Markus Weinmann is an agricultural scientist specialising in the area of Plant Physiology at the University of Hohenheim, and ranks as one of the pioneers of Bioeffector-Research aimed at improving plant growth, vitality and disease resistance. He is also coordinator of field experiments in the EU-Biofector-Project.
Kornelia Smalla is a chemist and biotechnologist at the Julius Kuehn Institute (JKI) in Braunschweig and a university lecturer in microbiology at the Technical University of Braunschweig.
Alessandro Piccolo is an Italian chemist and agricultural scientist, with particular expertise in soil science. He is a professor at the University of Naples Federico II and has been honoured by the prize for chemistry in 1999 by the Humboldt Foundation. He received the Doctorate Honoris Causa by the University of Life Sciences of Prague, Czech Republic in 2009. He is chief editor of the Springer journal Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture. He has been coordinator of two research EU projects and a member of numerous other EU research projects such as the project Biofector with the University of Hohenheim. He has published more than 300 peer reviewed scientific papers and he is ranked among the top Italian scientists.
Kristen M. DeAngelis is a professor in the department of Microbiology at the University of Massachusetts where she studies soil microbes in relation to climate change.

The plant microbiome, also known as the phytomicrobiome, plays roles in plant health and productivity and has received significant attention in recent years. The microbiome has been defined as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well-defined habitat which has distinct physio-chemical properties. The term thus not only refers to the microorganisms involved but also encompasses their theatre of activity".
Jennifer B. H. Martiny is an American ecologist who is a professor at the University of California, Irvine. Her research considers microbial diversity in marine and terrestrial ecosystems. In 2020 she was elected a Fellow of the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Catalina Cuellar-Gempeler is a Colombian microbial ecologist and marine microbiologist, currently teaching and doing research at Cal Poly Humboldt. Her research focuses mainly on understanding microbial meta-community, eco-evolutionary dynamics, and ecosystem dynamics. The Catalina Cuellar-Gempeler lab is currently focused on studying the interactions between hosts and their microbial communities. The lab's main emphasis is on the microbes used in digestion in the Californian and Eastern carnivorous pitcher plants. In March 2021, Cuellar-Gempeler was awarded an Early Career grant of $1 million by the National Science Foundation.
Ashley L. Shade is the Director of Research at the Institute of Ecology and the Environment within Le Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique. Shade is an associate professor at Michigan State University in the Department of Microbiology and Molecular Genetics and Department of Plant, Soil and Microbial Sciences. She is best known for her work in microbial ecology and plant-microbe interactions.
References
- ↑ Ellen Kandeler on the web page of the der University of Hohenheim
- ↑ "Ellen Kandeler on the Biofector Project Page". Archived from the original on 2014-10-18. Retrieved 2017-07-24.