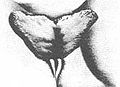
In amniotes, the clitoris is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings.

Female genital mutilation (FGM) is the cutting or removal of some or all of the vulva for non-medical reasons. FGM prevalence varies worldwide, but is majorly present in some countries of Africa, Asia and Middle East, and within their diasporas. As of 2024, UNICEF estimates that worldwide 230 million girls and women had been subjected to one or more types of FGM.

The labia minora, also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the inner vaginal and urethral openings to encompass the vestibule. At the glans clitoris, each labium splits, above forming the clitoral hood, and below the frenulum of the clitoris. At the bottom, the labia meet at the labial commissure. The labia minora vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual.
Genital modifications are forms of body modifications applied to the human sexual organs. When there's cutting involved, genital cutting or surgery can be used. The term genital enhancement seem to be generally used for genital modifications that modify the external aspect, the way the patient wants it. The term genital mutilation is used for genital modifications that drastically diminish the recipient's quality of life and result in adverse health outcomes, whether physical or mental.

Khoisan or Khoe-Sān is a catch-all term for the indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who traditionally speak non-Bantu languages, combining the Khoekhoen and the Sān peoples. Khoisan populations traditionally speak click languages and are considered to be the historical communities throughout Southern Africa, remaining predominant until European colonisation in areas climatically unfavorable to Bantu (sorghum-based) agriculture, such as the Cape region, through to Namibia, where Khoekhoe populations of Nama and Damara people are prevalent groups, and Botswana. Considerable mingling with Bantu-speaking groups is evidenced by prevalence of click phonemes in many especially Xhosa Southern African Bantu languages.

The human female reproductive system is made up of the internal and external sex organs that function in the reproduction of new offspring. The reproductive system is immature at birth and develops at puberty to be able to release matured ova from the ovaries, facilitate their fertilization, and create a protective environment for the developing fetus during pregnancy. The female reproductive tract is made of several connected internal sex organs—the vagina, uterus, and fallopian tubes—and is prone to infections. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse, and is connected to the uterus at the cervix. The uterus accommodates the embryo by developing the uterine lining.

Steatopygia is the state of having substantial levels of tissue on the buttocks and thighs. This build is not confined to the gluteal regions, but extends to the outside and front of the thighs, and tapers to the knee producing a curvilinear figure. The term is from the Greek stéar (στέαρ), meaning "tallow", and pugḗ, meaning "rump".

A fourchette piercing is a female genital piercing. It is a piercing done at the rear rim of the vulva, in the area of frenulum of labia minora. Many women do not have a pinchable flap of skin in the area, and are not suited for this piercing. Otherwise, placement and piercing tends to be relatively easy.

The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the labia majora are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the labia minora are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings, as well as the glans clitoris.
Vulvitis is inflammation of the vulva, the external female mammalian genitalia that include the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, and introitus. It may co-occur as vulvovaginitis with vaginitis, inflammation of the vagina, and may have infectious or non-infectious causes. The warm and moist conditions of the vulva make it easily affected. Vulvitis is prone to occur in any female especially those who have certain sensitivities, infections, allergies, or diseases that make them likely to have vulvitis. Postmenopausal women and prepubescent girls are more prone to be affected by it, as compared to women in their menstruation period. It is so because they have low estrogen levels which makes their vulvar tissue thin and dry. Women having diabetes are also prone to be affected by vulvitis due to the high sugar content in their cells, increasing their vulnerability. Vulvitis is not a disease, it is just an inflammation caused by an infection, allergy or injury. Vulvitis may also be symptom of any sexually transmitted infection or a fungal infection.

Labiaplasty is a plastic surgery procedure for creating or altering the labia minora and the labia majora, the folds of skin of the human vulva. It is a type of vulvoplasty. There are two main categories of women seeking cosmetic genital surgery: those with conditions such as intersex, and those with no underlying condition who experience physical discomfort or wish to alter the appearance of their vulvas because they believe they do not fall within a normal range.

Labia piercings are a type of female genital piercing. This piercing can be placed either through the labia minora or the labia majora. They are one of the simpler and more common genital piercings performed on vulvas, and are often pierced in symmetrical pairs. Like all genital piercings, depending on jewellery and placement, they may provide additional stimulation to one or both partners during sexual intercourse.
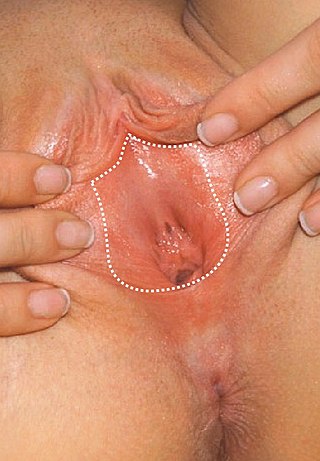
The vulval vestibule is the part of the vulva between the labia minora. At the innermost part are the vaginal introitus and urinary meatus. The Bartholin's and Skene's glands each have two openings to the vestibule on the inside. The outer edge, marked by a coloration difference in the tissues, is called Hart's line, named after David Berry Hart.
Labia stretching, also referred to as labia elongation or labia pulling, is the act of lengthening the labia minora through manual manipulation (pulling) or physical equipment. It is a familial cultural practice in parts of Eastern and Southern Africa, and a body modification practice elsewhere. It is performed for sexual enhancement for the benefit of both partners, aesthetics, symmetry and gratification.

Clitoral hood reduction, also termed clitoral hoodectomy, clitoral unhooding, clitoridotomy, or (partial) hoodectomy, is a plastic surgery procedure for reducing the size and the area of the clitoral hood in order to further expose the glans of the clitoris.
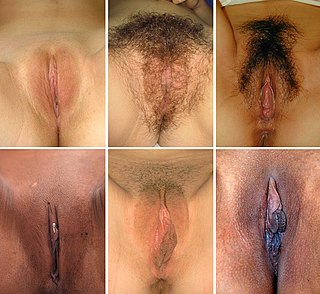
In mammals, the vulva comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands. The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support.
A vulvar disease is a particular abnormal, pathological condition that affects part or all of the vulva. Several pathologies are defined. Some can be prevented by vulvovaginal health maintenance.
Female genital mutilation in Sierra Leone is the common practice of removing all or part of the female's genitalia for cultural and religious initiation purposes, or as a custom to prepare them for marriage. Sierra Leone is one of 28 countries in Africa where female genital mutilation (FGM) is known to be practiced and one of few that has not banned it. It is widespread in part due to it being an initiation rite into the "Bondo," though initiation rite-related FGM was criminalised in 2019. The type most commonly practised in Sierra Leone is Type IIb, removal of part or all of the clitoris and the labia minora. As of 2013, it had a prevalence of 89.6%.
Nigeria has the highest rate of female genital mutilation (FGM) in the world in total numbers. It is usually experienced by girls aged 0 to 15 years old. It involves either partial or complete removal of the vulva or other injury to the female genital organs and has no medical benefit.

Woman, Why Do You Weep? Circumcision and Its Consequences (1982) is a book by Sudanese physician Asma El Dareer about female genital mutilation in Sudan. Published in London by Zed Press in association with the Babiker Bedri Scientific Association for Women's Studies, the book summarizes research El Dareer conducted on female genital mutilation (FGM) for the medical faculty of the University of Khartoum.