An embolism is the lodging of an embolus, a blockage-causing piece of material, inside a blood vessel. The embolus may be a blood clot (thrombus), a fat globule, a bubble of air or other gas, amniotic fluid, or foreign material.
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.
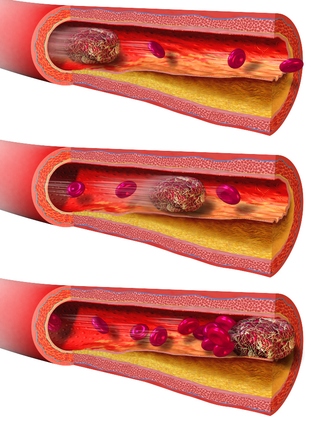
An embolus is an unattached mass that travels through the bloodstream and is capable of creating blockages. When an embolus occludes a blood vessel, it is called an embolism or embolic event. There are a number of different types of emboli, including blood clots, cholesterol plaque or crystals, fat globules, gas bubbles, and foreign bodies, which can result in different types of embolisms.

A thrombus, colloquially called a blood clot, is the final product of the blood coagulation step in hemostasis. There are two components to a thrombus: aggregated platelets and red blood cells that form a plug, and a mesh of cross-linked fibrin protein. The substance making up a thrombus is sometimes called cruor. A thrombus is a healthy response to injury intended to stop and prevent further bleeding, but can be harmful in thrombosis, when a clot obstructs blood flow through a healthy blood vessel in the circulatory system.
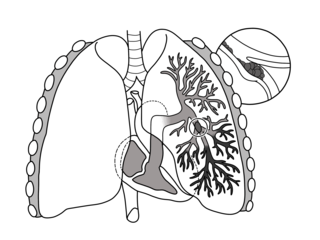
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing in, and coughing up blood. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg may also be present, such as a red, warm, swollen, and painful leg. Signs of a PE include low blood oxygen levels, rapid breathing, rapid heart rate, and sometimes a mild fever. Severe cases can lead to passing out, abnormally low blood pressure, obstructive shock, and sudden death.
An air embolism, also known as a gas embolism, is a blood vessel blockage caused by one or more bubbles of air or other gas in the circulatory system. Air can be introduced into the circulation during surgical procedures, lung over-expansion injury, decompression, and a few other causes. In flora, air embolisms may also occur in the xylem of vascular plants, especially when suffering from water stress.
Decompression Illness (DCI) comprises two different conditions caused by rapid decompression of the body. These conditions present similar symptoms and require the same initial first aid. Scuba divers are trained to ascend slowly from depth to avoid DCI. Although the incidence is relatively rare, the consequences can be serious and potentially fatal, especially if untreated.

Ischemia or ischaemia is a restriction in blood supply to any tissue, muscle group, or organ of the body, causing a shortage of oxygen that is needed for cellular metabolism. Ischemia is generally caused by problems with blood vessels, with resultant damage to or dysfunction of tissue i.e. hypoxia and microvascular dysfunction. It also implies local hypoxia in a part of a body resulting from constriction.

A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the main pulmonary artery or pulmonary trunk from the heart, and the smallest ones are the arterioles, which lead to the capillaries that surround the pulmonary alveoli.

Embolization refers to the passage and lodging of an embolus within the bloodstream. It may be of natural origin (pathological), in which sense it is also called embolism, for example a pulmonary embolism; or it may be artificially induced (therapeutic), as a hemostatic treatment for bleeding or as a treatment for some types of cancer by deliberately blocking blood vessels to starve the tumor cells.
An embolus, is described as a free-floating mass, located inside blood vessels that can travel from one site in the blood stream to another. An embolus can be made up of solid, liquid, or gas. Once these masses get "stuck" in a different blood vessel, it is then known as an "embolism." An embolism can cause ischemia—damage to an organ from lack of oxygen. A paradoxical embolism is a specific type of embolism in which the embolus travels from the right side of the heart to the left side of the heart and lodges itself in a blood vessel known as an artery. Thus, it is termed "paradoxical" because the embolus lands in an artery, rather than a vein.

Fat embolism syndrome occurs when fat enters the blood stream and results in symptoms. Symptoms generally begin within a day. This may include a petechial rash, decreased level of consciousness, and shortness of breath. Other symptoms may include fever and decreased urine output. The risk of death is about 10%.
In chest radiography, the Westermark sign is a sign that represents a focus of oligemia (hypovolemia) seen distal to a pulmonary embolism (PE). While the chest x-ray is normal in the majority of PE cases, the Westermark sign is seen in 2% of patients.

A ventilation/perfusion lung scan, also called a V/Q lung scan, or ventilation/perfusion scintigraphy, is a type of medical imaging using scintigraphy and medical isotopes to evaluate the circulation of air and blood within a patient's lungs, in order to determine the ventilation/perfusion ratio. The ventilation part of the test looks at the ability of air to reach all parts of the lungs, while the perfusion part evaluates how well blood circulates within the lungs. As Q in physiology is the letter used to describe bloodflow the term V/Q scan emerged.

A CT pulmonary angiogram (CTPA) is a medical diagnostic test that employs computed tomography (CT) angiography to obtain an image of the pulmonary arteries. Its main use is to diagnose pulmonary embolism (PE). It is a preferred choice of imaging in the diagnosis of PE due to its minimally invasive nature for the patient, whose only requirement for the scan is an intravenous line.
Teds or TEDS may refer to

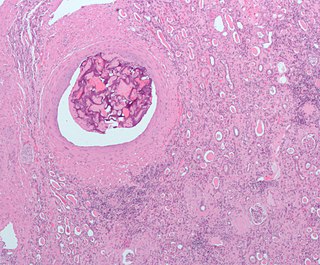
Cholesterol embolism occurs when cholesterol is released, usually from an atherosclerotic plaque, and travels as an embolus in the bloodstream to lodge causing an obstruction in blood vessels further away. Most commonly this causes skin symptoms, gangrene of the extremities and sometimes kidney failure; problems with other organs may arise, depending on the site at which the cholesterol crystals enter the bloodstream. When the kidneys are involved, the disease is referred to as atheroembolic renal disease. The diagnosis usually involves biopsy from an affected organ. Cholesterol embolism is treated by removing the cause and giving supportive therapy; statin drugs have been found to improve the prognosis.
Embolectomy is the emergency interventional or surgical removal of emboli which are blocking blood circulation. It usually involves removal of thrombi, and is then referred to as thromboembolectomy or thrombectomy. Embolectomy is an emergency procedure often as the last resort because permanent occlusion of a significant blood flow to an organ leads to necrosis. Other involved therapeutic options are anticoagulation and thrombolysis.

Arterial embolism is a sudden interruption of blood flow to an organ or body part due to an embolus adhering to the wall of an artery blocking the flow of blood, the major type of embolus being a blood clot (thromboembolism). Sometimes, pulmonary embolism is classified as arterial embolism as well, in the sense that the clot follows the pulmonary artery carrying deoxygenated blood away from the heart. However, pulmonary embolism is generally classified as a form of venous embolism, because the embolus forms in veins. Arterial embolism is the major cause of infarction.

Arterial occlusion is a condition involving partial or complete blockage of blood flow through an artery. Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to body tissues. An occlusion of arteries disrupts oxygen and blood supply to tissues, leading to ischemia. Depending on the extent of ischemia, symptoms of arterial occlusion range from simple soreness and pain that can be relieved with rest, to a lack of sensation or paralysis that could require amputation.













