Related Research Articles
The Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) of the United States are a set of publicly announced standards that the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has developed for use in computer systems of non-military United States government agencies and contractors. FIPS standards establish requirements for ensuring computer security and interoperability, and are intended for cases in which suitable industry standards do not already exist. Many FIPS specifications are modified versions of standards the technical communities use, such as the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).

The Emergency Broadcast System (EBS), sometimes called the Emergency Action Notification System (EANS), was an emergency warning system used in the United States. It was the most commonly used, along with the Emergency Override system. It replaced the previous CONELRAD system and was used from 1963 to 1997, at which point it was replaced by the Emergency Alert System.

The Emergency Alert System (EAS) is a national warning system in the United States designed to allow authorized officials to broadcast emergency alerts and warning messages to the public via cable, satellite, or broadcast television, and both AM/FM and satellite radio.
The Open Software License (OSL) is a software license created by Lawrence Rosen. The Open Source Initiative (OSI) has certified it as an open-source license, but the Debian project judged version 1.1 to be incompatible with the DFSG. The OSL is a copyleft license, with a termination clause triggered by filing a lawsuit alleging patent infringement.

The defense readiness condition (DEFCON) is an alert state used by the United States Armed Forces.
Specific Area Message Encoding (SAME) is a protocol used for framing and classification of broadcasting emergency warning messages. It was developed by the United States National Weather Service for use on its NOAA Weather Radio (NWR) network, and was later adopted by the Federal Communications Commission for the Emergency Alert System, then subsequently by Environment Canada for use on its Weatheradio Canada service. It is also used to set off receivers in Mexico City and surrounding areas as part of the Mexican Seismic Alert System (SASMEX).
Exit(s) may refer to:
A distress signal, also known as a distress call, is an internationally recognized means for obtaining help. Distress signals are communicated by transmitting radio signals, displaying a visually observable item or illumination, or making a sound audible from a distance.

Abortion laws vary widely among countries and territories, and have changed over time. Such laws range from abortion being freely available on request, to regulation or restrictions of various kinds, to outright prohibition in all circumstances. Many countries and territories that allow abortion have gestational limits for the procedure depending on the reason; with the majority being up to 12 weeks for abortion on request, up to 24 weeks for rape, incest, or socioeconomic reasons, and more for fetal impairment or risk to the woman's health or life. As of 2022, countries that legally allow abortion on request or for socioeconomic reasons comprise about 60% of the world's population.

The nuclear football is a briefcase, the contents of which are to be used by the president of the United States to communicate and authorize a nuclear attack while away from fixed command centers, such as the White House Situation Room or the Presidential Emergency Operations Center. Functioning as a mobile hub in the strategic defense system of the United States, the football is carried by a military aide when the President is traveling.

Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment. Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials. An example for dangerous goods is hazardous waste which is waste that has substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment.
In the United States military's strategic nuclear weapon nuclear command and control (NC2) system, an Emergency Action Message (EAM) is a preformatted message that directs nuclear-capable forces to execute specific Major Attack Options (MAOs) or Limited Attack Options (LAOs) in a nuclear war. They are the military commands that the US military chain of command would use to launch a nuclear strike. Individual countries or specific regions may be included or withheld in the EAM, as specified in the Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP). The SIOP was updated annually until February 2003, when it was replaced by Operations Plan (OPLAN) 8044. Since July 2012, the US nuclear war plan has been OPLAN 8010-12, Strategic Deterrence and Force Employment.

The National Emergencies Act (NEA) is a United States federal law passed to end all previous national emergencies and to formalize the emergency powers of the President.

Hazchem is a warning plate system used in Australia, Hong Kong, Malaysia, New Zealand, India and the United Kingdom for vehicles transporting hazardous substances, and on storage facilities. The top-left section of the plate gives the Emergency Action Code (EAC) telling the fire brigade what actions to take if there's an accident or fire. The middle-left section containing a 4 digit number gives the UN Substance Identification Number describing the material. The lower-left section gives the telephone number that should be called if special advice is needed. The warning symbol in the top right indicates the general hazard class of the material. The bottom-right of the plate carries a company logo or name.

Capital punishment in Armenia was a method of punishment that was implemented within Armenia's Criminal Code and Constitution until its eventual relinquishment in the 2003 modifications made to the Constitution. Capital punishment's origin in Armenia is unknown, yet it remained present in the Armenia Criminal Code of 1961, which was enforced and applied until 1999. Capital punishment was incorporated in Armenian legislation and effectuated for capital crimes, which were crimes that were classified to be punishable by death, this included: treason, espionage, first-degree murder, acts of terrorism and grave military crimes.

The Emergency Rocket Communications System (ERCS) was designed to provide a reliable and survivable emergency communications method for the United States National Command Authority, using a UHF repeater placed atop a Blue Scout rocket or Minuteman II intercontinental ballistic missile. ERCS was deactivated as a communication means when President George H.W. Bush issued a message to stand down SIOP-committed bombers and Minuteman IIs on 27 September 1991. Headquarters SAC was given approval by the Joint Chiefs of Staff to deactivate the 494L payloads beginning 1 October 1992. However, Headquarters SAC believed it was inefficient and unnecessary to support ERCS past fiscal year 1991, and kept the accelerated deactivation schedule.
Abortion in Belgium was fully legalised on 4 April 1990. Abortion is legal until 12 weeks after conception. The woman is required to receive counselling at least six days prior to the abortion and to check in with her doctor to monitor her health in the weeks after the procedure. Later abortions are permitted if there is a risk to the woman's life or the fetus shows risk of birth defects.
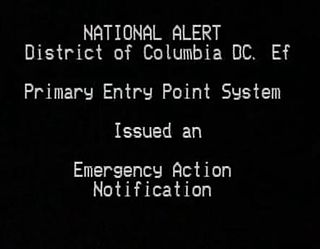
A National Emergency Message, formerly known until 2022 as an Emergency Action Notification, is the national activation of the Emergency Alert System (EAS) used to alert the residents of the United States of a national or global emergency such as a nuclear war or any other mass casualty situation. This alert can only be activated by the president of the United States or a designated representative thereof, such as the vice president. The Emergency Broadcast System (EBS) also carried the Emergency Action Notification. No president has ever activated the alert aside from the 2011 national EAS test.
An emergency locator beacon is a radio beacon, a portable battery powered radio transmitter, used to locate airplanes, vessels, and persons in distress and in need of immediate rescue. Various types of emergency locator beacons are carried by aircraft, ships, vehicles, hikers and cross-country skiers. In case of an emergency, such as the aircraft crashing, the ship sinking, or a hiker becoming lost, the transmitter is deployed and begins to transmit a continuous radio signal, which is used by search and rescue teams to quickly find the emergency and render aid. The purpose of all emergency locator beacons is to help rescuers find survivors within the so-called "golden day", the first 24 hours following a traumatic event, during which the majority of survivors can usually be saved.
Executive Order 14054, officially titled Termination of Emergency With Respect to the Situation in Burundi, was signed on November 18, 2021, and is the 70th executive order signed by U.S. President Joe Biden. The telos of the order is terminating the national emergency in Burundi.
References
- ↑ "Federal Communications Commission Fifth Report and Order" (PDF). 10 January 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2021.