Related Research Articles
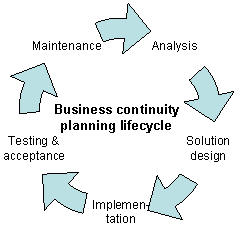
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.

An emergency is an urgent, unexpected, and usually dangerous situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or environment and requires immediate action. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening of the situation, although in some situations, mitigation may not be possible and agencies may only be able to offer palliative care for the aftermath.
The Civil Contingencies Secretariat (CCS), created in July 2001 and disbanded in July 2022, was the executive department of the British Cabinet Office responsible for emergency planning in the UK. The role of the secretariat was to ensure the United Kingdom's resilience against disruptive challenge, and to do this by working with others to anticipate, assess, prevent, prepare, respond and recover. Until its creation in 2001, emergency planning in Britain was the responsibility of the Home Office. The CCS also supports the Civil Contingencies Committee, also known as COBR.
Crisis management is the process by which an organization deals with a disruptive and unexpected event that threatens to harm the organization or its stakeholders. The study of crisis management originated with large-scale industrial and environmental disasters in the 1980s. It is considered to be the most important process in public relations.

The buddy check is a procedure carried out by scuba divers using the buddy system where each dive buddy checks that the other's diving equipment is configured and functioning correctly just before the start of the dive. A study of pre-dive equipment checks done by individual divers showed that divers often fail to recognize common equipment faults. By checking each other's equipment as well as their own, it is thought to be more likely that these faults will be identified prior to the start of the dive. The correct use of a well designed written checklist is known to be more reliable, and is more likely to be used by professional divers, where it may be required by occupational health and safety legislation, and by technical divers, where the equipment checks are more complex.
The Common Alerting Protocol (CAP) is an XML-based data format for exchanging public warnings and emergencies between alerting technologies. CAP allows a warning message to be consistently disseminated simultaneously over many warning systems to many applications, such as Google Public Alerts and Cell Broadcast. CAP increases warning effectiveness and simplifies the task of activating a warning for responsible officials.

Emergency management is a science and a system charged with creating the framework within which communities reduce vulnerability to hazards and cope with disasters. Emergency management, despite its name, does not actually focus on the management of emergencies; emergency management or disaster management can be understood as minor events with limited impacts and are managed through the day-to-day functions of a community. Instead, emergency management focuses on the management of disasters, which are events that produce more impacts than a community can handle on its own. The management of disasters tends to require some combination of activity from individuals and households, organizations, local, and/or higher levels of government. Although many different terminologies exist globally, the activities of emergency management can be generally categorized into preparedness, response, mitigation, and recovery, although other terms such as disaster risk reduction and prevention are also common. The outcome of emergency management is to prevent disasters and where this is not possible, to reduce their harmful impacts.
The project documentation (PID) is one of the most significant artifacts in project management, which provides the foundation for the business project.
An incident is an event that could lead to loss of, or disruption to, an organization's operations, services or functions. Incident management (IcM) is a term describing the activities of an organization to identify, analyze, and correct hazards to prevent a future re-occurrence. These incidents within a structured organization are normally dealt with by either an incident response team (IRT), an incident management team (IMT), or Incident Command System (ICS). Without effective incident management, an incident can disrupt business operations, information security, IT systems, employees, customers, or other vital business functions.

Hazus is a geographic information system-based natural hazard analysis tool developed and freely distributed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).

In the U.S., critical infrastructure protection (CIP) is a concept that relates to the preparedness and response to serious incidents that involve the critical infrastructure of a region or the nation. The American Presidential directive PDD-63 of May 1998 set up a national program of "Critical Infrastructure Protection". In 2014 the NIST Cybersecurity Framework was published after further presidential directives.
Crisis communication is a sub-specialty of the public relations profession that is designed to protect and defend an individual, company, or organization facing a public challenge to its reputation. Crisis communication is aimed at raising awareness of a specific type of threat, the magnitude, outcomes, and specific behaviors to adopt to reduce the threat. The communication scholar Timothy Coombs defines crisis as "the perception of an unpredictable event that threatens important expectancies of stakeholders and can seriously impact an organization's performance and generate negative outcomes" and crisis communication as "the collection, processing, and dissemination of information required to address a crisis situation."
A contingency plan, or alternate plan, also known colloquially as Plan B, is a plan devised for an outcome other than in the usual (expected) plan. It is often used for risk management for an exceptional risk that, though unlikely, would have catastrophic consequences.
An emergency procedure is a plan of actions to be conducted in a certain order or manner, in response to a specific class of reasonably foreseeable emergency, a situation that poses an immediate risk to health, life, property, or the environment. Where a range of emergencies are reasonably foreseeable, an emergency plan may be drawn up to manage each threat. Most emergencies require urgent intervention to prevent a worsening of the situation, although in some situations, mitigation may not be possible and agencies may only be able to offer palliative care for the aftermath. The emergency plan should allow for these possibilities.
A Risk Breakdown Structure (RBS) within risk management is a hierarchically organised depiction of the identified project risks arranged by category.

UN-SPIDER is a platform which facilitates the use of space-based technologies for disaster management and emergency response. It is a programme under the auspices of the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA).
Next Generation 911 refers to an initiative aimed at updating the 911 service infrastructure in the United States and Canada to improve public emergency communications services in a growing wireless mobile society. In addition to calling 911 from a phone, it intends to enable the public to transmit text, images, video and data to the 911 center. The initiative also envisions additional types of emergency communications and data transfer. This NG911 infrastructure is intended to replace the current services over time. The National Emergency Number Association (NENA) first identified the need for NG911 in 2000, and started development actions in 2003, and is nearing full definition and standards for NG911. Since 2006, the US Department of Transportation (DOT) in the United States and the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) in Canada have been leading their respective initiatives, which include research and development projects aimed at advancing NG911. On January 24, 2013, the CRTC announced the first step toward a Canadian implementation of NG911 and, in March 2016, began a consultation with the public to discuss what services should be offered, who will play a role in offering these services and how these services should be paid for. Several US states have implemented versions of NG911, as of October 2013.
The Emergency Data Exchange Language (EDXL) is a suite of XML-based messaging standards that facilitate emergency information sharing between government entities and the full range of emergency-related organizations. EDXL standardizes messaging formats for communications between these parties. EDXL was developed as a royalty-free standard by the OASIS International Open Standards Consortium.

Disaster preparedness in museums, galleries, libraries, archives and private collections, involves any actions taken to plan for, prevent, respond or recover from natural disasters and other events that can cause damage or loss to cultural property. 'Disasters' in this context may include large-scale natural events such as earthquakes, flooding or bushfire, as well as human-caused events such as theft and vandalism. Increasingly, anthropogenic climate change is a factor in cultural heritage disaster planning, due to rising sea levels, changes in rainfall patterns, warming average temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events.

The Coordination Centre for Health Alerts and Emergencies is a body of the Spanish Ministry of Health responsible for coordinating the management of information and supporting all health authorities in cases of national or international health alert or emergency situations that pose a threat to the health of the population. This centre is also the unit responsible in Spain for preparing and developing response plans to deal with public health threats.
References
- ↑ "What is an Emergency Management Information System (EMIS)?". Archived from the original on 2006-10-21. Retrieved 2007-04-26. Alt URL