Related Research Articles
In the United States, a 401(k) plan is an employer-sponsored, defined-contribution, personal pension (savings) account, as defined in subsection 401(k) of the U.S. Internal Revenue Code. Periodic employee contributions come directly out of their paychecks, and may be matched by the employer. This pre-tax option is what makes 401(k) plans attractive to employees, and many employers offer this option to their (full-time) workers. 401(k) payable is a general ledger account that contains the amount of 401(k) plan pension payments that an employer has an obligation to remit to a pension plan administrator. This account is classified as a payroll liability, since the amount owed should be paid within one year.

A pension is a fund into which amounts are paid regularly during an individual's working career, and from which periodic payments are made to support the person's retirement from work. A pension may be:

National Insurance (NI) is a fundamental component of the welfare state in the United Kingdom. It acts as a form of social security, since payment of NI contributions establishes entitlement to certain state benefits for workers and their families.
A pay-as-you-earn tax (PAYE), or pay-as-you-go (PAYG) in Australia, is a withholding of taxes on income payments to employees. Amounts withheld are treated as advance payments of income tax due. They are refundable to the extent they exceed tax as determined on tax returns. PAYE may include withholding the employee portion of insurance contributions or similar social benefit taxes. In most countries, they are determined by employers but subject to government review. PAYE is deducted from each paycheck by the employer and must be remitted promptly to the government. Most countries refer to income tax withholding by other terms, including pay-as-you-go tax.

Payroll taxes are taxes imposed on employers or employees, and are usually calculated as a percentage of the salaries that employers pay their employees. By law, some payroll taxes are the responsibility of the employee and others fall on the employer, but almost all economists agree that the true economic incidence of a payroll tax is unaffected by this distinction, and falls largely or entirely on workers in the form of lower wages. Because payroll taxes fall exclusively on wages and not on returns to financial or physical investments, payroll taxes may contribute to underinvestment in human capital, such as higher education.
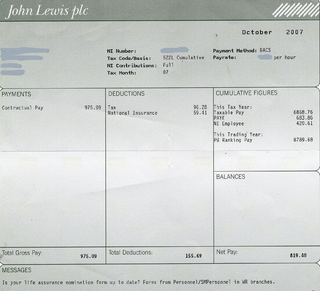
A payroll is a list of employees of a company who are entitled to receive compensation as well as other work benefits, as well as the amounts that each should obtain. Along with the amounts that each employee should receive for time worked or tasks performed, payroll can also refer to a company's records of payments that were previously made to employees, including salaries and wages, bonuses, and withheld taxes, or the company's department that deals with compensation. A company may handle all aspects of the payroll process in-house or can outsource aspects to a payroll processing company.

The Federal Insurance Contributions Act is a United States federal payroll tax payable by both employees and employers to fund Social Security and Medicare—federal programs that provide benefits for retirees, people with disabilities, and children of deceased workers.
Garnishment is a legal process for collecting a monetary judgment on behalf of a plaintiff from a defendant. Garnishment allows the plaintiff to take the money or property of the debtor from the person or institution that holds that property. A similar legal mechanism called execution allows the seizure of money or property held directly by the debtor.

Employee benefits and benefits in kind, also called fringe benefits, perquisites, or perks, include various types of non-wage compensation provided to employees in addition to their normal wages or salaries. Instances where an employee exchanges (cash) wages for some other form of benefit is generally referred to as a "salary packaging" or "salary exchange" arrangement. In most countries, most kinds of employee benefits are taxable to at least some degree. Examples of these benefits include: housing furnished or not, with or without free utilities; group insurance ; disability income protection; retirement benefits; daycare; tuition reimbursement; sick leave; vacation ; social security; profit sharing; employer student loan contributions; conveyancing; long service leave; domestic help (servants); and other specialized benefits.
Misclassification of employees as independent contractors is the way in which the United States and other countries classify the problem of false self-employment. In the U.S., it can occur with respect to tax treatment or the Fair Labor Standards Act.
Labour in India refers to employment in the economy of India. In 2020, there were around 476.67 million workers in India, the second largest after China. Out of which, agriculture industry consist of 41.19%, industry sector consist of 26.18% and service sector consist 32.33% of total labour force. Of these over 94 percent work in unincorporated, unorganised enterprises ranging from pushcart vendors to home-based diamond and gem polishing operations. The organised sector includes workers employed by the government, state-owned enterprises and private sector enterprises. In 2008, the organised sector employed 27.5 million workers, of which 17.3 million worked for government or government owned entities.
Tuition.io is an American company that enables other companies to provide employer-paid student loan contributions as an employee benefit. The company is headquartered in Santa Monica, California.
Navient Corporation is an American student loan servicer based in Wilmington, Delaware. Managing nearly $300 billion in student loans for more than 12 million debtors, the company was formed in 2014 by the split of Sallie Mae into two distinct entities: Sallie Mae Bank and Navient. Navient employs 6,000 people at offices across the U.S. As of 2018, Navient services 25% of student loans in the United States.

Unemployment insurance in the United States, colloquially referred to as unemployment benefits, refers to social insurance programs which replace a portion of wages for individuals during unemployment. The first unemployment insurance program in the U.S. was created in Wisconsin in 1932, and the federal Social Security Act of 1935 created programs nationwide that are administered by state governments. The constitutionality of the program was upheld by the Supreme Court in 1937.

The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, also known as the CARES Act, is a $2.2 trillion economic stimulus bill passed by the 116th U.S. Congress and signed into law by President Donald Trump on March 27, 2020, in response to the economic fallout of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States. The spending primarily includes $300 billion in one-time cash payments to individual people who submit a tax return in America, $260 billion in increased unemployment benefits, the creation of the Paycheck Protection Program that provides forgivable loans to small businesses with an initial $350 billion in funding, $500 billion in loans for corporations, and $339.8 billion to state and local governments.

The COVID-19 pandemic impacted the United States restaurant industry via government closures, resulting in layoffs of workers and loss of income for restaurants and owners and threatening the survival of independent restaurants as a category. Within a week after the first closures, industry groups representing independent restaurateurs were asking for immediate relief measures from local, state, and federal governments, saying that as many as 75 percent of independent restaurants could not survive closures of more than a few weeks. By late July, nearly 16,000 restaurants had permanently closed.

The Paycheck Protection Program (PPP) is a $953-billion business loan program established by the United States federal government during the Trump administration in 2020 through the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act to help certain businesses, self-employed workers, sole proprietors, certain nonprofit organizations, and tribal businesses continue paying their workers.

The Health and Economic Recovery Omnibus Emergency Solutions Act, or Heroes Act, was proposed legislation acting as a $3 trillion stimulus package in response to the COVID-19 pandemic, intended to supplement the earlier CARES Act stimulus package. The bill for this Act of Congress was proposed by Representative Nita Lowey, a Democrat from New York, on May 12, 2020, and was passed by the United States House of Representatives by a vote of 208–199 on May 15, 2020.

The Government of Canada introduced multiple temporary social security and financial aid programs in response to the economic impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The initial CA$82-billion aid package was announced on March 18, 2020 by Justin Trudeau.

The Health, Economic Assistance, Liability Protection and Schools (HEALS) Act was a $1 trillion economic stimulus bill introduced in 2020 by the United States Senate during the COVID-19 pandemic, to supplement the earlier CARES Act.
References
- ↑ Fernandes, Deirdre (March 15, 2016). "Fidelity's student loan debt repayment benefit draws 5,000 workers". The Boston Globe. Retrieved April 21, 2016.
- 1 2 McGregor, Jena (March 15, 2016). "The popular new perk companies are using to attract millennials". The Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286 . Retrieved April 21, 2016.
- 1 2 3 Bernard, Tara Siegel (March 25, 2016). "Medical, Dental, 401(k)? Now Add School Loan Aid to Job Benefits". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331 . Retrieved April 21, 2016.
- ↑ White, Gillian B. (July 10, 2016). "When Employers Pay Student Loans, Those Who Most Need Help Are Left Out". The Atlantic. Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ↑ Olson, Elizabeth (July 15, 2016). "Firms Offer Cash to Help New Lawyers Pay Student Debt". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331 . Retrieved October 11, 2016.
- ↑ "Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, Section 2206". United States Congress. govtrack. March 27, 2020.