Related Research Articles
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol is an open, vendor-neutral, industry standard application protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Directory services play an important role in developing intranet and Internet applications by allowing the sharing of information about users, systems, networks, services, and applications throughout the network. As examples, directory services may provide any organized set of records, often with a hierarchical structure, such as a corporate email directory. Similarly, a telephone directory is a list of subscribers with an address and a phone number.
Java and C++ are two prominent object-oriented programming languages. By many language popularity metrics, the two languages have dominated object-oriented and high-performance software development for much of the 21st century, and are often directly compared and contrasted. Java's syntax was based on C/C++.
Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1) is a standard interface description language (IDL) for defining data structures that can be serialized and deserialized in a cross-platform way. It is broadly used in telecommunications and computer networking, and especially in cryptography.
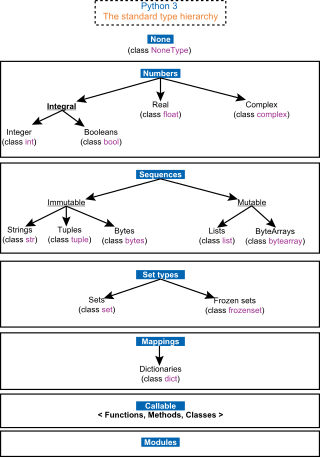
In computer science and computer programming, a data type is a collection or grouping of data values, usually specified by a set of possible values, a set of allowed operations on these values, and/or a representation of these values as machine types. A data type specification in a program constrains the possible values that an expression, such as a variable or a function call, might take. On literal data, it tells the compiler or interpreter how the programmer intends to use the data. Most programming languages support basic data types of integer numbers, floating-point numbers, characters and Booleans.
The Vienna Development Method (VDM) is one of the longest-established formal methods for the development of computer-based systems. Originating in work done at the IBM Laboratory Vienna in the 1970s, it has grown to include a group of techniques and tools based on a formal specification language—the VDM Specification Language (VDM-SL). It has an extended form, VDM++, which supports the modeling of object-oriented and concurrent systems. Support for VDM includes commercial and academic tools for analyzing models, including support for testing and proving properties of models and generating program code from validated VDM models. There is a history of industrial usage of VDM and its tools and a growing body of research in the formalism has led to notable contributions to the engineering of critical systems, compilers, concurrent systems and in logic for computer science.
A Universally Unique Identifier (UUID) is a 128-bit label used to uniquely identify objects in computer systems. The term Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) is also used, mostly in Microsoft systems.

The syntax of the C programming language is the set of rules governing writing of software in C. It is designed to allow for programs that are extremely terse, have a close relationship with the resulting object code, and yet provide relatively high-level data abstraction. C was the first widely successful high-level language for portable operating-system development.
This article compares two programming languages: C# with Java. While the focus of this article is mainly the languages and their features, such a comparison will necessarily also consider some features of platforms and libraries.
A management information base (MIB) is a database used for managing the entities in a communication network. Most often associated with the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), the term is also used more generically in contexts such as in OSI/ISO Network management model. While intended to refer to the complete collection of management information available on an entity, it is often used to refer to a particular subset, more correctly referred to as MIB-module.
In class-based, object-oriented programming, a constructor is a special type of function called to create an object. It prepares the new object for use, often accepting arguments that the constructor uses to set required member variables.
In public key infrastructure (PKI) systems, a certificate signing request is a message sent from an applicant to a certificate authority of the public key infrastructure (PKI) in order to apply for a digital identity certificate. The CSR usually contains the public key for which the certificate should be issued, identifying information and a proof of authenticity including integrity protection. The most common format for CSRs is the PKCS #10 specification; others include the more capable Certificate Request Message Format (CRMF) and the SPKAC format generated by some web browsers.
STEP-file is a widely used data exchange form of STEP. ISO 10303 can represent 3D objects in computer-aided design (CAD) and related information. Due to its ASCII structure, a STEP-file is easy to read, with typically one instance per line. The format of a STEP-file is defined in ISO 10303-21 Clear Text Encoding of the Exchange Structure.
Fast Infoset is an international standard that specifies a binary encoding format for the XML Information Set as an alternative to the XML document format. It aims to provide more efficient serialization than the text-based XML format.
SystemVerilog, standardized as IEEE 1800, is a hardware description and hardware verification language used to model, design, simulate, test and implement electronic systems. SystemVerilog is based on Verilog and some extensions, and since 2008, Verilog is now part of the same IEEE standard. It is commonly used in the semiconductor and electronic design industry as an evolution of Verilog.
A class in C++ is a user-defined type or data structure declared with any of the keywords class, struct or union that has data and functions as its members whose access is governed by the three access specifiers private, protected or public. By default access to members of a C++ class declared with the keyword class is private. The private members are not accessible outside the class; they can be accessed only through member functions of the class. The public members form an interface to the class and are accessible outside the class.
C++11 is a version of a joint technical standard, ISO/IEC 14882, by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), for the C++ programming language. C++11 replaced the prior version of the C++ standard, named C++03, and was later replaced by C++14. The name follows the tradition of naming language versions by the publication year of the specification, though it was formerly named C++0x because it was expected to be published before 2010.
This is an overview of Fortran 95 language features. Included are the additional features of TR-15581:Enhanced Data Type Facilities, which have been universally implemented. Old features that have been superseded by new ones are not described – few of those historic features are used in modern programs although most have been retained in the language to maintain backward compatibility. The additional features of subsequent standards, up to Fortran 2023, are described in the Fortran 2023 standard document, ISO/IEC 1539-1:2023. Many of its new features are still being implemented in compilers.
ASN.1 Information Object Class is a concept widely used in ASN.1 specifications to address issues related to protocol specification similar to issues addressed by CORBA/IDL specifications.
X.690 is an ITU-T standard specifying several ASN.1 encoding formats:
References
- ↑ "ITU-T Rec. X.680 / ISO/IEC 8824-1" . Retrieved 2008-08-28.
- ↑ "ITU-T Rec. X.692 / ISO/IEC 8825-3" . Retrieved 2008-08-28.