Related Research Articles

The United States does not have an official language at the federal level, but the most commonly used language is English, which is the de facto national language. In addition, 32 U.S. states out of 50 and all five U.S. territories have declared English as an official language. The majority of the U.S. population (78%) speaks only English at home as of 2023. The remainder of the population speaks many other languages at home, most notably Spanish, according to the American Community Survey (ACS) of the U.S. Census Bureau; others include indigenous languages originally spoken by Native Americans, Alaska Natives, Native Hawaiians, and native populations in the U.S. unincorporated territories. Other languages were brought in by people from Europe, Africa, Asia, other parts of the Americas, and Oceania, including multiple dialects, creole languages, pidgin languages, and sign languages originating in what is now the United States. Interlingua, an international auxiliary language, was also created in the U.S.

Spanglish is any language variety that results from conversationally combining Spanish and English. The term is mostly used in the United States and refers to a blend of the words and grammar of the two languages. More narrowly, Spanglish can specifically mean a variety of Spanish with heavy use of English loanwords.

Spanish is the second most spoken language in the United States. Over 43.4 million people aged five or older speak Spanish at home (13.7%). Spanish is also the most learned language other than English, with about 8 million students. Estimates count up to 58.9 million native speakers, heritage language speakers, and second-language speakers. There is an Academy of the Spanish Language located in the United States as well.

The English-only movement, also known as the Official English movement, is a political movement that advocates for the exclusive use of the English language in official United States government communication through the establishment of English as the only official language in the United States. The United States has never had an official national language. However, at some times and places, there have been various moves to promote or require the use of English, such as in Native American boarding schools.

California Proposition 187 was a 1994 ballot initiative to establish a state-run citizenship screening system and prohibit illegal immigrants from using non-emergency health care, public education, and other services in the State of California. Voters passed the proposed law at a referendum on November 8, 1994. The law was challenged in a legal suit the day after its passage, and found unconstitutional by a federal district court on November 11. In 1999, Governor Gray Davis halted state appeals of this ruling.

Hispanic and Latino Americans are Americans of full or partial Spanish and/or Latin American background, culture, or family origin. These demographics include all Americans who identify as Hispanic or Latino regardless of race. As of 2020, the Census Bureau estimated that there were almost 65.3 million Hispanics and Latinos living in the United States and its territories.

Immigration reduction refers to a government and social policy in the United States that advocates a reduction in the amount of immigration allowed into the country. Steps advocated for reducing the numbers of immigrants include advocating stronger action to prevent illegal entry and illegal migration, and reductions in non-immigrant temporary work visas. Some advocate tightening the requirements for legal immigration requirements to reduce numbers or move the proportions of legal immigrants away from those on family reunification programs to skills-based criteria.

The Federation for American Immigration Reform (FAIR) is a nonprofit, anti-immigration organization in the United States. The group publishes position papers, organizes events, and runs campaigns in order to advocate for changes in U.S. immigration policy. The Southern Poverty Law Center classifies FAIR as a hate group with ties to white supremacist groups.

John Hamilton Tanton was an American ophthalmologist, white nationalist, and anti-immigration activist. He was the founder and first chairman of the Federation for American Immigration Reform (FAIR), an anti-immigration organization. He was the co-founder of the Center for Immigration Studies, an anti-immigration think tank; and NumbersUSA, an anti-immigration lobbying group.

Arizona Proposition 203, also known as English for the Children, is a ballot initiative that was passed by 63% of Arizona voters on November 7, 2000. It limited the type of instruction available to English language learner (ELL) students. Before Proposition 203, schools were free in terms of ELL instruction to use bilingual or immersion methods. According to a cover letter from the Arizona Department of Education Superintendent of Public Instruction Lisa Graham Keegan to the Arizona Legislature, it was impossible to make a correct analysis regarding how many students were learning through English as a second language programs, as opposed to bilingual education. The school districts had submitted "conflicting information," and 40% had not submitted any data, in spite of three deadline extensions.

ProEnglish is an American nonprofit lobbying organization that is part of the English-only movement. The group supports making English the only official language of the United States. The group has also campaigned against immigration reform and bilingual education.
Nativo Lopez-Vigil was an American political leader and immigrant rights activist in Southern California. Lopez was a national president of the Mexican American Political Association and the national director of the Hermandad Mexicana Latinoamericana, a community service and advocacy organization for Mexican and Latin American immigrants throughout the United States.

Turkish Americans or American Turks are Americans of ethnic Turkish origin. The term "Turkish Americans" can therefore refer to ethnic Turkish immigrants to the United States, as well as their American-born descendants, who originate either from the Ottoman Empire or from post-Ottoman modern nation-states. The majority trace their roots to the Republic of Turkey, however, there are also significant ethnic Turkish communities in the US which descend from the island of Cyprus, the Balkans, North Africa, the Levant and other areas of the former Ottoman Empire. Furthermore, in recent years there has been a significant number of ethnic Turkish people coming to the US from the modern Turkish diaspora, especially from the Turkish Meskhetian diaspora in Eastern Europe and "Euro-Turks" from Central and Western Europe.

Americanization is the process of an immigrant to the United States becoming a person who shares American culture, values, beliefs, and customs by assimilating into the American nation. This process typically involves learning the American English language and adjusting to American culture, values, and customs. It can be considered another form of, or an American subset of Anglicization.

Lawrence D. Pratt is the executive director emeritus of Gun Owners of America, a United States–based firearms lobbying group, and a former member of the Virginia House of Delegates.
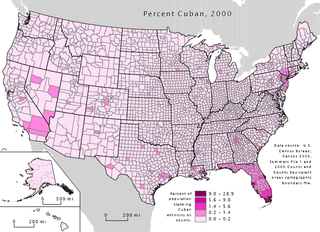
Cuban immigration has greatly affected Miami-Dade County since 1959, creating what is known as "Cuban Miami." However, Miami reflects global trends as well, such as the growing trends of multiculturalism and multiracialism; this reflects the way in which international politics shape local communities.
Nicholasa Mohr is one of the best known Nuyorican writers, born in the United States to Puerto Rican parents. In 1973, she became the first Nuyorican woman in the 20th century to have her literary works published by the major commercial publishing houses, and has had the longest creative writing career of any Nuyorican female writer for these publishing houses. She centers her works on the female experience as a child and adult in Puerto Rican communities in New York City, with much of writing containing semi-autobiographical content. In addition to her prominent novels and short stories, she has written screenplays, plays, and television scripts.

The League of United Latin American Citizens (LULAC) is the largest and oldest Hispanic and Latin-American civil rights organization in the United States. It was established on February 17, 1929, in Corpus Christi, Texas, largely by Hispanics returning from World War I who sought to end ethnic discrimination against Latinos in the United States. The goal of LULAC is to advance the economic condition, educational attainment, political influence, housing, health, and civil rights of Hispanic people in the United States. LULAC uses nationwide councils and group community organizations to achieve all these goals. LULAC has about 132,000 members in the United States.

LatinoJustice PRLDEF, long known by its former name the Puerto Rican Legal Defense and Education Fund, is a New York–based national civil rights organization with the goal of changing discriminatory practices via advocacy and litigation. Privately funded, nonprofit and nonpartisan, it is part of the umbrella Leadership Conference on Civil and Human Rights.

The City of Houston includes a significant population of Central American origin due to Texas' proximity to Central America, including origins from El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and other countries.
References
- ↑ Tatalovich, Raymond (1995). Nativism Reborn?: The Official English Language Movement and the American States. Lexington: University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 9780813119182. JSTOR j.ctt130j39p.
English First was founded by Larry Pratt, former Virginia state representative and the president of Gun Owners of America. English First is affiliated with the Committee to Protect the Family.
- ↑ "English First official site". Archived from the original on 2021-03-14.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link)