In quantum computing, a qubit or quantum bit is the basic unit of quantum information—the quantum version of the classical binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state quantum-mechanical system, one of the simplest quantum systems displaying the peculiarity of quantum mechanics. Examples include: the spin of the electron in which the two levels can be taken as spin up and spin down; or the polarization of a single photon in which the two states can be taken to be the vertical polarization and the horizontal polarization. In a classical system, a bit would have to be in one state or the other. However, quantum mechanics allows the qubit to be in a coherent superposition of both states/levels simultaneously, a property which is fundamental to quantum mechanics and quantum computing.
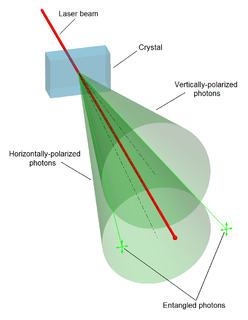
Quantum entanglement is a physical phenomenon that occurs when pairs or groups of particles are generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in ways such that the quantum state of each particle cannot be described independently of the state of the other(s), even when the particles are separated by a large distance.
Lemon v. Kurtzman, 403 U.S. 602 (1971), was a case argued before the Supreme Court of the United States. The court ruled in an 8–1 decision that Pennsylvania's Nonpublic Elementary and Secondary Education Act from 1968 was unconstitutional, violating the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment. The act allowed the Superintendent of Public Schools to reimburse private schools for the salaries of teachers who taught in these private schools, from public textbooks and with public instructional materials. The decision also upheld a decision of the United States District Court for the District of Rhode Island, which had struck down the Rhode Island Salary Supplement Act providing state funds to supplement salaries at private elementary schools by 15%. As in Pennsylvania, most of these funds were spent on Catholic schools.
Induced gravity is an idea in quantum gravity that space-time curvature and its dynamics emerge as a mean field approximation of underlying microscopic degrees of freedom, similar to the fluid mechanics approximation of Bose–Einstein condensates. The concept was originally proposed by Andrei Sakharov in 1967.
In quantum mechanics, separable quantum states are states without quantum entanglement.

In physics, topological order is a kind of order in the zero-temperature phase of matter. Macroscopically, topological order is defined and described by robust ground state degeneracy and quantized non-Abelian geometric phases of degenerate ground states. Microscopically, topological orders correspond to patterns of long-range quantum entanglement. States with different topological orders cannot change into each other without a phase transition.
Quantum metrology is the study of making high-resolution and highly sensitive measurements of physical parameters using quantum theory to describe the physical systems, particularly exploiting quantum entanglement and quantum squeezing. This field promises to develop measurement techniques that give better precision than the same measurement performed in a classical framework.
Squashed entanglement, also called CMI entanglement, is an information theoretic measure of quantum entanglement for a bipartite quantum system. If is the density matrix of a system composed of two subsystems and , then the CMI entanglement of system is defined by

Flavors of Entanglement is the seventh studio album, fifth international release and last Maverick Records release by Canadian singer-songwriter Alanis Morissette. The album, which was originally set for an April release, was released May 30, 2008 in Germany, Benelux and Ireland, released internationally on June 2 and in the United States on June 10. It was produced by Guy Sigsworth. The album has sold 233,000 copies in the USA and over 600,000 worldwide. Flavors won a Juno for Pop Album of the Year at the 2009 Juno Awards. The album gets its name from a lyric in the track "Moratorium".
In quantum information and quantum computing, a cluster state is a type of highly entangled state of multiple qubits. Cluster states are generated in lattices of qubits with Ising type interactions. A cluster C is a connected subset of a d-dimensional lattice, and a cluster state is a pure state of the qubits located on C. They are different from other types of entangled states such as GHZ states or W states in that it is more difficult to eliminate quantum entanglement in the case of cluster states. Another way of thinking of cluster states is as a particular instance of graph states, where the underlying graph is a connected subset of a d-dimensional lattice. Cluster states are especially useful in the context of the one-way quantum computer. For a comprehensible introduction to the topic see.
In the case of systems composed of subsystems, the classification of quantum-entangledstates is richer than in the bipartite case. Indeed, in multipartite entanglement apart from fully separable states and fully entangled states, there also exists the notion of partially separable states.
In quantum information science, the concurrence is a state invariant involving qubits.
Entanglement distillation is the transformation of N copies of an arbitrary entangled state into some number of approximately pure Bell pairs, using only local operations and classical communication (LOCC).
In the theory of quantum communication, the entanglement-assisted stabilizer formalism is a method for protecting quantum information with the help of entanglement shared between a sender and receiver before they transmit quantum data over a quantum communication channel. It extends the standard stabilizer formalism by including shared entanglement . The advantage of entanglement-assisted stabilizer codes is that the sender can exploit the error-correcting properties of an arbitrary set of Pauli operators. The sender's Pauli operators do not necessarily have to form an Abelian subgroup of the Pauli group over qubits. The sender can make clever use of her shared ebits so that the global stabilizer is Abelian and thus forms a valid quantum error-correcting code.

Zygmunt Miłoszewski is an award-winning Polish writer. Previously he was a journalist and editor for the Polish edition of Newsweek. He is an author of novels, features and short stories.
In the theory of quantum communication, the entanglement-assisted classical capacity of a quantum channel is the highest rate at which classical information can be transmitted from a sender to receiver when they share an unlimited amount of noiseless entanglement. It is given by the quantum mutual information of the channel, which is the input-output quantum mutual information maximized over all pure bipartite quantum states with one system transmitted through the channel. This formula is the natural generalization of Shannon's noisy channel coding theorem, in the sense that this formula is equal to the capacity, and there is no need to regularize it. An additional feature that it shares with Shannon's formula is that a noiseless classical or quantum feedback channel cannot increase the entanglement-assisted classical capacity. The entanglement-assisted classical capacity theorem is proved in two parts: the direct coding theorem and the converse theorem. The direct coding theorem demonstrates that the quantum mutual information of the channel is an achievable rate, by a random coding strategy that is effectively a noisy version of the super-dense coding protocol. The converse theorem demonstrates that this rate is optimal by making use of the strong subadditivity of quantum entropy.
The entropy of entanglement is an entanglement measure for a many-body quantum state. If a state is a seperable state, then the reduced desity matrix is a pure state, thus the entropy of the state is zero. Similar result holds for . The nonzero value of the entropy of the reduced desity matrix therefore is a signal of the existence of entanglement.
In quantum computing, the cat state, named after Schrödinger's cat, is a quantum state that is composed of two diametrically opposed conditions at the same time, such as the possibilities that a cat be alive and dead at the same time.
ER=EPR is a conjecture in physics stating that entangled particles are connected by a wormhole and may be a basis for unifying general relativity and quantum mechanics into a theory of everything.

Sandu Popescu is a Romanian-British physicist working in the foundations of quantum mechanics and quantum information.






