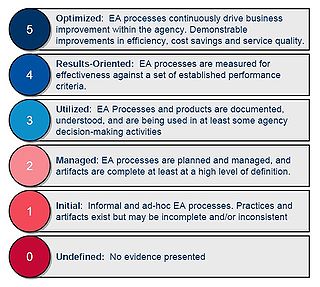
The Capability Maturity Model (CMM) is a development model created in 1986 after a study of data collected from organizations that contracted with the U.S. Department of Defense, who funded the research. The term "maturity" relates to the degree of formality and optimization of processes, from ad hoc practices, to formally defined steps, to managed result metrics, to active optimization of the processes.

The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States (EOP). OMB's most prominent function is to produce the president's budget, but it also examines agency programs, policies, and procedures to see whether they comply with the president's policies and coordinates inter-agency policy initiatives.
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations is "a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes."

The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 is a United States federal law enacted in 2002 as Title III of the E-Government Act of 2002. The act recognized the importance of information security to the economic and national security interests of the United States. The act requires each federal agency to develop, document, and implement an agency-wide program to provide information security for the information and information systems that support the operations and assets of the agency, including those provided or managed by another agency, contractor, or other source.
A federal enterprise architecture framework (FEAF) is the U.S. reference enterprise architecture of a federal government. It provides a common approach for the integration of strategic, business and technology management as part of organization design and performance improvement.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models – typically matrices and diagrams – for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.
The Information Technology Management Reform Act of 1996 is a United States federal law, designed to improve the way the federal government acquires, uses and disposes information technology (IT). It was passed as Division E of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 1996. Together with the Federal Acquisition Reform Act of 1996, it is known as the Clinger–Cohen Act.
Value measuring methodology (VMM) is a tool that helps financial planners balance both tangible and intangible values when making investment decisions, and monitor benefits.
Enterprise systems engineering (ESE) is the discipline that applies systems engineering to the design of an enterprise. As a discipline, it includes a body of knowledge, principles, and processes tailored to the design of enterprise systems.
The Program Assessment Rating Tool, or PART, was a program run through the United States Office of Management and Budget to rate the effectiveness of all federal programs, PART was instituted by President George W. Bush in 2002. It was discontinued by the Obama administration.
OMB Circular A-130, titled Managing Information as a Strategic Resource, is one of many Government circulars produced by the United States Federal Government to establish policy for executive branch departments and agencies.
The Queensland Government Enterprise Architecture is an initiative of the Queensland Government Chief Information Office (QGCIO) in Australia. QGEA 2.0 is the collection of ICT policies and associated documents that guides agency ICT initiatives and investments to improve the compatibility and cost-effectiveness of ICT across the government. The QGEA provides the decision making and management structures to support the development of better services for Queenslanders, more efficient and effective use of information and ICT in government and effective partnering with the private sector through the application of whole-of-Government, cross agency and agency information and information communications technology policies and practices.

The Business Transformation Agency (BTA) was an organization of the United States Department of Defense responsible for guiding the department's business operations modernization. The BTA was active from 2005 until its closure in 2011.

Enterprise life cycle (ELC) in enterprise architecture is the dynamic, iterative process of changing the enterprise over time by incorporating new business processes, new technology, and new capabilities, as well as maintenance, disposition and disposal of existing elements of the enterprise.

A view model or viewpoints framework in systems engineering, software engineering, and enterprise engineering is a framework which defines a coherent set of views to be used in the construction of a system architecture, software architecture, or enterprise architecture. A view is a representation of the whole system from the perspective of a related set of concerns.

FDIC Enterprise Architecture Framework was the enterprise architecture framework of the United States Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). A lot of the current article is about the enterprise architecture framework developed around 2005, and currently anno 2011 out-of-date.
The United States Congress established the Joint Planning and Development Office (JPDO) in 2003 to plan and coordinate the development of the Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen). The JPDO is a multi-agency public/private initiative to include: United States Department of Transportation, United States Department of Defense, Department of Commerce, Department of Homeland Security, Federal Aviation Administration, National Aeronautics and Space Administrations, and White House Office of Science and Technology Policy. Congress ended funding for JPDO in 2014.
Segment architecture is a detailed, formal description of areas within an enterprise, used at the program or portfolio level to organize and align change activity.
The Analysis of Alternatives (AoA) in the United States is a requirement of military acquisition policy, as controlled by the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the United States Department of Defense (DoD). It ensures that at least three feasible alternatives are analyzed prior to making costly investment decisions. The AoA establishes and benchmarks metrics for Cost, Schedule, Performance (CSP) and Risk (CSPR) depending on military "needs" derived from the Joint Capabilities Integration Development System process. It moves away from employing a single acquisition source to the exploration of multiple alternatives so agencies have a basis for funding the best possible projects in a rational, defensible manner considering risk and uncertainty.

The Federal Information Technology Acquisition Reform Act made changes to the ways the U.S. federal government buys and manages computer technology. It became law as a part of the National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2015 (Title VIII, Subtitle D, H.R. 3979.