An entity is something that exists as itself.
Contents
- Arts and entertainment
- Film and television
- Music
- Other uses in arts and entertainment
- Specific uses of entity
- In the humanities
- In computing
- See also
Entity may also refer to:
An entity is something that exists as itself.
Entity may also refer to:

In computing, a database is an organized collection of data stored and accessed electronically. Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling, efficient data representation and storage, query languages, security and privacy of sensitive data, and distributed computing issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance.
An entity is something that exists as itself, as a subject or as an object, actually or potentially, concretely or abstractly, physically or not. It does not need to be of material existence. In particular, abstractions and legal fictions are usually regarded as entities. In general, there is also no presumption that an entity is animate, or present.
A conceptual schema is a high-level description of informational needs underlying the design of a database. It typically includes only the main concepts and the main relationships among them. Typically this is a first-cut model, with insufficient detail to build an actual database. This level describes the structure of the whole database for a group of users. The conceptual model is also known as the data model that can be used to describe the conceptual schema when a database system is implemented. It hides the internal details of physical storage and targets on describing entities, datatypes, relationships and constraints.
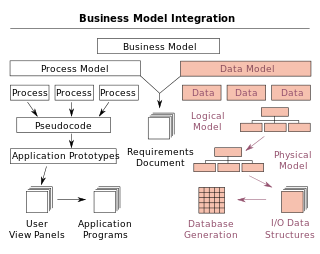
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be composed of a number of other elements which, in turn, represent the color and size of the car and define its owner.
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin modulus, a measure.

An entity–relationship model describes interrelated things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. A basic ER model is composed of entity types and specifies relationships that can exist between entities.

Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques.

Object-role modeling (ORM) is used to model the semantics of a universe of discourse. ORM is often used for data modeling and software engineering.
Database design is the organization of data according to a database model. The designer determines what data must be stored and how the data elements interrelate. With this information, they can begin to fit the data to the database model. Database management system manages the data accordingly.
Peter Pin-Shan Chen is a Taiwanese American computer scientist. He is a (retired) distinguished career scientist and faculty member at Carnegie Mellon University and Distinguished Chair Professor Emeritus at LSU. He is known for the development of the entity–relationship model in 1976.

An information model in software engineering is a representation of concepts and the relationships, constraints, rules, and operations to specify data semantics for a chosen domain of discourse. Typically it specifies relations between kinds of things, but may also include relations with individual things. It can provide sharable, stable, and organized structure of information requirements or knowledge for the domain context.
A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people know, understand, or simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, physical models are physical object such as a toy model that may be assembled and made to work like the object it represents.

In software engineering, a class diagram in the Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a type of static structure diagram that describes the structure of a system by showing the system's classes, their attributes, operations, and the relationships among objects.

Integration DEFinition for information modeling (IDEF1X) is a data modeling language for the development of semantic data models. IDEF1X is used to produce a graphical information model which represents the structure and semantics of information within an environment or system.
Object-oriented design (OOD) is the process of planning a system of interacting objects for the purpose of solving a software problem. It is one approach to software design.
Entity Framework (EF) is an open source object–relational mapping (ORM) framework for ADO.NET. It was originally shipped as an integral part of .NET Framework, however starting with Entity Framework version 6.0 it has been delivered separately from the .NET Framework.
Domain-driven design (DDD) is a major software design approach, focusing on modeling software to match a domain according to input from that domain's experts.
A geographic data model, geospatial data model, or simply data model in the context of geographic information systems, is a mathematical and digital structure for representing phenomena over the Earth. Generally, such data models represent various aspects of these phenomena by means of geographic data, including spatial locations, attributes, change over time, and identity. For example, the vector data model represents geography as collections of points, lines, and polygons, and the raster data model represent geography as cell matrices that store numeric values. Data models are implemented throughout the GIS ecosystem, including the software tools for data management and spatial analysis, data stored in a variety of GIS file formats, specifications and standards, and specific designs for GIS installations.

Semantic data model (SDM) is a high-level semantics-based database description and structuring formalism (database model) for databases. This database model is designed to capture more of the meaning of an application environment than is possible with contemporary database models. An SDM specification describes a database in terms of the kinds of entities that exist in the application environment, the classifications and groupings of those entities, and the structural interconnections among them. SDM provides a collection of high-level modeling primitives to capture the semantics of an application environment. By accommodating derived information in a database structural specification, SDM allows the same information to be viewed in several ways; this makes it possible to directly accommodate the variety of needs and processing requirements typically present in database applications. The design of the present SDM is based on our experience in using a preliminary version of it. SDM is designed to enhance the effectiveness and usability of database systems. An SDM database description can serve as a formal specification and documentation tool for a database; it can provide a basis for supporting a variety of powerful user interface facilities, it can serve as a conceptual database model in the database design process; and, it can be used as the database model for a new kind of database management system.
The following is provided as an overview of and topical guide to databases: