Related Research Articles
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography that deals with the study of people and their communities, cultures, economies, and interactions with the environment by studying their relations with and across space and place. Human geography attends to human patterns of social interaction, as well as spatial level interdependencies, and how they influence or affect the earth's environment. As an intellectual discipline, geography is divided into the sub-fields of physical geography and human geography, the latter concentrating upon the study of human activities, by the application of qualitative and quantitative research methods.

Physical geography is one of the two major fields of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the study of processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere, as opposed to the cultural or built environment, the domain of human geography.
Physical science is a branch of natural science that studies non-living systems, in contrast to life science. It in turn has many branches, each referred to as a "physical science", together called the "physical sciences".
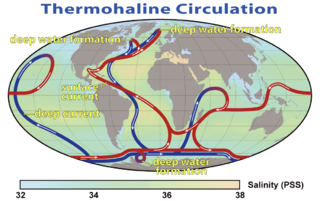
Oceanography, also known as oceanology, is the study of the physical and biological aspects of the ocean. It is an important Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and the geology of the sea floor; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers blend to further knowledge of the world ocean and understanding of processes within: astronomy, biology, chemistry, climatology, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans including marine geology, physics, chemistry and biology.
In geography, regions are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics, human impact characteristics, and the interaction of humanity and the environment. Geographic regions and sub-regions are mostly described by their imprecisely defined, and sometimes transitory boundaries, except in human geography, where jurisdiction areas such as national borders are defined in law.

Environmental science is an interdisciplinary academic field that integrates physical, biological and information sciences to the study of the environment, and the solution of environmental problems. Environmental science emerged from the fields of natural history and medicine during the Enlightenment. Today it provides an integrated, quantitative, and interdisciplinary approach to the study of environmental systems.

Environmental geography is the branch of geography that describes and explains the spatial aspects of interactions between human individuals or societies and their natural environment, these interactions being called coupled human–environment system. Summed up, environmental geography is about humans and nature and how we affect the environment and our planet.

A geographer is a scientist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society. The Greek prefix, "geo," means "earth" and the Greek suffix, "graphy," meaning "description," so a geographer is someone who studies the earth. The word "geography" is a Middle French word that is believed to have been first used in 1540.

Palaeogeography is the study of historical geography, generally physical landscapes. Palaeogeography can also include the study of human or cultural environments. When the focus is specifically on the study of landforms, the term paleogeomorphology is sometimes used instead.

The Geographic Names Information System (GNIS) is a database that contains name and locative information about more than two million physical and cultural features located throughout the United States of America and its territories. It is a type of gazetteer. GNIS was developed by the United States Geological Survey in cooperation with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of feature names.
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps form a distinctive category of maps due to the problem of projection. Maps by necessity distort the presentation of the earth's surface. These distortions reach extremes in a world map. The many ways of projecting the earth reflect diverse technical and aesthetic goals for world maps.
The Anton Melik Geographical Institute was founded in 1946 by the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts. In 1976 it was named after the Slovene geographer and academy member Anton Melik (1890–1966), who was the first head of the institute. Since 1981, the institute has been a member of the Scientific Research Center of the Slovenian Academy of Sciences and Arts. Until 1992 the institute was mainly engaged with researching glaciers, glacial and fluvial transformations of land surfaces, flooded areas, natural disasters, mountain farms, and social geography. Since 1993 the institute's main task has been to conduct geographical studies of Slovenia and its landscapes and to prepare basic geographical texts on Slovenia as a country and as part of the world.
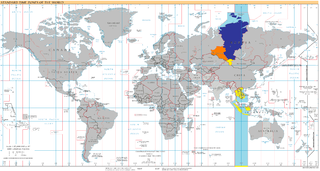
UTC+07:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +07:00. In ISO 8601 the associated time would be written as 2020-02-23T20:38:08+07:00. It is 7 hours ahead of the UTC, meaning areas in this time zone would be 07:00 while UTC is shown to midnight (00:00).

The five themes of geography is an educational tool for teaching geography. Adopted in 1984 by the Association of American Geographers, those five themes were published in the NCGE/AAG publication Guidelines for Geographic Education, Elementary, and Secondary Schools. Most American geography and social studies classrooms have adopted the five themes in teaching practices.
Physiographic regions of the world are a means of defining the Earth's landforms into distinct regions, based upon the classic three-tiered approach by Nevin M. Fenneman in 1916, that separates landforms into physiographic divisions, physiographic provinces, and physiographic sections. The model became the basis for similar classifications of other continents, and is still considered valid as of 1951.
Geographical features are naturally-created features of the Earth. Natural geographical features consist of landforms and ecosystems. For example, terrain types, are natural geographical features. Conversely, human settlements or other engineered forms are considered types of artificial geographical features.

Geography is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of the Earth and planets. The first person to use the word γεωγραφία was Eratosthenes. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be.
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical constitution of the Earth and its atmosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science, but with a much older history. Earth science encompasses four main branches of study, the lithosphere, the hydrosphere, the atmosphere, and the biosphere, each of which is further broken down into more specialized fields.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:
GEOBASE is a database, multidisciplinary in scope, which indexes bibliographic information and abstracts for the Geographical, Earth, and Ecological sciences, published by Engineering Information, a subsidiary of Elsevier. The broad subject coverage includes earth sciences, ecology, geomechanics, human geography, physical geography, social geography and oceanography. Development studies are also included in this database.
References
- ↑ Thomas,D.S.G. and Goudie, A. (Eds.), The Dictionary of Physical Geography (3rd edition), Blackwell Publishers, Great Britain, 2000
| This article about geography terminology is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |