Related Research Articles
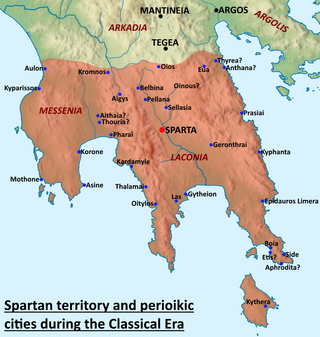
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon, while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement on the banks of the Eurotas River in the Eurotas valley of Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. Around 650 BC, it rose to become the dominant military land-power in ancient Greece.

Cleomenes III was one of the two kings of Sparta from 235 to 222 BC. He was a member of the Agiad dynasty and succeeded his father, Leonidas II. He is known for his attempts to reform the Spartan state.
The ephors were a board of five magistrates in ancient Sparta. They had an extensive range of judicial, religious, legislative, and military powers, and could shape Sparta's home and foreign affairs.
Agis II was the 18th Eurypontid king of Sparta, the eldest son of Archidamus II by his first wife, and half-brother of Agesilaus II. He ruled with his Agiad co-monarch Pausanias.

The Gerousia (γερουσία) was the council of elders in ancient Sparta. Sometimes called Spartan senate in the literature, it was made up of the two Spartan kings, plus 28 men over the age of sixty, known as gerontes. The Gerousia was a prestigious body, holding extensive judicial and legislative powers, which shaped Sparta's policies.
Lycurgus was the legendary lawgiver of Sparta, credited with the formation of its eunomia, involving political, economic, and social reforms to produce a military-oriented Spartan society in accordance with the Delphic oracle. The Spartans in the historical period honoured him as god.
Agis I was a king of Sparta and eponym of the Agiad dynasty. He was possibly the first historical king of Sparta, reigning at the end of the tenth century BC, during the emergence of the Dorians in Laconia. He is said by most ancient authors to have conquered the region and enslaved the helots.

Agis IV, the elder son of Eudamidas II, was the 25th king of the Eurypontid dynasty of Sparta. Posterity has reckoned him an idealistic but impractical monarch.
A Spartiate or Homoios was an elite full-citizen male of the ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. Spartiate-class males were a small minority: estimates are that they made up between 1/10 and 1/32 of the population, with the proportion decreasing over time; the vast majority of the people of Sparta were helots (slaves).

Agriculture was the foundation of the Ancient Greek economy. Nearly 80% of the population was involved in this activity.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining mathematics, science, artistic thought, theatre, literature, philosophy, and politics of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.

The Great Rhetra was used in two senses by the classical authors. In one sense, it was the Spartan Constitution, believed to have been formulated and established by the quasi-legendary lawgiver, Lycurgus. In the legend, Lycurgus forbade any written constitution. It was therefore presumed to have been oral.

The Agiad dynasty was one of the two royal families of the Ancient Greek city-state of Sparta. They ruled jointly along with the Eurypontid dynasty, possibly from the 8th century BC onwards, being the senior of the two houses. The hypothetical founder of the dynasty was Agis I, possibly the first king of Sparta at the end of the 10th century BC, who subsequently gave his name to the dynasty. The two lines, who maintained an enduring rivalry, were, according to tradition, respectively descended from the twins Eurysthenes and Procles, both descendants of Heracles. The most famous member of the Agiad dynasty was Leonidas I, known for his heroic death at the Battle of Thermopylae in 480 BC. The last Agiad king was Agesipolis III, deposed by the Eurypontid Lycurgus in 215 BC.

The history of Sparta describes the history of the ancient Doric Greek city-state known as Sparta from its beginning in the legendary period to its incorporation into the Achaean League under the late Roman Republic, as Allied State, in 146 BC, a period of roughly 1000 years. Since the Dorians were not the first to settle the valley of the Eurotas River in the Peloponnesus of Greece, the preceding Mycenaean and Stone Age periods are described as well. Sparta went on to become a district of modern Greece. Brief mention is made of events in the post-classical periods.
The Spartan Constitution are the government and laws of the classical Greek city-state of Sparta. All classical Greek city-states had a politeia; the politeia of Sparta however, was noted by many classical authors for its unique features, which supported a rigidly layered social system and a strong hoplite army.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Greece:
Polydorus (Polydoros) was the 10th Agiad dynasty king of Sparta. He succeeded his father Alcmenes and was succeeded by his son king Eurycrates.
Two land reforms were attempted at ancient Sparta in the 3rd century BC.

Pausanias was the Agiad King of Sparta; the son of Pleistoanax. He ruled Sparta from 445 BC to 427 BC and again from 409 BC to 395 BC. He was the leader of the faction in Sparta that opposed the imperialist policy conducted by Lysander.
References
- ↑ Hazel, John. Who's Who in the Greek World, p. 96 (2000)
- ↑ Roisman, Joseph & J.C. Yardley. Ancient Greece from Homer to Alexander: The Evidence, p. 420-21 (2011)
- ↑ Michell, Humfrey Sparta, p. 215-18 (1964)
- ↑ Isager, Signe Isager & Jens Erik Skydsgaard Ancient Greek Agriculture: An Introduction, p. 133 (1992)
- ↑ Schütrumpf, Eckart. The Rhetra of Epitadeus: A Platonist’s Fiction, Greek, Roman and. Byzantine Studies 28, 441-457 (1987) (“the account in Agis 5 is a mere fiction in a Platonic spirit and is therefore historically useless”.)