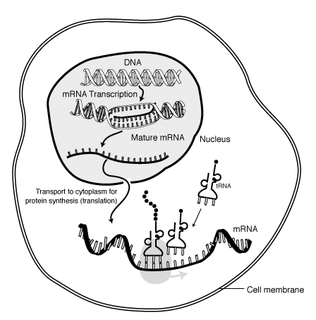
Messenger RNA (mRNA) is a large family of RNA molecules that convey genetic information from DNA to the ribosome, where they specify the amino acid sequence of the protein products of gene expression. RNA polymerase transcribes primary transcript mRNA into processed, mature mRNA. This mature mRNA is then translated into a polymer of amino acids: a protein, as summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology.

In genetics, a promoter is a region of DNA that initiates transcription of a particular gene. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, on the same strand and upstream on the DNA . Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long.

RNA polymerase, abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, officially DNA-directed RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides.

Flavivirus is a genus of viruses in the family Flaviviridae. This genus includes the West Nile virus, dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus, yellow fever virus, Zika virus and several other viruses which may cause encephalitis, as well as insect-specific flaviviruses (ISFs) such as cell fusing agent virus (CFAV), Palm Creek virus (PCV), and Parramatta River virus (PaRV).
The 5′ untranslated region is the region of an mRNA that is directly upstream from the initiation codon. This region is important for the regulation of translation of a transcript by differing mechanisms in viruses, prokaryotes and eukaryotes. While called untranslated, the 5′ UTR or a portion of it is sometimes translated into a protein product. This product can then regulate the translation of the main coding sequence of the mRNA. In many organisms, however, the 5′ UTR is completely untranslated, instead forming complex secondary structure to regulate translation. The 5′ UTR has been found to interact with proteins relating to metabolism; and proteins translate sequences within the 5′ UTR. In addition, this region has been involved in transcription regulation, such as the sex-lethal gene in Drosophila. Regulatory elements within 5′ UTRs have also been linked to mRNA export.
Arterivirus is the former genus of viruses in the family Arteriviridae, which is within the order Nidovirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. There are currently four species in this genus including the type species Equine arteritis virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: EAV: vascular lesions, fever, edema, abortion. PRRSV: abortions and respiratory disease. SHFV: fever, edema, dehydration, hemorragies, death.
Ribosome shunting is a mechanism of translation initiation in which ribosomes bypass, or "shunt over", parts of the 5' untranslated region to reach the start codon, enabling viruses to have more information than usual in an mRNA molecule. Some viral RNAs have been shown to use ribosome shunting as a more efficient form of translation during certain stages of viral life cycle or when translation initiation factors are scarce. Some viruses known to use this mechanism include adenovirus, Sendai virus, human papillomavirus, duck hepatitis B pararetrovirus, rice tungro bacilliform viruses, and cauliflower mosaic virus. In these viruses the ribosome is directly translocated from the upstream initiation complex to the start codon (AUG) without the need to unwind RNA secondary structures.
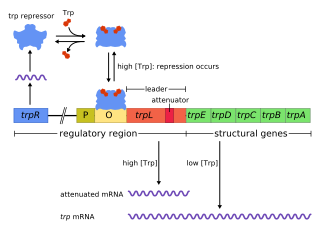
The trp operon is an operon—a group of genes that is used, or transcribed, together—that codes for the components for production of tryptophan. The trp operon is present in many bacteria, but was first characterized in Escherichia coli. The operon is regulated so that when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are not expressed. It was an important experimental system for learning about gene regulation, and is commonly used to teach gene regulation.
Long terminal repeats (LTRs) are identical sequences of DNA that repeat hundreds or thousands of times found at either end of retrotransposons or proviral DNA formed by reverse transcription of retroviral RNA. They are used by viruses to insert their genetic material into the host genomes.
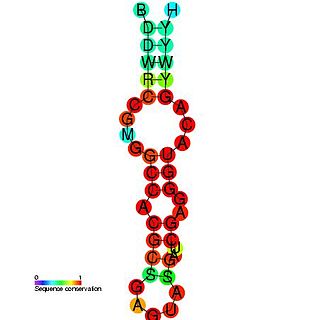
The Coronavirus 3' stem-loop II-like motif is a secondary structure motif identified in the 3'untranslated region (3'UTR) of astrovirus, coronavirus and equine rhinovirus genomes. Its function is unknown, but various viral 3' UTR regions have been found to play roles in viral replication and packaging.

The PreQ1-I riboswitch is a cis-acting element identified in bacteria which regulates expression of genes involved in biosynthesis of the nucleoside queuosine (Q) from GTP. PreQ1 (pre-queuosine1) is an intermediate in the queuosine pathway, and preQ1 riboswitch, as a type of riboswitch, is an RNA element that binds preQ1. The preQ1 riboswitch is distinguished by its unusually small aptamer, compared to other riboswitches. Its atomic-resolution three-dimensional structure has been determined, with the PDB ID 2L1V.

Retroviral Psi packaging element is a cis-acting RNA element identified in the genomes of the retroviruses Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and Simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV). It is involved in regulating the essential process of packaging the retroviral RNA genome into the viral capsid during replication. The final virion contains a dimer of two identical unspliced copies of the viral genome.

Usually found in gram-positive bacteria, the T box leader sequence is an RNA element that controls gene expression through the regulation of translation by binding directly to a specific tRNA and sensing its aminoacylation state. This interaction controls expression of downstream aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase genes, amino acid biosynthesis, and uptake-related genes in a negative feedback loop. The uncharged tRNA acts as the effector for transcription antitermination of genes in the T-box leader family. The anticodon of a specific tRNA base pairs to a specifier sequence within the T-box motif, and the NCCA acceptor tail of the tRNA base pairs to a conserved bulge in the T-box antiterminator hairpin.
The Hepatitis B virus PRE stem-loop alpha is an RNA structure that is shown to play a role in nuclear export of HBV mRNAs.
Rev is a transactivating protein that is essential to the regulation of HIV-1 protein expression. A nuclear localization signal is encoded in the rev gene, which allows the Rev protein to be localized to the nucleus, where it is involved in the export of unspliced and incompletely spliced mRNAs. In the absence of Rev, mRNAs of the HIV-1 late (structural) genes are retained in the nucleus, preventing their translation.
In molecular biology, the PyrC leader is a cis-regulatory RNA element found at the 5' of the PyrC mRNA in Enterobacteria. The PyrC gene encodes Dihydroorotase, an enzyme involved in pyrimidine biosynthesis. The PyrC leader regulates expression of PyrC. Translation initiation can occur at four different sites within this leader sequence, under high CTP conditions the translation initiation site is upstream of that used under low CTP conditions, additional cytosine residues are incorporated into the mRNA resulting in the formation of an RNA hairpin. This hairpin blocks ribosome-binding at the Shine-Dalgarno sequence, and therefore blocks expression of PyrC. Under low CTP conditions the initiation site is further downstream and does not result in hairpin formation, so the ribosome can bind to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and PyrC is expressed.
In molecular biology, Turnip crinkle virus (TCV) hairpin H4 is an RNA hairpin found at the 3' end of the Turnip crinkle virus (TCV) genome.
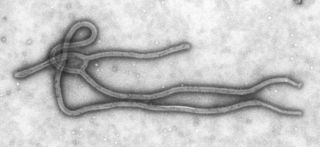
A negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus is a virus that uses negative sense, single-stranded RNA as its genetic material. Single stranded RNA viruses are classified as positive or negative depending on the sense or polarity of the RNA. The negative viral RNA is complementary to the mRNA and must be converted to a positive RNA by RNA polymerase before translation. Therefore, the purified RNA of a negative sense virus is not infectious by itself, as it needs to be converted to a positive sense RNA for replication. These viruses belong to Group V on the Baltimore classification.










