Related Research Articles

Bash, short for Bourne-Again SHell, is a shell program and command language supported by the Free Software Foundation and first developed for the GNU Project by Brian Fox. Designed as a 100% free software alternative for the Bourne shell, it was initially released in 1989. Its moniker is a play on words, referencing both its predecessor, the Bourne shell, and the concept of rebirth.

Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program. Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices.

GNU is an extensive collection of free software, which can be used as an operating system or can be used in parts with other operating systems. The use of the completed GNU tools led to the family of operating systems popularly known as Linux. Most of GNU is licensed under the GNU Project's own General Public License (GPL).

A Linux distribution is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro, if distributed on its own, is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers to servers and from embedded devices to supercomputers.

Loki Software, Inc. was an American video game developer based in Tustin, California, that ported several video games from Microsoft Windows to Linux. It took its name from the Norse deity Loki. Although successful in its goal of bringing games to the Linux platform, the company folded in January 2002 after filing for bankruptcy.

The GNU Project is a free software, mass collaboration project announced by Richard Stallman on September 27, 1983. Its goal is to give computer users freedom and control in their use of their computers and computing devices by collaboratively developing and publishing software that gives everyone the rights to freely run the software, copy and distribute it, study it, and modify it. GNU software grants these rights in its license.

The GNU/Linux naming controversy is a controversy regarding whether computer operating systems that use GNU software and the Linux kernel should be referred to as "GNU/Linux" or "Linux" systems.

The Free Software Foundation (FSF) grants two annual awards. Since 1998, FSF has granted the award for Advancement of Free Software and since 2005, also the Free Software Award for Projects of Social Benefit.
GNU Radio is a free software development toolkit that provides signal processing blocks to implement software-defined radios and signal processing systems. It can be used with external radio frequency (RF) hardware to create software-defined radios, or without hardware in a simulation-like environment. It is widely used in hobbyist, academic, and commercial environments to support both wireless communications research and real-world radio systems.
Alternative terms for free software, such as open source, FOSS, and FLOSS, have been a recurring issue among free and open-source software users from the late 1990s onwards. These terms share almost identical licence criteria and development practices.

Richard Matthew Stallman, also known by his initials, rms, is an American free software movement activist and programmer. He campaigns for software to be distributed in such a manner that its users have the freedom to use, study, distribute, and modify that software. Software which ensures these freedoms is termed free software. Stallman launched the GNU Project, founded the Free Software Foundation (FSF) in October 1985, developed the GNU Compiler Collection and GNU Emacs, and wrote all versions of the GNU General Public License.
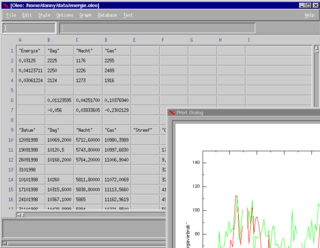
GNU Oleo is a discontinued lightweight free software spreadsheet originally designed as a text-based spreadsheet using the curses library. The last development version of Oleo, 1.99.16, was released in 2001.

Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution (distro), which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries—most of which are provided by third parties—to create a complete operating system, designed as a clone of Unix and released under the copyleft GPL license.
SlickEdit, previously known as Visual SlickEdit, is a cross-platform commercial source code editor, text editor, and Integrated Development Environment developed by SlickEdit, Inc. SlickEdit has integrated debuggers for GNU C/C++, Java, WinDbg, Clang C/C++ LLDB, Groovy, Google Go, Python, Perl, Ruby, Scala, PHP, Xcode, and Android JVM/NDK. SlickEdit includes features such as built-in "beautifiers" that can enhance code as you type, code navigation, context tagging, symbol references, third-party tool integration, DIFFZilla, syntax highlighting, and 15 emulations.

The history of free and open-source software begins at the advent of computer software in the early half of the 20th century. In the 1950s and 1960s, computer operating software and compilers were delivered as a part of hardware purchases without separate fees. At the time, source code—the human-readable form of software—was generally distributed with the software, providing the ability to fix bugs or add new functions. Universities were early adopters of computing technology. Many of the modifications developed by universities were openly shared, in keeping with the academic principles of sharing knowledge, and organizations sprung up to facilitate sharing.
TkDesk, released under the GNU GPL, is a graphical file manager for the X Window System, a standard component of Unix and Unix-like systems. TkDesk saw its last update in 2004.
Linux began in 1991 as a personal project by Finnish student Linus Torvalds to create a new free operating system kernel. The resulting Linux kernel has been marked by constant growth throughout its history. Since the initial release of its source code in 1991, it has grown from a small number of C files under a license prohibiting commercial distribution to the 4.15 version in 2018 with more than 23.3 million lines of source code, not counting comments, under the GNU General Public License v2 with a syscall exception meaning anything that uses the kernel via system calls are not subject to the GNU GPL.
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985. The organisation supports the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, United States, where it is also based.
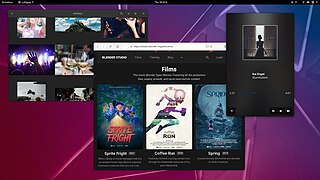
PureOS is a Linux distribution focusing on privacy and security, using the GNOME or KDE Plasma desktop environment. It is maintained by Purism for use in the company's Librem laptop computers as well as the Librem 5 smartphone.
References
- ↑ Edwards, John (2005). Telecosmos: the next great telecom revolution. John Wiley and Sons. pp. 130–. ISBN 978-0-471-65533-6 . Retrieved 9 June 2011.
- ↑ Marti, Don (May 7, 2004). "An Interview with Eric Blossom Linux Journal". www.linuxjournal.com. Retrieved 21 September 2018.
- 1 2 Blossom, Eric (June 1, 2004). "GNU Radio: Tools for Exploring the Radio Frequency Spectrum Linux Journal". www.linuxjournal.com. Retrieved 21 September 2018.
- ↑ McCullagh, Declan (August 12, 1999). "Starium Promises Phone Privacy". WIRED. Retrieved 21 September 2018.
- ↑ "Abstract/Bio". web.stanford.edu. Retrieved 21 September 2018.
- ↑ "GNU Radio A Free Software Defined Radio Eric Blossom Blossom Research Lighthouse Ave., Suite 109 Monterey, CA USA. - ppt download". slideplayer.com. Retrieved 21 September 2018.