
The economy of Eritrea has experienced considerable growth in recent years, indicated by an improvement in gross domestic product (GDP) in October 2012 of 7.5 percent over 2011. However, worker remittances from abroad are estimated to account for 32 percent of gross domestic product. Eritrea has an extensive amount of resources such as copper, gold, granite, marble, and potash. The Eritrean economy has undergone extreme changes due to the War of Independence.

Finance is a term for the management, creation, and study of money and investments. Specifically, it deals with the questions of how an individual, company or government acquires money – called capital in the context of a business – and how they spend or invest that money. Finance is then often divided into the following broad categories: personal finance, corporate finance, and public finance.

The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD) is an international financial institution, established in 1944 and headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, that is the lending arm of World Bank Group. The IBRD offers loans to middle-income developing countries. The IBRD is the first of five member institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The initial mission of the IBRD in 1944, was to finance the reconstruction of European nations devastated by World War II. The IBRD and its concessional lending arm, the International Development Association (IDA), are collectively known as the World Bank as they share the same leadership and staff.

The World Bank Group (WBG) is a family of five international organizations that make leveraged loans to developing countries. It is the largest and best-known development bank in the world and an observer at the United Nations Development Group. The bank is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States. It provided around $98.83 billion in loans and assistance to "developing" and transition countries in the 2021 fiscal year. The bank's stated mission is to achieve the twin goals of ending extreme poverty and building shared prosperity. Total lending as of 2015 for the last 10 years through Development Policy Financing was approximately $117 billion. Its five organizations are the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD), the International Development Association (IDA), the International Finance Corporation (IFC), the Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA) and the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID). The first two are sometimes collectively referred to as the World Bank.

The International Finance Corporation (IFC) is an international financial institution that offers investment, advisory, and asset-management services to encourage private-sector development in less developed countries. The IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C. in the United States.

The European Investment Bank (EIB) is the European Union's investment bank and is owned by the EU Member States. It is one of the largest supranational lenders in the world. The EIB is a not-for-profit organisation which funds projects that achieve the policy aims of the European Union through loans, guarantees and technical assistance.

Financial institutions, otherwise known as banking institutions, are corporations that provide services as intermediaries for different types of financial monetary transactions. Broadly speaking, there are three major types of financial institutions:
- Depository institutions – deposit-taking institutions that accept and manage deposits and make loans, including banks, building societies, credit unions, trust companies, and mortgage loan companies;
- Contractual institutions – insurance companies and pension funds
- Investment institutions – investment banks, underwriters, and other different types of financial entities managing investments.
A community development financial institution (US) or community development finance institution (UK) - abbreviated in both cases to CDFI - is a financial institution that provides credit and financial services to underserved markets and populations, primarily in the USA but also in the UK. A CDFI may be a community development bank, a community development credit union (CDCU), a community development loan fund (CDLF), a community development venture capital fund (CDVC), a microenterprise development loan fund, or a community development corporation.

The Nordic Investment Bank (NIB) is an international financial institution founded in 1975 by the five Nordic countries. In 2005, the three Baltic states also became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland. NIB acquires the funds for its lending by borrowing on the international capital markets.
An international financial institution (IFI) is a financial institution that has been established by more than one country, and hence is subject to international law. Its owners or shareholders are generally national governments, although other international institutions and other organizations occasionally figure as shareholders. The most prominent IFIs are creations of multiple nations, although some bilateral financial institutions exist and are technically IFIs. The best known IFIs were established after World War II to assist in the reconstruction of Europe and provide mechanisms for international cooperation in managing the global financial system.
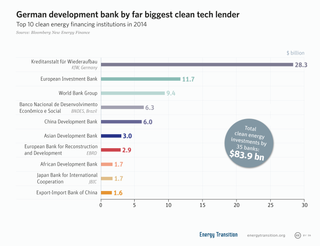
A development financial institution (DFI), also known as a development bank or development finance company (DFC), is a financial institution that provides risk capital for economic development projects on a non-commercial basis.

FMO is a Dutch development bank structured as a bilateral private-sector international financial institution based in the Hague, the Netherlands. FMO manages funds for the Ministries of Foreign Affairs and Economic Affairs of the Dutch government to maximize the development impact of private sector investments. It is licensed as a bank and supervised by the Dutch Central Bank.
A non-banking financial institution (NBFI) or non-bank financial company (NBFC) is a financial institution that does not have a full banking license or is not supervised by a national or international banking regulatory agency. NBFC facilitate bank-related financial services, such as investment, risk pooling, contractual savings, and market brokering. Examples of these include insurance firms, pawn shops, cashier's check issuers, check cashing locations, payday lending, currency exchanges, and microloan organizations. Alan Greenspan has identified the role of NBFIs in strengthening an economy, as they provide "multiple alternatives to transform an economy's savings into capital investment which act as backup facilities should the primary form of intermediation fail."
The Export–Import Bank of China is one of three institutional banks in China chartered to implement the state policies in industry, foreign trade, economy, and foreign aid to other developing countries, and provide policy financial support so as to promote the export of Chinese products and services. Established in 1994, the bank is subordinated to the State Council.
The Industrial Investment Bank of India (IIBI) was a government of India-owned financial investment institution that operated from its inception in 1971 until it was closed down by the Indian government in 2012. It was a type of development bank with the aim of rehabilitating sick industrial companies in India. IIBI offered a wide range of products and services, including term loan assistance for project finance, short duration non-project asset-backed financing, working capital/other short-term

The New Development Bank (NDB), formerly referred to as the BRICS Development Bank, is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states. According to the Agreement on the NDB, "the Bank shall support public or private projects through loans, guarantees, equity participation and other financial instruments." Moreover, the NDB "shall cooperate with international organizations and other financial entities, and provide technical assistance for projects to be supported by the Bank."

The Ministry of Finance is a ministry of Bangladesh. The ministry is responsible for state finance, including the state budget, taxation and economic policy in Bangladesh. It is led by the Finance Minister of Bangladesh. The department must report to the Parliament of Bangladesh. It contains four divisions:

The Ministry of Finance, abbreviated MOF, is a ministry of the Government of Somalia that is charged with the responsibility for government expenditure and revenue raising. The ministry's role is to develop economic policy and prepare the federal budget. The Ministry of Finance also oversees financial legislation and regulation. Each year in October, the Minister of Finance presents the Somali federal budget to the Parliament.
Events in the year 1996 in Eritrea.













