
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Saltwater is desalinated to produce water suitable for human consumption or irrigation. The by-product of the desalination process is brine. Desalination is used on many seagoing ships and submarines. Most of the modern interest in desalination is focused on cost-effective provision of fresh water for human use. Along with recycled wastewater, it is one of the few rainfall-independent water resources.

Chuquicamata is the largest open pit copper mine in terms of excavated volume in the world. It is located in the north of Chile, just outside Calama, at 2,850 m (9,350 ft) above sea level. It is 215 km (134 mi) northeast of Antofagasta and 1,240 km (770 mi) north of the capital, Santiago. Flotation and smelting facilities were installed in 1952, and expansion of the refining facilities in 1968 made 500,000 tons annual copper production possible in the late 1970s. Previously part of Anaconda Copper, the mine is now owned and operated by Codelco, a Chilean state enterprise, since the Chilean nationalization of copper in the late 1960s and early 1970s. Its depth of 850 metres (2,790 ft) makes it the second deepest open-pit mine in the world, after Bingham Canyon Mine in Utah, United States.

Codelco is a Chilean state-owned copper mining company. It was formed in 1976 from foreign-owned copper companies that were nationalised in 1971.

Leonora is a town in the Goldfields-Esperance region of Western Australia, located 833 kilometres (518 mi) northeast of the state capital, Perth, and 237 kilometres (147 mi) north of the city of Kalgoorlie.

Kennecott Utah Copper LLC (KUC), a division of Rio Tinto Group, is a mining, smelting, and refining company. Its corporate headquarters are located in South Jordan, Utah. Kennecott operates the Bingham Canyon Mine, one of the largest open-pit copper mines in the world in Bingham Canyon, Salt Lake County, Utah. The company was first formed in 1898 as the Boston Consolidated Mining Company. The current corporation was formed in 1989. The mine and associated smelter produce 1% of the world's copper.
Antofagasta plc is a Chilean multinational. It is one of the most important conglomerates of Chile with equity participation in Antofagasta Minerals, the railroad from Antofagasta to Bolivia, Twin Metals in Minnesota and other exploration joint ventures in different parts from the world. Antofagasta is listed on the London Stock Exchange and is a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.

Osmotic power, salinity gradient power or blue energy is the energy available from the difference in the salt concentration between seawater and river water. Two practical methods for this are reverse electrodialysis (RED) and pressure retarded osmosis (PRO). Both processes rely on osmosis with membranes. The key waste product is brackish water. This byproduct is the result of natural forces that are being harnessed: the flow of fresh water into seas that are made up of salt water.

In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, in situ. In situ leach works by artificially dissolving minerals occurring naturally in a solid state. For recovery of material occurring naturally in solution, see: Brine mining.
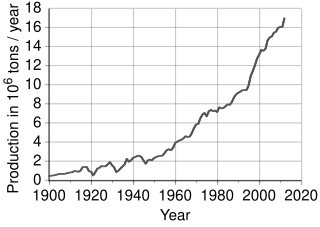
Peak copper is the point in time at which the maximum global copper production rate is reached. Since copper is a finite resource, at some point in the future new production from mining will diminish, and at some earlier time production will reach a maximum. When this will occur is a matter of dispute. Unlike fossil fuels, copper is scrapped and reused, and it has been estimated that at least 80% of all copper ever mined is still available.

Southern Copper Corporation is a mining company that was founded in 1952. The current incarnation of Southern Copper can be traced to the 2005 acquisition of Southern Peru Copper Corporation by the Mexican copper producer Minera México.

Mining in the United Kingdom produces a wide variety of fossil fuels, metals, and industrial minerals due to its complex geology. In 2013, there were over 2,000 active mines, quarries, and offshore drilling sites on the continental land mass of the United Kingdom producing £34bn of minerals and employing 36,000 people.
Mining in Ecuador was slow to develop in comparison to other Latin American countries, in spite of large mineral reserves. As late as 2012, according to the United Nations, Ecuador received less foreign direct investment per person than any other country in Latin America. During the 1980s, mining contributed only 0.7 percent to the Ecuadorian economy and employed around 7,000 people. Minerals were located in regions with little to no access, hindering exploration. Ecuador has reserves of gold, silver, copper, zinc, uranium, lead, sulfur, kaolin and limestone. The latter practically dominated the early industry as it was used in local cement plants.

The El Indio Gold Belt is a mineral-rich region spanning the border between Chile and Argentina that contains large quantities of gold, silver and copper. On both sides of the border the belt is located within the Andes. The El Indio mine within the district was the first modern mine in Chile to produce gold as its main product. In Chile the main precious metal containing mineral is enargite. The El Indio belt is bordered in the north by another gold-silver mining district known as the Frontera District. Rodalquilarite, alunite and poughite are some of the minerals present in the area. The deposits of the belt formed during the Late Miocene period.

Los Pelambres mine is a copper mine located in the north-central of Chile in Coquimbo Region. It is one of the largest copper reserves in the world, having estimated reserves of 4.9 billion tonnes of ore grading 0.65% copper.
The El Morro mine is one of the largest gold mines in Chile and in the world. The mine is located in the north of the country in the Atacama Region. The mine has estimated reserves of 6.7 million oz of gold. The mine also holds reserves amounting to 449.5 million tonnes of ore grading 0.49% copper.

The Buenavista mine, historically known as the Cananea copper mine, is a large open pit copper mine located in the north-west of Mexico in Cananea, Sonora. It lies 35 km (22 mi) south of the international border near Nogales, Arizona. Buenavista mine represents one of the largest copper reserves in Mexico and in the world. As of 2013, it had estimated reserves of 36 million tonnes of ore grading 0.69% copper, 3.3% zinc and 33.4 million oz of silver. Cananea represents one of the largest copper reserves in Mexico and in the world, having estimated reserves of 4.52 billion tonnes of ore with a grade of 0.42% copper.
The Candelaria mine is a large open pit and underground copper-gold mine located in northern Chile in the Atacama Region. Candelaria has Proven and Probable Reserves of 676 million tonnes of ore grading 0.53% copper, 0.13 g/t gold, and 1.79 g/t silver; containing 3.58 million tonnes of copper, 3.0 million oz of gold and 39 million oz of silver. The mine project incorporates a reverse osmosis plant at the port of Caldera, commissioned in 2013, with a capacity to produce 500 litres per second of desalinated industrial water, piping it 115 km from the Pacific Ocean to the minesite.

The Collahuasi mine is a large copper mine located at high altitude in the north of Chile in the Tarapaca Region. Collahuasi represents one of the largest copper reserves in Chile and in the world having estimated reserves of 3.93 billion tonnes of ore grading 0.66% copper.
Sierra Gorda Mine in Chile is a copper and molybdenum open pit mine which started production on October 1, 2014. The mine is located 2 km north-west of the village of Sierra Gorda in the Antofagasta Province of northern Chile.














