Related Research Articles

The country of Brazil occupies roughly half of South America, bordering the Atlantic Ocean. Brazil covers a total area of 8,514,215 km2 (3,287,357 sq mi) which includes 8,456,510 km2 (3,265,080 sq mi) of land and 55,455 km2 (21,411 sq mi) of water. The highest point in Brazil is Pico da Neblina at 2,994 m (9,823 ft). Brazil is bordered by the countries of Argentina, Bolivia, Colombia, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, Venezuela, and France.

The Tocantins River is a river in Brazil, the central fluvial artery of the country. In the Tupi language, its name means "toucan's beak". It runs from south to north for about 2,450 km. It is not really a branch of the Amazon River, since its waters flow into the Atlantic Ocean alongside those of the Amazon. It flows through four Brazilian states and gives its name to one of Brazil's newest states, formed in 1988 from what was until then the northern portion of Goiás.

Tocantins is one of the 26 states of Brazil. It is the newest state, formed in 1988 and encompassing what had formerly been the northern two-fifths of the state of Goiás. Tocantins covers 277,620.91 square kilometres (107,190.03 sq mi) and had an estimated population of 1,496,880 in 2014. Construction of its capital, Palmas, began in 1989; most of the other cities in the state date to the Portuguese colonial period. With the exception of Araguaína, there are few other cities with a significant population in the state. The government has invested in a new capital, a major hydropower dam, railroads and related infrastructure to develop this primarily agricultural area. The state has 0.75% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 0.5% of the Brazilian GDP.

The Araguaia River is one of the major rivers of Brazil though it is almost equal in volume at its confluence with the Tocantins. It has a total length of approximately 2,627 km.

Palmas is the capital and largest city of the state of Tocantins, Brazil. According to IBGE estimates from 2020, the city had 306,296 inhabitants.

Imperatriz is the second most populated city in the northeastern Brazilian state of Maranhão. The city extends along the right bank of the Tocantins River and is crossed by the Belém-Brasília Highway, standing on the border with the state of Tocantins.

Weston is a ghost town in Washington State founded circa 1885. Located at the foot of the western 2.2 percent grade of the Northern Pacific Railway's climb up Stampede Pass to Stampede Tunnel, the town served as the western helper station on the pass, counterpart to Easton, Washington. Facilities included an engine house, telegraph station, water tank, turntable and some ancillary residences and eating houses.

The Paranã River is located in Goiás and Tocantins states, Brazil. It divides two regions - the Northeast and north-central Goiás. It is formed by tributaries that descend the Serra Geral, the mountains that divide eastern Goiás and Bahia. One of the most important tributaries is the Crixás, which has its source near Formosa. Farther to the north the Paranã becomes the main tributary of the Tocantins River on the right bank. Today it is crossed by a long concrete bridge between the municipalities of Iaciara and Nova Roma. It forms the valley which makes up a vast region called the Vão do Paranã Microregion.
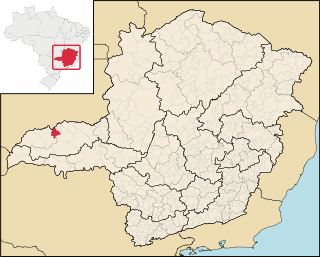
Canápolis is a Brazilian municipality located in the west of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 12,201 living in a total area of 845 km². The city belongs to the statistical mesoregion of Triângulo Mineiro and Alto Paranaíba and to the statistical microregion of Uberlândia. It became a municipality in 1948.
The Manuel Alves Grande River is a river of Maranhão and Tocantins states in northeastern Brazil. It is a tributary of the Tocantins River.
The Manuel Alves Pequeno River is a river of Tocantins state in central Brazil.
The Palma River is a river of Tocantins state in central Brazil.
The Perdida River is a river of Tocantins state in central Brazil.
The Urubu Grande River is a river of Tocantins state in central Brazil.
Filadélfia, Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.
São Salvador do Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.
Pindorama do Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.

Lagoa do Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.

Ponte Alta do Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.

Santa Tereza do Tocantins is a municipality in the state of Tocantins in the Northern region of Brazil.
References
Coordinates: 10°01′12″S47°12′14″W / 10.02000°S 47.20389°W