
The codex was the historical ancestor of the modern book. Instead of being composed of sheets of paper, it used sheets of vellum, papyrus, or other materials. The term codex is often used for ancient manuscript books, with handwritten contents. A codex, much like the modern book, is bound by stacking the pages and securing one set of edges by a variety of methods over the centuries, yet in a form analogous to modern bookbinding. Modern books are divided into paperback and those bound with stiff boards, called hardbacks. Elaborate historical bindings are called treasure bindings. At least in the Western world, the main alternative to the paged codex format for a long document was the continuous scroll, which was the dominant form of document in the ancient world. Some codices are continuously folded like a concertina, in particular the Maya codices and Aztec codices, which are actually long sheets of paper or animal skin folded into pages. In Japan, concertina-style codices called orihon developed during the Heian period (794–1185) were made of paper.

Embroidery is the art of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to stitch thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on hats, clothing, blankets, and handbags. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. It is often used to personalize gifts or clothing items.

A sewing machine is a machine used to sew fabric and materials together with thread. Sewing machines were invented during the first Industrial Revolution to decrease the amount of manual sewing work performed in clothing companies. Since the invention of the first sewing machine, generally considered to have been the work of Englishman Thomas Saint in 1790, the sewing machine has greatly improved the efficiency and productivity of the clothing industry.

A lockstitch is the most common mechanical stitch made by a sewing machine. The term "single needle stitching", often found on dress shirt labels, refers to lockstitch.

Chain stitch is a sewing and embroidery technique in which a series of looped stitches form a chain-like pattern. Chain stitch is an ancient craft – examples of surviving Chinese chain stitch embroidery worked in silk thread have been dated to the Warring States period. Handmade chain stitch embroidery does not require that the needle pass through more than one layer of fabric. For this reason the stitch is an effective surface embellishment near seams on finished fabric. Because chain stitches can form flowing, curved lines, they are used in many surface embroidery styles that mimic "drawing" in thread.

The St Cuthbert Gospel, also known as the Stonyhurst Gospel or the St Cuthbert Gospel of St John, is an early 8th-century pocket gospel book, written in Latin. Its finely decorated leather binding is the earliest known Western bookbinding to survive, and both the 94 vellum folios and the binding are in outstanding condition for a book of this age. With a page size of only 138 by 92 millimetres, the St Cuthbert Gospel is one of the smallest surviving Anglo-Saxon manuscripts. The essentially undecorated text is the Gospel of John in Latin, written in a script that has been regarded as a model of elegant simplicity.

A hem in sewing is a garment finishing method, where the edge of a piece of cloth is folded and sewn to prevent unravelling of the fabric and to adjust the length of the piece in garments, such as at the end of the sleeve or the bottom of the garment.
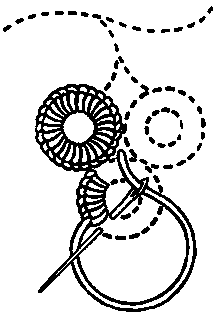
In everyday language, a stitch in the context of embroidery or hand-sewing is defined as the movement of the embroidery needle from the back of the fibre to the front side and back to the back side. The thread stroke on the front side produced by this is also called stitch. In the context of embroidery, an embroidery stitch means one or more stitches that are always executed in the same way, forming a figure. Embroidery stitches are also called stitches for short.

A sewing needle, used for hand-sewing, is a long slender tool with a pointed tip at one end and a hole to hold the sewing thread. The earliest needles were made of bone or wood; modern needles are manufactured from high carbon steel wire and are nickel- or 18K gold-plated for corrosion resistance. High-quality embroidery needles are plated with two-thirds platinum and one-third titanium alloy. Traditionally, needles have been kept in needle books or needlecases which have become objects of adornment. Sewing needles may also be kept in an étui, a small box that held needles and other items such as scissors, pencils and tweezers.

A stitching awl is a tool with which holes can be punctured in a variety of materials, or existing holes can be enlarged. It is also used for sewing heavy materials, such as leather or canvas. It is a thin, tapered metal shaft, coming to a sharp point, either straight or slightly bent. These shafts are often in the form of interchangeable needles. They usually have an eye piercing at the pointed end to aid in drawing thread through holes for the purpose of manual lockstitch sewing, in which case it is also called a sewing awl. Stitching awls are frequently used by shoe repairers and other leatherworkers. Sewing awls are used to make lock stitches. The needle, with the thread in the eye is pushed through the material. The thread is then pulled through the eye to extend it. As the needle is pushed through the material, the extra thread from the first stitch is then threaded through the loops of successive stitches creating a lock stitch. The action is likened to that of a "miniature sewing machine". Styles may vary, as they are adapted to specific trades, such as making shoes or saddles. They are also used in the printing trades to aid in setting movable type and in bookbinding.
Saddle stitch is a hand-sewing stitch commonly used in bookbinding, saddle and bridle making, leathercraft, and shoemaking.

A treasure binding or jewelled bookbinding is a luxurious book cover using metalwork in gold or silver, jewels, or ivory, perhaps in addition to more usual bookbinding material for book covers such as leather, velvet, or other cloth. The actual bookbinding technique is the same as for other medieval books, with the folios, normally of vellum, stitched together and bound to wooden cover boards. The metal furnishings of the treasure binding are then fixed, normally by tacks, onto these boards. Treasure bindings appear to have existed from at least Late Antiquity, though there are no surviving examples from so early, and Early Medieval examples are very rare. They were less used by the end of the Middle Ages, but a few continued to be produced in the West even up to the present day, and many more in areas where Eastern Orthodoxy predominated. The bindings were mainly used on grand illuminated manuscripts, especially gospel books designed for the altar and use in church services, rather than study in the library.

Traditional Chinese bookbinding, also called stitched binding, is the method of bookbinding that the Chinese, Koreans, Japanese, and Vietnamese used before adopting the modern codex form.
In knitting, binding off, or casting off, is a family of techniques for ending a column of stitches. Binding off is typically used to define the final edge of a knitted fabric, although it may also be used in other contexts, e.g., in making button holes. In principle, binding off is the opposite of casting on, but the techniques are generally not mirror images of one another. Sometimes, however, they can produce a mirror image appearance.

A bookmark is a thin marking tool, commonly made of card, leather, or fabric, used to keep track of a reader's progress in a book and allow the reader to easily return to where the previous reading session ended. Alternate materials for bookmarks are paper, metals like silver and brass, silk, wood, cord (sewing), and plastic. Some books may have one or more bookmarks made of woven ribbon sewn into the binding. Furthermore, other bookmarks incorporate a page-flap that enables them to be clipped on a page.

Coptic binding or Coptic sewing comprises methods of bookbinding employed by early Christians in Egypt, the Copts, and used from as early as the 2nd century AD to the 11th century. The term is also used to describe modern bindings sewn in the same style.

In the art of bookbinding, the longstitch technique is used for binding the sections (signatures) of a book without using glue. In Non-adhesive Binding: Books without Paste of Glue (1999) Keith A. Smith describes that binding a book with a "longstitch through a slotted cover" involves directly sewing each section through the cover, which has slots for attaching each section, and creates a pattern of staggered lines that is visible on the spine of the book.

Bookbinding is the process of building a book, usually in codex format, from an ordered stack of paper sheets with one's hands and tools, or in modern publishing, by a series of automated processes. Firstly, one binds the sheets of papers along an edge with a thick needle and strong thread. One can also use loose-leaf rings, binding posts, twin-loop spine coils, plastic spiral coils, and plastic spine combs, but they last for a shorter time. Next, one encloses the bound stack of paper in a cover. Finally, one places an attractive cover onto the boards, and features the publisher's information and artistic decorations.
Sewing is the craft of fastening or attaching objects using stitches made with needle and thread. Sewing is one of the oldest of the textile arts, arising in the Paleolithic Era. Although usually associated with clothing and household linens, sewing is used in a variety of crafts and industries, including shoemaking, upholstery, sailmaking, bookbinding and the manufacturing of some kinds of sporting goods. Sewing is the fundamental process underlying a variety of textile arts and crafts, including embroidery, tapestry, quilting, appliqué and patchwork.
Keith A. Smith is an American artist and author. He has taught at the Visual Studies Workshop, the School of the Art Institute of Chicago, and the University of Illinois. He is a recipient of two Guggenheim Fellowships, a National Endowment of the Arts grant and a Pollock-Krasner Foundation grant. Smith creates books as works of art, as well as instructional texts on how to make books. Permanent collections which hold works by Smith include the National Gallery of Art, Museum of Modern Art, the National Gallery of Canada, and the Center for Creative Photography.















