Wireless local loop (WLL), is the use of a wireless communications link as the "last mile / first mile" connection for delivering plain old telephone service (POTS) or Internet access to telecommunications customers. Various types of WLL systems and technologies exist.
The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) is a standards organization which develops protocols for mobile telephony. Its best known work is the development and maintenance of:

Magyar Telekom Nyrt. is the largest Hungarian telecommunications company. The former monopolist is now a subsidiary of Deutsche Telekom. Until 6 May 2005, it was known as MATÁV. The company was formed under the name of Magyar Távközlési Vállalat in December 1989, when Magyar Posta was split to three separate enterprises. On 31 December 1991, the company was re-structured as a Public Limited Company, as Magyar Távközlési Rt., and the company remained in 100% state ownership until the end of 1993. On 1 July 1993, the Telecommunications Act came into effect, and now it was possible to privatise the company. A consortium was formed by Deutsche Telekom and Ameritech International, which was named MagyarCom, and bought into the company a share of 30.1% for a price of 875 million USD.
The Open Mobile Alliance (OMA) is a standards body which develops open standards for the mobile phone industry. It is not a formal government-sponsored standards organization like the ITU, but a forum for industry stakeholders to agree on common specifications for products and services.
The next-generation network (NGN) is a body of key architectural changes in telecommunication core and access networks. The general idea behind the NGN is that one network transports all information and services by encapsulating these into IP packets, similar to those used on the Internet. NGNs are commonly built around the Internet Protocol, and therefore the term all IP is also sometimes used to describe the transformation of formerly telephone-centric networks toward NGN.

Türk Telekom is the formerly state-owned Turkish telecommunications company. Türk Telekom was separated from Turkish Post (PTT) in 1995. In November 2005, it was privatized to Oger Telecom.
The Fixed-Mobile Convergence Alliance, formed in mid-2004, was a global non-profit organisation for improving products for providing convergence between fixed and mobile networks. The FMCA was incorporated as a not-for-profit association under New York law in August 2006. The Alliance had a membership base of 20 leading global telecom operators, most of which were integrated telecom operators owning both fixed and mobile networks. The included vendor affiliation programme made the operators able to work closely with the associate members, who were all telecommunication vendors.
The telecommunications industry in China is dominated by three state-run businesses: China Telecom, China Unicom and China Mobile. The three companies were formed by restructuring launched in May 2008, directed by Ministry of Information Industry (MII), Nationals Development and Reform Commissions (NDRC) and Minister of Finance. Since then, all the three companies gained 3G licenses and engaged fixed-line and mobile business in China.

Orbitel is Bulgarian wireline telecommunications and Internet service provider with national licenses for voice and data. Through its national packet-switched network Orbitel provides convergent telecommunication solutions for telephony, high speed Internet and VPNs throughout Bulgaria. Orbitel also provides services such as web site hosting, domain registration, corporate e-mail and professional consultations.
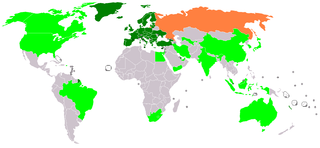
The European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) is an independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, headquartered in Sophia-Antipolis, France, with worldwide projection. ETSI produces globally-applicable standards for Information and Communications Technologies (ICT), including fixed, mobile, radio, converged, broadcast and internet technologies.

The Next Generation Mobile Networks (NGMN) Alliance is a mobile telecommunications association of mobile operators, vendors, manufacturers and research institutes. It was founded by major mobile operators in 2006 as an open forum to evaluate candidate technologies to develop a common view of solutions for the next evolution of wireless networks. Its objective is to ensure the successful commercial launch of future mobile broadband networks through a roadmap for technology and friendly user trials. Its office is in Frankfurt, Germany.

The Telecommunications Software & Systems Group (TSSG) is a large Irish information and communications technologies (ICT) research institute in Waterford Institute of Technology. It is based in the WIT West Campus, having brought in the funding for the two research buildings located there: ArcLabs Research and Innovation Centre, combining the TSSG with incubation and innovation space, formally opened by the Taoiseach in October 2006, and NetLabs, formally opened by Minister of Education in March 2014.
Telekom Innovation Laboratories is the R&D unit of Deutsche Telekom and is in a close partnership with the Technische Universität Berlin. Here, at T-Labs, more than 300 international experts and scientists work together on blockchain technology, smart city concepts, artificial intelligence and new media experiences. At its sites in Berlin, Darmstadt, Budapest, Be'er Sheva (Israel) and Vienna, T-Labs sits amongst a world-class host of universities, startups, investors, research institutes and corporate innovation hubs to jointly shape the future of communication services. T-Labs are working since 2006 in close cooperation with the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev and other universities, such as the Berlin University of the Arts, the Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest, and the TU Wien (Austria).
webinos is a computing platform for the development of software components that are independent of the utilized computer hardware or operating system. At the same time, webinos is the name of the EU-funded project aiming to deliver this platform. The webinos platform is based on open-source software. Its objective is to enable web applications and services to be used and shared consistently and securely over a broad spectrum of converged and connected devices, including mobile, PC, home media (TV) and in-car units. More than 5,400 developers have already downloaded the webinos operating system.
Qivicon is an alliance of companies from different industries that was founded in 2011 by Deutsche Telekom. The companies are collaborating on a cross-vendor, wireless-based home automation solution that has been available in the German market since fall 2013. It includes products in the areas of energy, security, and comfort. Qivicon won repeat awards from the international management consulting company Frost & Sullivan’s. In 2016, Frost & Sullivan has awarded Qivicon with the European Connected Home New Product Innovation Award. In 2014, the smart home platform has been awarded with the European Visionary Innovation Leadership Award in recognition of what the management consulting company saw as the most innovative Smart Home solution of the year.
Multi-access edge computing (MEC), formerly mobile edge computing, is a network architecture concept that enables cloud computing capabilities and an IT service environment at the edge of the cellular network and, more in general at the edge of any network. The basic idea behind MEC is that by running applications and performing related processing tasks closer to the cellular customer, network congestion is reduced and applications perform better. MEC technology is designed to be implemented at the cellular base stations or other edge nodes, and enables flexible and rapid deployment of new applications and services for customers. Combining elements of information technology and telecommunications networking, MEC also allows cellular operators to open their radio access network (RAN) to authorized third parties, such as application developers and content providers.

The National Telecommunications Regulatory Authority, commonly known as NTRA, is the Egypt government-approved regulatory and competition authority that was established in accordance of the Egyptian telecommunication regulation law No. 10/ 2003 as the national authority equipped to regulate and administer the telecommunications region..Regulating the competition environment between the operators inside the industry according to the Egyptian constitution was a huge mandatory case after the huge rate of telecommunication technology growth, as well as ensuring the availability of qualitative and green telecommunications services.












