The European Union has a number of relationships with foreign states. According to the European Union's official site, and a statement by Commissioner Günter Verheugen, the aim is to have a ring of countries, sharing EU's democratic ideals and joining them in further integration without necessarily becoming full member states.
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union and its policies.

The European Union–Turkey Customs Union is a trade agreement between the European Union (EU) and Turkey. The agreement came into effect on 31 December 1995, following a 6 March 1995 decision of the European Community–Turkey Association Council to implement a customs union between the two parties. Goods may travel between the two entities without any customs restrictions. The Customs Union does not cover essential economic areas such as agriculture, services or public procurement.

The Council of Arab Economic Unity (CAEU) was founded by Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Libya, Mauritania, Palestine, Saudi Arabia, Sudan, Tunisia, Syria, United Arab Emirates and Yemen on May 30, 1964, following an agreement in 1957 by the Economic Council of the Arab League.

The European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) is a foreign relations instrument of the European Union (EU) which seeks to tie those countries to the east and south of the European territory of the EU to the Union. These countries include some who seek to one day become either a member state of the European Union, or become more closely integrated with the European Union. The ENP does not apply to neighbours of the EU's outermost regions, specifically France's territories in South America, but only to those countries close to EU member states' territories in mainland Europe.
The European Union-Mediterranean Free Trade Area, also called the Euro-Mediterranean Free Trade Area or Euromed FTA, is based on the Barcelona Process and European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP). The Barcelona Process, developed after the Barcelona Conference in successive annual meetings, is a set of goals designed to lead to a free trade area in the Mediterranean Region and the Middle East by 2010.

The European Common Aviation Area (ECAA) is a single market in aviation services.

Morocco is a neighbouring and associated country of the European Union. The nation has a territorial land border with EU member Spain in the exclaves of Ceuta and Melilla. It also has a maritime border with Spain through the Gibraltar Strait and Exclusive Economic Zone borders with EU member Portugal in the Atlantic. The relations between the two are framed in the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP) and the Union for the Mediterranean. Among the ENP countries, Morocco has been recognised an advanced status, opening up to high levels of political cooperation.

Israel is an associated state of the European Union. The relations between the two are framed in the European Neighbourhood Policy (ENP), the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership, and the Union for the Mediterranean.
EuroMed Rights, formerly the Euro-Mediterranean Human Rights Network is a network of 68 human rights organisations, institutions and individuals based in 30 countries in Europe and the Mediterranean region. It was established in 1997 in response to the Barcelona Declaration, which led to the establishment of the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership.

The Parliamentary Assembly of the Union for the Mediterranean (PAUfM), previously known as the Euro-Mediterranean Parliamentary Assembly (EMPA), established in Naples on 3 December 2003 by decision of the Ministerial Conference of the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership, is an institution of the Barcelona Process. The EMPA opened its proceedings in Vouliagmeni (Athens) on 22 and 23 March 2004. Its first Bureau comprises the Presidents of the Egyptian People's Assembly, the European Parliament (EP), the Tunisian Chamber of Deputies and the Greek Parliament.
The Standing Committee for Euro Mediterranean Partnership of Local and Regional Authorities (COPPEM), was created in 2000 to promote dialogue and development between local and regional authorities in the Euro-Mediterranean area.
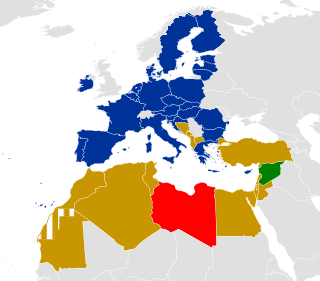
The Union for the Mediterranean is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 16 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
The EuroNest Parliamentary Assembly is the inter-parliamentary forum in which members of the European Parliament and the national parliaments of Ukraine, Moldova, Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia participate and forge closer political and economic ties with the European Union. It was established in 2011 by the European Commission as a component of the Eastern Partnership. After the elections in Belarus in 2010 were declared as flawed by the OSCE, the membership of Belarus in Euronest was automatically suspended. Belarus is welcome to re-join the Assembly once political requirements have been fulfilled. In 2015, Azerbaijan's membership was suspended due to the European Union's criticism of human rights abuses by the government. In September 2016, it was announced that Azerbaijan would take the necessary steps towards restoring ties. As of 2017, the combined population of Euronest members stands at 61,927,521 people.
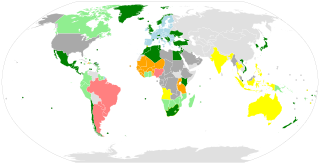
The European Union has concluded free trade agreements (FTAs) and other agreements with a trade component with many countries worldwide and is negotiating with many others. The European Union negotiates free trade deals on behalf of all of its member states, as the member states have granted the EU has an "exclusive competence" to conclude trade agreements. Even so, member states' governments control every step of the process :
ARLEM is a permanent, joint assembly, bringing together local and regional authorities from the three shores of the Mediterranean. This assembly is designed to provide an institutional framework to bring together CoR members and representatives of European associations involved in Euro-Mediterranean co-operation with their counterparts from the Mediterranean partners in a permanent joint body.
The Eurosphere or the European Empire is a concept centered around the European Union's sphere of influence, a term associated with the public intellectual Mark Leonard, Oxford University academic Jan Zielonka, the European Union Director-General for Politico-Military Affairs Robert Cooper and the former European Commission President José Manuel Barroso.
Events in the year 2015 in the European Union.

Tunisia–European Union relations are the foreign relations between the country of Tunisia and the European Union.

Egypt–European Union relations are the foreign relations between the country of Egypt and the European Union.












