Related Research Articles

The Australian Human Rights Commission is the national human rights institution of the Commonwealth of Australia, established in 1986 as the Human Rights and Equal Opportunity Commission (HREOC) and renamed in 2008. It is a statutory body funded by, but operating independently of, the Australian Government. It is responsible for investigating alleged infringements of Australia's anti-discrimination legislation in relation to federal agencies.
A national human rights institution (NHRI) is an independent state-based institution with the responsibility to broadly protect and promote human rights in a given country. The growth of such bodies has been encouraged by the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR), which has provided advisory and support services, and facilitated access for NHRIs to the United Nations (UN) treaty bodies and other committees. There are over one hundred such institutions, about two-thirds assessed by peer review as compliant with the United Nations standards set out in the Paris Principles. Compliance with the Principles is the basis for accreditation at the UN, which, uniquely for NHRIs, is not conducted directly by a UN body but by a sub-committee of the Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI) called the Sub-Committee on Accreditation. The secretariat to the review process is provided by the National Institutions and Regional Mechanisms Section of the OHCHR.

The Uganda Human Rights Commission (UHRC) serves to monitor and advance human rights in Uganda. The UHRC is a body established under the 1995 Constitution Article 51 under the Bill of Rights found in Chapter four of the Constitution. It is based on the Paris Principles which are the guidelines for the establishment of a national human rights institution. Its mandate is spelled out in Article 52 of the Constitution.
The Northern Ireland Human Rights Commission (NIHRC) is a non-departmental public body funded through the Northern Ireland Office but operating independently of government as the national human rights institution (NHRI) for Northern Ireland. It came into existence on 1 March 1999, having been created by the Parliament of the United Kingdom through section 68 of the Northern Ireland Act 1998, in compliance with a commitment made by the UK Government in the Belfast Agreement of 10 April 1998. Its powers were amended by the Justice and Security Act 2007.

The Human Rights Commission of Malaysia better known by its acronym SUHAKAM is the national human rights institution (NHRI) of Malaysia. It was established by the Malaysian Parliament under the Human Rights Commission of Malaysia Act 1999, Act 597, and began its work in April 2000. Its mandate is to promote human rights education, advise on legislation and policy, and conduct investigations.

Maurice Manning is an Irish academic and former Fine Gael politician. Manning was a member of the Oireachtas for 21 years, serving in both the Dáil and the Seanad. On 12 March 2009 he was elected Chancellor of the National University of Ireland, while remaining president of the Human Rights Commission. From 2002 to 2014, he was president of the Irish Human Rights Commission.
The Human Rights Commission is the national human rights institution (NHRI) for New Zealand, operating independently from direction by the Cabinet. Founded in 1977, the commission addresses issues of discrimination, equality, and human rights through education, advocacy, and resolving complaints. It provides guidance on anti-discrimination law.
The Danish Institute for Human Rights (DIHR), formerly the Danish Centre for Human Rights, is a national human rights institution (NHRI) operating in accordance with the UN Paris Principles.
The Fiji Human Rights Commission (FHRC) was created by presidential decree in 2009, succeeding the entity of the same name established as an independent statutory body under the 1997 Constitution of the Republic of the Fiji Islands.
The Paris Principles were defined at the first International Workshop on National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights held in Paris on 7–9 October 1991. They were adopted by the United Nations Human Rights Commission by Resolution 1992/54 of 1992, and by the UN General Assembly in its Resolution 48/134 of 1993. In addition to exchanging views on existing arrangements, the workshop participants drew up a comprehensive series of recommendations on the role, composition, status and also functions of national human rights institutions (NHRIs). These built on standards previously adopted by the 1978 Geneva Seminar on National and Local Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights’, which produced the ‘Guidelines on the Structure and Functioning of National and Local Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights’. The 1993 Paris Principles regulate to the status and functioning of national institutions for the protection and promotion of human rights known as National Human Rights Institutions.
The Scottish Human Rights Commission (SHRC) is the national human rights institution for Scotland. It was established by the Scottish Commission for Human Rights Act and started its work in 2008. The Commission is independent of the Scottish and UK Government, and of Parliament.
The Office of the Ombudsman is an independent officer of Parliament appointed under Section 66 of the Antigua and Barbuda Constitution. It is accredited as a national human rights institution (NHRI) but with the lowest ('C') status accorded by the International Co-ordinating Committee of NHRIs (ICC). It has only limited participation in the regional NHRI network, the Network of National Institutions in the Americas. Like most ombudsman offices it is primarily concerned with addressing maladministration in public bodies, rather than human rights violations.
The Asia Pacific Forum (APF) is one of four regional networks of national human rights institutions (NHRIs) within the International Co-ordinating Committee of NHRIs. The APF formerly accredited NHRIs for compliance with the United Nations' Paris Principles, but now acknowledges the accreditation decisions of an ICC sub-committee on which the APF has one of the four (regional) seats.
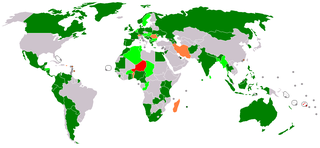
The Global Alliance of National Human Rights Institutions is a global network of national human rights institutions (NHRIs) which coordinates the relationship between NHRIs and the United Nations human rights system, and is unique as the only non-UN body whose internal accreditation system, based on compliance with the 1993 Paris Principles, grants access to UN committees. Institutions accredited by the Subcommittee for Accreditation (SCA) of GANHRI with "A status", meaning full compliance with the Paris Principles, are usually accorded speaking rights and seating at human rights treaty bodies and other UN organs, mainly to the Human Rights Council. GANHRI representatives often present statements on behalf of individual NHRIs or the regional groups.
The Network of African National Human Rights Institutions (NANHRI) is one of four regional groupings within the global network, the Global Alliance for National Human Rights Institutions (GANHRI). NANHRI promotes the establishment of national human rights institutions throughout Africa, and supports co-operation and training to strengthen and develop the monitoring, promotion, protection and advocacy work of African NHRIs.
The Network of National Institutions in the Americas is one of four regional groups of national human rights institutions (NHRIs) within the global network, the International Co-ordinating Committee of NHRIs. The Americas group, which largely consists of ombudsman agencies rather than multi-member human rights commissions, is currently chaired by the National Human Rights Commission of Mexico, which represents the region on the ICC Bureau.
The International Ombudsman Institute (IOI), established in 1978, is the only global organisation for the cooperation of more than 200 independent Ombudsman institutions operating on a local, regional and national level from more than 100 countries worldwide. The Ombudsman of Western Australia, Chris Field, is the current President of the IOI since May 2021. Werner Amon, Chair of the Austrian Ombudsman Board, is the IOI's Secretary General since July 2019.
The ICC Working Group on Business and Human Rights is a thematic Working Group of the International Coordinating Committee of National Institutions for the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights (ICC). The Working Group was established by the ICC Bureau in March 2009 and held its first meeting in Copenhagen in August 2009[usurped]. The Working Group includes 2 members from each of the 4 ICC Regions. The Danish Institute for Human Rights (DIHR) currently holds the Chair of the Working Group.
The European Network of National Human Rights Institutions (ENNHRI) is a membership international not-for-profit association (AISBL) under Belgian law. In 2013 it established its Permanent Secretariat in Brussels bringing together National Human Rights Institutions (NHRIs) from across the wider European region. Formerly known as European Group of National Human Rights Institutions, ENNHRI has been actively working in the field of promotion and protection of human rights in wider Europe for 15 years. ENNHRI essentially assists in the establishment and accreditation of European NHRIs, coordinates the exchange of information and best practices among its members, facilitates capacity building and training, engages with international and regional mechanisms for protection and promotion of human right and intervenes on legal and policy developments in Europe.

Laila Susanne Vars is a Norwegian-Sami human rights lawyer and former politician. Elected rector of Sámi University of Applied Sciences 2019-2023. First Sámi woman to achieve a PhD in Law. She is former research director at the Norwegian National Human Rights Institution (NHRI). Expert member of the United Nations' Expert Mechanism on the Rights of Indigenous Peoples (EMRIP) 2017-2023.
References
- ↑ Staff writer (2024). "European Network of National Human Rights Institutions (ENNHRI)". UIA Global Civil Society Database. uia.org. Brussels, Belgium: Union of International Associations. Yearbook of International Organizations Online. Retrieved 12 January 2025.
- ↑ "About ENNHRI". ENNHRI. Archived from the original on 17 July 2015. Retrieved 30 July 2015.