Related Research Articles

The European Investment Bank (EIB) is a publicly owned international financial institution whose shareholders are the EU member states. It was established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome as a "policy-driven bank" using financing operations to further EU policy goals such as European integration and social cohesion. It should not be confused with the European Central Bank, which is based in Frankfurt (Germany) or with the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) which is based in London.

The economy of Austria is a well-developed social market economy, with the country being one of the fourteen richest in the world in terms of GDP per capita. Until the 1980s, many of Austria's largest industry firms were nationalised; in recent years, however, privatisation has reduced state holdings to a level comparable to other European economies. Labour movements are particularly strong in Austria and have large influence on labour politics. Next to a highly developed industry, international tourism is the most important part of the national economy.

Public finance is the study of the role of the government in the economy. It is the branch of economics that assesses the government revenue and government expenditure of the public authorities and the adjustment of one or the other to achieve desirable effects and avoid undesirable ones. The purview of public finance is considered to be threefold, consisting of governmental effects on:
- The efficient allocation of available resources;
- The distribution of income among citizens; and
- The stability of the economy.

A public–private partnership is a cooperative arrangement between two or more public and private sectors, typically of a long-term nature. In other words, it involves government(s) and business(es) that work together to complete a project and/or to provide services to the population. They are an example of multistakeholder governance which is a key target of United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 17. Public–private partnerships have been implemented in multiple countries, are primarily used for infrastructure projects, such as the building and equipping of schools, hospitals, transport systems, and water and sewerage systems.

Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Its main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU) and to promote the harmonisation of statistical methods across its member states and candidates for accession as well as EFTA countries. The organisations in the different countries that cooperate with Eurostat are summarised under the concept of the European Statistical System.
Austerity is a set of political-economic policies that aim to reduce government budget deficits through spending cuts, tax increases, or a combination of both. Austerity measures are often used by governments that find it difficult to borrow or meet their existing obligations to pay back loans. The measures are meant to reduce the budget deficit by bringing government revenues closer to expenditures. This reduces the amount of borrowing required and may also demonstrate a government's fiscal discipline to creditors and credit rating agencies and make borrowing easier or cheaper as a result.
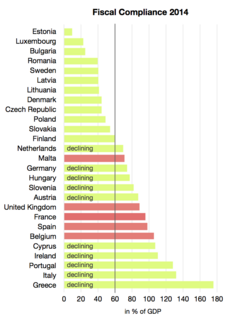
The Stability and Growth Pact (SGP) is an agreement, among the 27 member states of the European Union, to facilitate and maintain the stability of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). Based primarily on Articles 121 and 126 of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, it consists of fiscal monitoring of members by the European Commission and the Council of Ministers, and the issuing of a yearly recommendation for policy actions to ensure a full compliance with the SGP also in the medium-term. If a Member State breaches the SGP's outlined maximum limit for government deficit and debt, the surveillance and request for corrective action will intensify through the declaration of an Excessive Deficit Procedure (EDP); and if these corrective actions continue to remain absent after multiple warnings, the Member State can ultimately be issued economic sanctions. The pact was outlined by a resolution and two council regulations in July 1997. The first regulation "on the strengthening of the surveillance of budgetary positions and the surveillance and coordination of economic policies", known as the "preventive arm", entered into force 1 July 1998. The second regulation "on speeding up and clarifying the implementation of the excessive deficit procedure", known as the "dissuasive arm", entered into force 1 January 1999.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the second largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP was estimated to be $18.8 trillion (nominal) in 2018, representing about 22% of the global economy.
The Phare programme is one of the three pre-accession instruments financed by the European Union to assist the applicant countries of Central and Eastern Europe in their preparations for joining the European Union.

The European Union has a budget to finance policies carried out at European level.
Romania’s current national currency is the leu. However, being bound by its EU accession agreement, Romania has to replace the leu with the euro, as soon as Romania will fulfil all of the four nominal euro convergence criteria as states in the Treaty of Functioning the European Union in article 140. At the moment, the only currency on the market is leu, euro is not yet used in shops. The Romanian leu is not part of the European Exchange Rate Mechanism, although the Romanian authorities are working to prepare the changeover to the euro. In order to achieve the change of the currency, Romania is required to undergo at least two years of sustainable stability within the limits of the convergence criteria. The current Romanian Government in addition established a self-imposed criterion to reach a certain level of real convergence, as a steering anchor to decide the appropriate target year for ERM II membership and euro adoption. As of March 2018, the scheduled date for euro adoption in Romania is 2024, according to the National Plan to Changeover to the Euro.
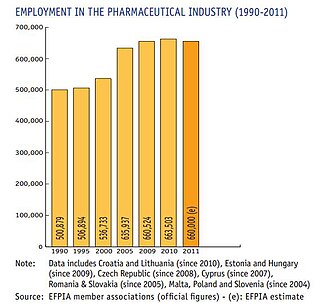
The European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industries and Associations (EFPIA) is a Brussels-based trade association founded in 1978 representing the research-based pharmaceutical industry operating in Europe.

The Caisse des Dépôts et Consignations is a French public sector financial institution created in 1816, and part of the government institutions under the control of the Parliament. Often described as the "investment arm" of the French State, it is defined in the French Monetary and Financial Code as a "public group serving the public interest" and a "long-term investor". Since 2017, Éric Lombard has served as its CEO.

The Center for Adaptation of the Civil Service to the Standards of the European Union was established under the National Agency of Ukraine on Civil Service in order to provide informational and analytical, expert and organizational support to public administration development, strengthening of institutional capacity of the civil service of Ukraine and its adaptation to the standards of the European Union.

The Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) is an umbrella term for the group of policies aimed at converging the economies of member states of the European Union at three stages. The policies cover the 19 eurozone states, as well as non-euro European Union states.
Water supply and sanitation in Lebanon is characterized by a number of achievements and challenges. The achievements include the reconstruction of infrastructure after the 1975–90 Civil War and the 2006 war with Israel, as well as the reform of the water and sanitation sector through a water law passed in 2000. The law created four Regional Water Establishments to consolidate numerous smaller utilities.
Natural capital accounting is the process of calculating the total stocks and flows of natural resources and services in a given ecosystem or region. Accounting for such goods may occur in physical or monetary terms. This process can subsequently inform government, corporate and consumer decision making as each relates to the use or consumption of natural resources and land, and sustainable behaviour.
Hungarian Development Bank Private Limited Company or Hungarian Development Bank in short, is a credit institution fully owned by the Hungarian State. Its legal status, tasks and scope of activities are defined in Act XX of 2001, its Memorandum of Association, and the strategy approved by the Hungarian Parliament and Government. Its core tasks include the provision of funding for growth under favourable terms and conditions to Hungarian enterprises, supporting the long-term development objectives of the state, and obtaining funds from money markets for these purposes. MFB Zrt. has been receiving individual international credit ratings from Moody's Investors Service since 19 May 2003.
Poland has been a member state of the European Union since 1 May 2004, with the Treaty of Accession 2003 signed on 16 April 2003 in Athens as the legal basis for Poland's accession to the EU. The actual process of integrating Poland into the EU began with Poland's application for membership in Athens on 8 April 1994, and then the confirmation of the application by all member states in Essen from 9–10 December 1994. Poland's integration into the European Union is a dynamic and continuously ongoing process.
References
- ↑ "EPEC webpage - activities". www.eib.org. Archived from the original on 22 January 2011. Retrieved 7 April 2017.
- ↑ Mathieu Vervynckt and María José Romero (2017). "Public-Private Partnerships:Defusing the ticking time bomb" (PDF). eurodad .
- ↑ "EUROSTAT treatment / Debt and deficit treatment of PPPs according to Eurostat". European Investment Bank. 2015. Retrieved 2019-10-17.