In politics, lobbying or advocacy, is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies, but also judges of the judiciary. Lobbying, which usually involves direct, face-to-face contact in cooperation with support staff that may not meet directly face-to-face, is done by many types of people, associations and organized groups, including individuals on a personal level in their capacity as voters, constituents, or private citizens; it is also practiced by corporations in the private sector serving their own business interests; by non-profits and non-governmental organizations in the voluntary sector through advocacy groups to fulfil their mission such as requesting humanitarian aid or grantmaking; and by fellow legislators or government officials influencing each other through legislative affairs in the public sector. Lobbying or certain practices that share commonalities with lobbying are sometimes referred to as government relations, or government affairs and sometimes legislative relations, or legislative affairs. It is also an industry known by many of the aforementioned names, and has a near complete overlap with the public affairs industry. Lobbyists may be among a legislator's constituencies, for example amateur lobbyists such as a voter or a bloc of voters within their electoral district acting as private citizens; while others like professional lobbyists may engage in lobbying as a business or profession. Professional lobbyists are people whose business is trying to influence legislation, regulation, or other government decisions, actions, or policies on behalf of a group or individual who hires them. Nonprofit organizations whether as professional or amateur lobbyists can also lobby as an act of volunteering or as a small part of their normal job. Governments often define "lobbying" for legal purposes, and regulate organized group lobbying that has become influential.

Secrecy is the practice of hiding information from certain individuals or groups who do not have the "need to know", perhaps while sharing it with other individuals. That which is kept hidden is known as the secret.

Milan Kučan is a Slovenian former politician who served as the first President of Slovenia from 23 December 1991 until 22 December 2002. Before being president of Slovenia, he was the 13th President of the Presidency of SR Slovenia from 10 May 1990 to 23 December 1991.

A customs union is the principal area of robust formal agreement between the Principality of Andorra and the European Union (EU). Andorra borders two EU member states: France and Spain.
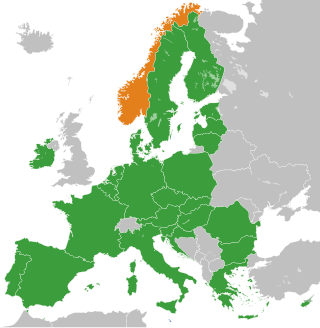
Norway is not a member state of the European Union (EU). However, it is associated with the Union through its membership of the European Economic Area (EEA), signed in 1992 and established in 1994. Norway was a founding member of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) in 1960, which was originally set up as an alternative to the European Economic Community (EEC), the main predecessor of the EU. Norway had considered joining both the EEC and the European Union, but opted to decline following referendums in 1972 and 1994. According to the European Social Survey conducted in 2018, 73.6% of Norwegians would vote 'No' in a referendum to join the European Union. Norway has two land borders with EU member states: Finland and Sweden.

European Digital Rights (EDRi) is an international advocacy group headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. EDRi is a network collective of non-profit organizations (NGO), experts, advocates and academics working to defend and advance digital rights across the continent. As of October 2022, EDRi is made of more than 40 NGOs, as well as experts, advocates and academics from all across Europe.

The International Life Sciences Institute (ILSI) is a global nonprofit 501(c)(3) organization headquartered in Washington, DC, United States that publishes peer-reviewed studies on nutrition and food safety. It was founded in 1978 by Alex Malaspina, a former Coca-Cola executive, and it is partially financed by its 300+ members, which includes food and chemical corporations such as BASF, McDonald’s, Syngenta and Pepsi. In 2020, the organization's revenue was US$10.1 million.
The European Federation of Biotechnology (EFB) was established by European scientists in 1978. It is a non-profit federation of national biotechnology associations, learned societies, universities, scientific institutes, biotechnology companies and individual biotechnologists working to promote biotechnology throughout Europe and beyond.
The European Chemical Society (EuChemS) is a European non-profit organisation which promotes collaboration between non-profit scientific and technical societies in the field of chemistry.

Friends of Europe is a Brussels-based, not-for-profit think tank for European Union policy analysis and debate.

Alber & Geiger is a political lobbying agency and a European-based government relations law firm, lobbying EU institutions in Brussels. The firm has also a litigation practice at the European Court of Justice and has offices in Brussels, Berlin, Beijing and Washington D.C.
The European Association of Urology (EAU) is a non-profit organisation committed to the representation of urology professionals worldwide. All active urology professionals, including urology nurses, are eligible for membership of the EAU.
The European Health Management Association (EHMA) was established in 1982 and is a non-profit membership organisation. Its focus is on health management capacity and capabilities and on supporting the implementation of health policy and practice.
A Lobby Registry, also named Lobbyist Registry, Register for Lobby Transparency or Registry of Lobbyists is a public database, in which information about lobbying actors and key data about their actions can be accessed.

EuroHealthNet is a non-profit partnership of organisations, agencies and statutory bodies working to contribute to a healthier Europe by promoting health and health equity between and within European countries. EuroHealthNet promotes health through its partnership framework by supporting members’ work in the EU and associated states through policy and project development, networking, and communications.

The sugar industry subsumes the production, processing and marketing of sugars. Globally, most sugar is extracted from sugar cane and sugar beet.

Best for Britain is a civil society campaign, launched on 26 April 2017, to stop Brexit and continue the UK's membership of the European Union (EU). Since 2021, the organisation's aim has changed to encourage greater internationalism rather than an immediate push to rejoin the EU.

The COVID-19 pandemic and its spread in Europe has had significant effects on some major EU members countries and on European Union institutions, especially in the areas of finance, civil liberties, and relations between member states.

Digital contact tracing is a method of contact tracing relying on tracking systems, most often based on mobile devices, to determine contact between an infected patient and a user. It came to public prominence in the form of COVID-19 apps during the COVID-19 pandemic. Since the initial outbreak, many groups have developed nonstandard protocols designed to allow for wide-scale digital contact tracing, most notably BlueTrace and Exposure Notification.














