Related Research Articles

Agriculture is a major industry in the United States, which is a net exporter of food. As of the 2017 census of agriculture, there were 2.04 million farms, covering an area of 900 million acres (1,400,000 sq mi), an average of 441 acres per farm.

Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope.

A fishing net is a net used for fishing. Some fishing nets are also called fish traps, for example fyke nets. Fishing nets are usually meshes formed by knotting a relatively thin thread. Early nets were woven from grasses, flaxes and other fibrous plant material. Later cotton was used. Modern nets are usually made of artificial polyamides like nylon, although nets of organic polyamides such as wool or silk thread were common until recently and are still used.
Bethal is a farming town in Mpumalanga, South Africa. The farms in the region produce maize, sunflower seeds, sorghum, rye and potatoes. The town lies 155 km (96 mi) east of Johannesburg on the N17 National Route.
El-Gadarif, also spelt Gedaref or Gedarif, is the capital of the state of Al Qadarif in Sudan. It lies on the road that connects Khartoum with Gallabat on the Ethiopian border, about 410 kilometres (250 mi) from the capital.

Cyclos is online banking software for microfinance institutions, local banks and complementary currency systems like LETS, TD4W Credits, Barter networks and time banks.

Camelina sativa is a flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae usually known as camelina, gold-of-pleasure, or false flax, but also occasionally as wild flax, linseed dodder, German sesame, or Siberian oilseed. It is native to Europe and areas of Central Asia, but cultivated as an oilseed crop mainly in Europe and in North America. It is not related to true flax, in the family Linaceae.

China FAW Group Corp., Ltd. is a Chinese state-owned automobile manufacturer headquartered in Changchun, Jilin. Founded the 15th July 1953, it is currently the second largest of the "Big Four" state-owned car manufacturers of China, together with SAIC Motor, Dongfeng Motor Corporation and Changan Automobile.

The 'International Fairtrede Certification Mark is an independent certification mark used in over 69 countries. It appears on products as an independent guarantee that a product has been produced according to Fairtrade political standards.
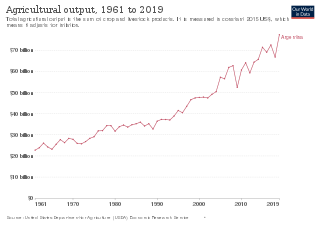
Agriculture is one of the bases of Argentina's economy.

Agriculture in Kyrgyzstan is a significant sector of the economy. According to the CIA World Factbook, it comprises 18% of the total GDP and occupies 48% of the total labor force. Only 6.8% of the total land area is used for crop cultivation, but 44% of the land is used as pastures for livestock. Because of the many mountains of Kyrgyzstan, animal husbandry remains a significant part of the agricultural economy.
Agriculture in Lithuania dates to the Neolithic period, about 3,000 to 1,000 BC. It has been one of Lithuania's most important occupations for many centuries.

Agriculture in Saskatchewan is the production of various food, feed, or fiber commodities to fulfill domestic and international human and animal sustenance needs. The newest agricultural economy to be developed in renewable biofuel production or agricultural biomass which is marketed as ethanol or biodiesel. Plant cultivation and livestock production have abandoned subsistence agricultural practices in favor of intensive technological farming resulting in cash crops which contribute to the economy of Saskatchewan. The particular commodity produced is dependent upon its particular biogeography or ecozone of Geography of Saskatchewan. Agricultural techniques and activities have evolved over the years. The first nation nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyle and the early immigrant ox and plow farmer proving up on his quarter section of land in no way resemble the present farmer operating huge amounts of land or livestock with their attendant technological mechanization. Challenges to the future of Saskatchewan agriculture include developing sustainable water management strategies for a cyclical drought prone climate in south western Saskatchewan, updating dryland farming techniques, stabilizing organic definitions or protocols and the decision to grow, or not to grow genetically modified foods. Domestically and internationally, some commodities have faced increased scrutiny from disease and the ensuing marketing issues.

Agriculture is an important sector of Turkey's economy, and the country is one of the world's top ten agricultural producers. Wheat, sugar beet, milk, poultry, cotton, vegetables and fruit are major products; and Turkey is the world's largest grower of hazelnuts, apricots, and oregano.

Centralina is a Brazilian municipality located in the west of the state of Minas Gerais. Its population as of 2020 was 10,346 living in a total area of 322 km². The city belongs to the statistical mesoregion of Triângulo Mineiro and Alto Paranaíba and to the statistical microregion of Uberlândia. It became a municipality in 1954.

Agricultural machinery relates to the mechanical structures and devices used in farming or other agriculture. There are many types of such equipment, from hand tools and power tools to tractors and the countless kinds of farm implements that they tow or operate. Diverse arrays of equipment are used in both organic and nonorganic farming. Especially since the advent of mechanised agriculture, agricultural machinery is an indispensable part of how the world is fed. Agricultural machinery can be regarded as part of wider agricultural automation technologies, which includes the more advanced digital equipment and robotics. While agricultural robots have the potential to automate the three key steps involved in any agricultural operation, conventional motorized machinery is used principally to automate only the performing step where diagnosis and decision-making are conducted by humans based on observations and experience.
P. Ananda Kumar is an Indian plant molecular biologist and biotechnologist.
FAW Bus and Coach is a bus manufacturer located in Wuxi, Jiangsu, China. Founded in 1959, it was assigned under the FAW Group in 1986. The buses are sold under the Taihu brand.
References
- ↑ "Apricot Network" http://agrowebcee.net/apricot/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Buffalo Network" http://agrowebcee.net/buffalo/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "CENTAUR Network" http://centaur.vri.cz/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Cotton Network" http://www.agrowebcee.net/cotton/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Farm Animal Welfare" http://www.agrowebcee.net/faw/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Flax and other Bast Plants Network" http://www.agrowebcee.net/flax/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Museum Network" http://www.vmp.cz/en/professional-activity/aima/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Network of Aquaculture Centres in Central and Eastern Europe" http://agrowebcee.net/nacee/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Network on Capacity Development on Nutrition" http://www.agrowebcee.net/ncdn/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "NCDN CEE Meeting" https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OGAaVs3po-c. Retrieved on 2011-07-26.
- ↑ "Nuts" http://www.iamz.ciheam.org/en/pages/contenidos/investigacion/info_detallada/frutos_secos.htm Archived 2012-03-28 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Olives Network" http://agrowebcee.net/olive/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Organic Edunet" http://portal.organic-edunet.eu/ Archived 2011-08-14 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Pastures Network" http://www.iamz.ciheam.org/en/pages/paginas/pag_investigacion3b.htm Archived 2011-07-23 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Rice Network" http://www.medrice.unito.it/ Archived 2012-03-28 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Sheep & Goats Network" http://www.iamz.ciheam.org/en/pages/paginas/pag_investigacion3a.htm Archived 2011-07-23 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Sunflower Network" http://www.agrowebcee.net/sunflower/. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Agromarketing Network" http://www.agrowebcee.net/agromarketing/. Retrieved on 2011-07-28.
- ↑ "Rye Network" http://www.agrowebcee.net/rye/. Retrieved on 2016-12-23.
- ↑ "Sustainable Rural Energy Network" http://www.petiteenergie.com/ Archived 2012-03-28 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-08-01.
- ↑ "Recycling of Agricultural, Municipal and Industrial Residues in Agricultural Network" http://www.ramiran.net/index.php Archived 2011-08-01 at the Wayback Machine . Retrieved on 2011-07-18.
- ↑ "Scientific Bulletin of ESCORENA" http://www.uav.ro/en/journals/scientific-bulletin-of-escorena. Retrieved on 2011-07-18.