
Richmond is the capital city of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city since 1871. The city's population in the 2020 census was 226,610, up from 204,214 in 2010, making it Virginia's fourth-most populous city. The Richmond metropolitan area, with over 1.3 million residents, is the Commonwealth's third-most populous.

The Congressional Cemetery, officially Washington Parish Burial Ground, is a historic and active cemetery located at 1801 E Street, S.E., in Washington, D.C., on the west bank of the Anacostia River. It is the only American "cemetery of national memory" founded before the Civil War. Over 65,000 individuals are buried or memorialized at the cemetery, including many who helped form the nation and Washington, D.C. in the early 19th century.
The Greater Richmond, Virginia area has many neighborhoods and districts.

Maggie Lena Walker was an American businesswoman and teacher. In 1903, Walker became both the first African American woman to charter a bank and the first African American woman to serve as a bank president. As a leader, Walker achieved successes with the vision to make tangible improvements in the way of life for African Americans. Disabled by paralysis and a wheelchair user later in life, Walker also paved the way for people with disabilities.

The Maggie L. Walker National Historic Site is a United States National Historic Landmark and a National Historic Site located at 110½ E. Leigh Street on "Quality Row" in the Jackson Ward neighborhood of Richmond, Virginia. The site was designated a U.S. National Historic Landmark in 1975. The National Historic Site was established in 1978 to tell the story of the life and work of Maggie L. Walker (1867-1934), the first woman to serve as president of a bank in the United States. It was built by George W. Boyd, father of physician, Sarah Garland Boyd Jones. The historic site protects the restored and originally furnished home of Walker. Tours of the home are offered by National Park Service rangers.

Jackson Ward, previously known as Central Wards, is a historically African-American district in Richmond, Virginia, with a long tradition of African-American businesses. It is located less than a mile from the Virginia State Capitol, sitting to the west of Court End and north of Broad Street. It was listed as a National Historic Landmark District in 1978. "Jackson Ward" was originally the name of the area's political district within the city, or ward, from 1871 to 1905, yet has remained in use long after losing its original meaning.

Oakwood Cemetery is a large, city-owned burial ground in the East End of Richmond, Virginia. It holds over 48,000 graves, including many soldiers from the Civil War.
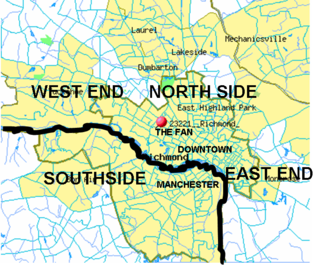
The East End of Richmond, Virginia is the quadrant of the City of Richmond, Virginia, and more loosely the Richmond metropolitan area, east of the downtown.

Eagle Rock is a census-designated place (CDP) in Botetourt County, Virginia, United States, located along the James River between Iron Gate and Buchanan. It was first listed as a CDP in the 2020 census with a population of 209.

The Shockoe Hill Cemetery is a historic cemetery located on Shockoe Hill in Richmond, Virginia.

Woodland Cemetery is a historically African American cemetery in Northeast Richmond, Virginia located directly east of the Highland Park neighborhood. Opening in 1916, it was built as a resting place for the Black elite of Richmond. Woodland was laid out in the shape of an arrowhead pointing north to symbolize the way enslaved blacks once looked north to freedom.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Richmond, Virginia, United States

Zachariah Dearborn Lewis was an influential Baptist church leader and the first president of the Southern Aid and Insurance Company based in Richmond, Virginia.

The Shockoe Hill African Burying Ground was established by the city of Richmond, Virginia, for the interment of free people of color, and the enslaved. The heart of this now invisible burying ground is located at 1305 N 5th St.
East End Cemetery is an historic African-American cemetery located at 50 Evergreen Rd., in the East End of Richmond, Virginia.

The Shockoe Hill Burying Ground Historic District, located in the city of Richmond, Virginia, is a significant example of a municipal almshouse-public hospital-cemetery complex of the sort that arose in the period of the New Republic following disestablishment of the Anglican Church. The District illustrates changing social and racial relationships in Richmond through the New Republic, Antebellum, Civil War, Reconstruction, and Jim Crow/Lost Cause eras of the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. The Shockoe Hill Burying Ground Historic District occupies 43 acres (17 ha) of land bounded to the south by E. Bates Street, to the north by the northern limit of the Virginia Passenger Rail Authority right-of-way at the southern margin of the Bacon's Quarter Branch valley, to the west by 2nd Street, and to the east by the historic edge of the City property at the former location of Shockoe Creek. The District encompasses most of a 28.5-acre (11.5 ha) tract acquired by the city of Richmond in 1799 to fulfill several municipal functions, along with later additions to this original tract.
Richard Fillmore Tancil (1859-1928) was a medical doctor, developer, and community leader who founded various institutions in Richmond, Virginia including Nickel Savings Bank in 1896. His office was at 601 North 30th Street.
The city of Richmond, Virginia has two African Burial Grounds, the "Shockoe Bottom African Burial Ground", and the "Shockoe Hill African Burying Ground". Additionally the city is home to several other important and historic African American cemeteries.













