Related Research Articles

Medicine is the science and practice of caring for patients, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, prevention, treatment, palliation of their injury or disease, and promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, genetics, and medical technology to diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, external splints and traction, medical devices, biologics, and ionizing radiation, amongst others.

Anatomical pathology (Commonwealth) or anatomic pathology (U.S.) is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination of organs and tissues. Over the 20th century, surgical pathology has evolved tremendously: from historical examination of whole bodies (autopsy) to a more modernized practice, centered on the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer to guide treatment decision-making in oncology. Its modern founder was the Italian scientist Giovanni Battista Morgagni from Forlì.
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and eventually people close to them, so to collect reliable/objective information for managing the medical diagnosis and proposing efficient medical treatments. The medically relevant complaints reported by the patient or others familiar with the patient are referred to as symptoms, in contrast with clinical signs, which are ascertained by direct examination on the part of medical personnel. Most health encounters will result in some form of history being taken. Medical histories vary in their depth and focus. For example, an ambulance paramedic would typically limit their history to important details, such as name, history of presenting complaint, allergies, etc. In contrast, a psychiatric history is frequently lengthy and in depth, as many details about the patient's life are relevant to formulating a management plan for a psychiatric illness.
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (paediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care. After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency to become a specialist.
An objective structured clinical examination (OSCE) is an approach to the assessment of clinical competence in which the components are assessed in a planned or structured way with attention being paid to the objectivity of the examination which is basically an organization framework consisting of multiple stations around which students rotate and at which students perform and are assessed on specific tasks. OSCE is a modern type of examination often used for assessment in health care disciplines.

Uroscopy is the historical medical practice of visually examining a patient's urine for pus, blood, or other symptoms of disease.
Medical model is the term coined by psychiatrist R. D. Laing in his The Politics of the Family and Other Essays (1971), for the "set of procedures in which all doctors are trained". It includes complaint, history, physical examination, ancillary tests if needed, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis with and without treatment.
Mystery Diagnosis is a television docudrama series that aired on Discovery Health Channel and OWN: Oprah Winfrey Network. Each episode focuses on two or more individuals who have struggled with obscure medical ailments, and their quest for a diagnosis. The program details the patients' and doctors' difficulty in pinpointing a diagnosis; often due to nonspecific symptoms, masquerading syndromes, the rarity of the condition or disease, or the patient's case being an unusual manifestation of said condition or disease.

Abraham Verghese is an American physician, author and Professor of the Theory and Practice of Medicine and Vice Chair of Education at Stanford University Medical School. He is the author of four best-selling books: two memoirs and two novels. In 2011, he was elected to be a member of the Institute of Medicine. He received the National Humanities Medal from President Barack Obama in 2015. He is the co-host with Eric Topol of the podcast Medscape Medicine and the Machine.
The doctor–patient relationship is a central part of health care and the practice of medicine. A doctor–patient relationship is formed when a doctor attends to a patient's medical needs and is usually through consent. This relationship is built on trust, respect, communication, and a common understanding of both the doctor and patients' sides. The trust aspect of this relationship goes is mutual: the doctor trusts the patient to reveal any information that may be relevant to the case, and in turn, the patient trusts the doctor to respect their privacy and not disclose this information to outside parties.

How Doctors Think is a book released in March 2007 by Jerome Groopman, the Dina and Raphael Recanati Chair of Medicine at Harvard Medical School, chief of experimental medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, and staff writer for The New Yorker magazine.
Tan Yunxian was a Chinese physician during the Ming dynasty in China.
A wastebasket diagnosis or trashcan diagnosis is a vague diagnosis given to a patient or to medical records department for essentially non-medical reasons. It may be given when the patient has an obvious but unidentifiable medical problem, when a doctor wants to reassure an anxious patient about the doctor's belief in the existence of reported symptoms, when a patient pressures a doctor for a label, or when a doctor wants to facilitate bureaucratic approval of treatment. It differs from a diagnosis of exclusion in that a wastebasket diagnosis is a diagnostic label of doubtful value, whereas a diagnosis of exclusion is characterized by the diagnosis being arrived at indirectly. Unlike a vague wastebasket diagnosis, the diagnostic label arrived at through a process of exclusion may be precise, accurate, and helpful.
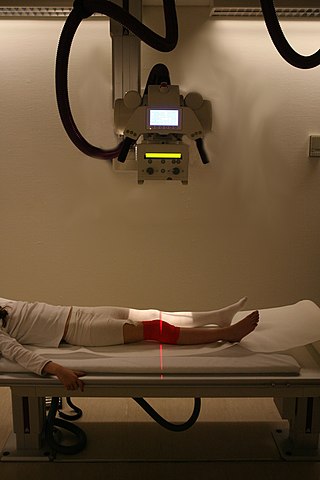
Medical diagnosis is the process of determining which disease or condition explains a person's symptoms and signs. It is most often referred to as a diagnosis with the medical context being implicit. The information required for a diagnosis is typically collected from a history and physical examination of the person seeking medical care. Often, one or more diagnostic procedures, such as medical tests, are also done during the process. Sometimes the posthumous diagnosis is considered a kind of medical diagnosis.
Lisa Sanders is an American physician, medical author and journalist, and associate professor of internal medicine and education at Yale School of Medicine. In 2002, she began writing a column for The New York Times called Diagnosis, that covered medical mystery cases. She is an attending physician at Yale-New Haven Hospital. Her column was the inspiration for the television series House M.D., with Yale-New Haven Hospital serving as the model for Princeton-Plainsboro Hospital in the series. Sanders worked as a consultant on the show. In 2019, Netflix aired the program Diagnosis, featuring a selection of cases from her column.
The Deadly Dinner Party and Other Medical Detective Stories is a nonfiction book by Jonathan A. Edlow, MD about medical mysteries.
The history of medical diagnosis began in earnest from the days of Imhotep in ancient Egypt and Hippocrates in ancient Greece but is far from perfect despite the enormous bounty of information made available by medical research including the sequencing of the human genome. The practice of diagnosis continues to be dominated by theories set down in the early 20th century.

Bad Pharma: How Drug Companies Mislead Doctors and Harm Patients is a book by the British physician and academic Ben Goldacre about the pharmaceutical industry, its relationship with the medical profession, and the extent to which it controls academic research into its own products. It was published in the UK in September 2012 by the Fourth Estate imprint of HarperCollins, and in the United States in February 2013 by Faber and Faber.
Gurumukh Sajanmal Sainani is an Indian general physician, medical researcher, medical writer and an Emeritus Professor of the National Academy of Medical Sciences. He is a former director of the All India Heart Foundation and the incumbent director of Jaslok Hospital, Mumbai. He is a recipient of the highest Indian award in the medical category, Dr. B. C. Roy Award, from the Medical Council of India and the rank of Honorary Brigadier from the President of India. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian award of the Padma Shri in 2000.
Diagnosis is a 2019 documentary television series. The series follows Dr. Lisa Sanders as she attempts to help patients with rare illnesses and searches for a diagnosis and cure using wisdom of the crowd methods. The show is based on her column for The New York Times Magazine. It was released on August 16, 2019, on Netflix.
References
- ↑ "Every patient tells a story". ABC Radio National. 2009-09-17. Retrieved 2020-06-05.
- ↑ Foster, Daniel W. (2010-01-04). "Every patient tells a story". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 120 (1): 4. doi:10.1172/JCI41900. ISSN 0021-9738. PMC 2798711 .
- ↑ Chen, Pauline W.; M.D (2009-10-08). "The Comfort of a Diagnosis". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331 . Retrieved 2020-06-05.
- ↑ Burch, Druin (2009-10-07). "Review: The Deadly Dinner Party by Jonathan Edlow; Diagnosis by Lisa Sanders". New Scientist. Archived from the original on 2023-03-06. Retrieved 2024-04-30.