This article needs additional citations for verification .(February 2013) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
| Look up evolution in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |

The English noun evolution (from Latin ēvolūtiō "unfolding, unrolling") refers to any kind of accumulation of change, or gradual directional change. It is the 3,117th most commonly used word in English. [1]

Latin is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. The Latin alphabet is derived from the Etruscan and Greek alphabets and ultimately from the Phoenician alphabet.
While the term primarily refers to biological evolution, there are various types of chemical evolution and it is also found in economics, historical linguistics, and many other technical fields where systems develop or change gradually over time, e.g. stellar evolution, cultural evolution, the evolution of an idea, metaphysical evolution, spiritual evolution, etc.
Biology is the natural science that studies life and living organisms, including their physical structure, chemical processes, molecular interactions, physiological mechanisms, development and evolution. Despite the complexity of the science, there are certain unifying concepts that consolidate it into a single, coherent field. Biology recognizes the cell as the basic unit of life, genes as the basic unit of heredity, and evolution as the engine that propels the creation and extinction of species. Living organisms are open systems that survive by transforming energy and decreasing their local entropy to maintain a stable and vital condition defined as homeostasis.
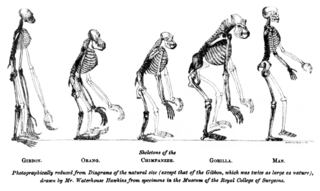
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes that are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Different characteristics tend to exist within any given population as a result of mutation, genetic recombination and other sources of genetic variation. Evolution occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on this variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more common or rare within a population. It is this process of evolution that has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms and molecules.
Chemistry is the scientific discipline involved with elements and compounds composed of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances.
The English term prior to the late 19th century was confined to referring to goal-directed, pre-programmed processes such as embryological development. A pre-programmed task, as in a military maneuver, using this definition, may be termed an "evolution."
The term evolution (from its literal meaning of "unfolding" of something into its true or explicit form) carries a connotation of gradual improvement or directionality from a beginning to an end point. This contrasts with the more general development, which can indicate change in any direction, or revolution, which implies recurring, periodic change. The term biological devolution is coined as an antonym to evolution, indicating such degeneration or decrease in quality or complexity. [2]

In political science, a revolution is a fundamental and relatively sudden change in political power and political organization which occurs when the population revolts against the government, typically due to perceived oppression or political incompetence. In book V of the Politics, the Ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle described two types of political revolution:
- Complete change from one constitution to another
- Modification of an existing constitution.