Related Research Articles
Pacta sunt servanda is a brocard and a fundamental principle of law which holds that treaties or contracts are binding upon the parties that entered into the treaty or contract. It is customary international law. According to Hans Wehberg, a professor of international law, "few rules for the ordering of Society have such a deep moral and religious influence" as this principle.

The history of Vietnam can be traced back to around 20,000 years ago. The first modern humans to arrive and settle in the area of modern-day Vietnam are known as the Hoabinhians, who can be traced as the ancestors of modern-day Negritos. Archaeological findings from 1965, which are still under research, show the remains of two hominins closely related to the Sinanthropus, dating as far back as the Middle Pleistocene era, roughly half a million years ago.
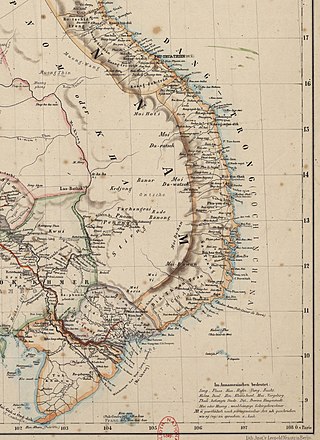
Cochinchina or Cochin-China is a historical exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer to the region south of the Gianh River.
Numerus clausus is one of many methods used to limit the number of students who may study at a university. In many cases, the goal of the numerus clausus is simply to limit the number of students to the maximum feasible in some particularly sought-after areas of studies with an intent to keep a constant supply of qualified workforce and thus limit competition. In historical terms however, in some countries, numerus clausus policies were religious or racial quotas, both in intent and function.

The Vietnam Fatherland Front is an umbrella group of mass movements in Vietnam aligned with the Communist Party of Vietnam forming the Vietnamese government. It was founded in February 1977 by the merger of the Vietnam Fatherland Front of North Vietnam and two Viet Cong groups, the National Liberation Front of South Vietnam and the Alliance of National, Democratic, and Peace Forces. It is an amalgamation of many smaller groups, including the Communist Party itself. Other groups that participated in the establishment of the Front were the Vietnam General Confederation of Labour, the Ho Chi Minh Communist Youth Union and the Ho Chi Minh Young Pioneer Organization. It also included the Democratic Party of Vietnam and Socialist Party of Vietnam, until they disbanded in 1988. It also incorporates some officially sanctioned religious groups.

Vovinam, officially known as Việt Võ Đạo is a Vietnamese martial art founded in 1938 by Nguyễn Lộc. It is based on traditional Vietnamese eclectic sources.

Trường Chinh, born Đặng Xuân Khu; 9 February 1907 – 30 September 1988) was a Vietnamese communist political leader, revolutionary and theoretician. He was one of the key figures of Vietnamese politics and the important Vietnamese leaders for over 40 years. He played a major role in the anti-French colonialism movement and finally after decades of protracted war in Vietnam, the Vietnamese defeated the colonial power. He was the think-tank of the Communist Party who determined the direction of the communist movement, particularly in the anti-French colonialism movement. After the declaration of independence in September 1945, Trường Chinh played an important role in shaping the politics of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV) and creating the socialist structure of the new Vietnam.

The National Assembly of the Socialist Republic of Vietnam is the unicameral parliament and the highest body of state power of Vietnam. The National Assembly is the only branch of government in Vietnam and, in accordance with the principle of unified power, all state organs are subservient to it.
Anarchist law is a term variously used to describe the apparent norms regarding behavior and decision-making operative within an anarchist community from the perspective of a law-normative viewpoint. Although many anarchists would consider "anarchist law" simply synonymous with natural law, others contend law as implied in anarchy by outside observers would have additional, unique elements. Over the course of the last two hundred years as anarchism has grown and evolved to include diverse strains, there have been different conceptions of "anarchist law" produced and discussed, or used in practice by anarchist networks such as Peoples' Global Action or Indymedia.
"Ratio scripta", or "written reason", was the assessment of Roman law commonly held in Europe during the Medieval period. It emerged during the revival of Roman law, serving as the basis of the ius commune. It was also used to evaluate the validity of leges propria or the local customs and positive legislation. Ratio scripta is also used to denote the popular opinion of Roman law held during the Medieval period. It could also mean the written opinion of a tribunal explaining its decision over a case.

Chu Van An High School, also known as Chu Van An National School or Pomelo School one of the three national high schools for the gifted in Vietnam along with Quoc Hoc High School in Huế and Le Hong Phong High School in Ho Chi Minh City. It is also one of the four magnet high schools in Hanoi, Vietnam, along with Hanoi-Amsterdam High School, Son Tay High School and Nguyen Hue High School. Established by the French authorities in 1908 as College of the Protectorate, Chu Van An is one of the oldest institutions for secondary education in Southeast Asia. Despite initially intending to train native civil servants to serve the French colonial establishments, Vietnamese students at Bưởi school often struggled against colonial doctrine. A lot of Bưởi alumni became renowned political leaders and cultural figures in many areas of Vietnamese society such as Nguyễn Văn Cừ – the fourth general secretary of Communist Party of Vietnam, Phạm Văn Đồng – the first prime minister of North Vietnam and united Vietnam, Nguyễn Cao Kỳ- former vice president and prime minister of South Vietnam, Kaysone Phomvihane- former leader of the Lao People's Revolutionary Party, Prince Souphanouvong- the first president of Laos.

Nam Nguyen is a Canadian retired competitive figure skater. He is the 2014 World Junior champion, 2019 Skate Canada silver medallist, and two-time Canadian national champion. He has placed as high as fifth at the World Championships, in 2015.

Nguyễn Xuân Phúc is a Vietnamese former politician who served as the 11th President of Vietnam from 2021 until his resignation from all state posts in 2023 amidst a series of corruption scandals. He also was the 7th Prime Minister of Vietnam from 2016 until 2021 and served as a member of the Politburo of the Communist Party of Vietnam for 3 terms from 2011 until his resignation in 2023.
Ho Chi Minh Thought is a political philosophy that builds upon Marxism–Leninism and the ideology of Vietnamese revolutionary Ho Chi Minh. It was developed and codified by the Communist Party of Vietnam and formalised in 1991. The term is used to cover political theories and policies considered as representing a form of Marxism–Leninism that has been adapted to Vietnamese circumstances and history. The ideology includes views on the basic issues of the Vietnamese Revolution, specifically the development and application of Marxism–Leninism to the material conditions of Vietnam.

The Confucian court examination system in Vietnam was a system for entry into the civil service, which was modelled after the Imperial examination in China, based on knowledge of the classics and literary style from 1075 to 1919.

The National Institute of Administration, is a Syrian government school responsible for the training of civil servants in management and administration. Its main office and training center is located in At-Tal, near Damascus.

Mother Mushroom is the pen name of the Vietnamese blogger and dissident, Nguyễn Ngọc Như Quỳnh. Mushroom or Nấm in Vietnamese is the name of her daughter. She first used the pen name in her popular blog "Mẹ Nấm".

Nguyễn Thanh Long is a Vietnamese politician and doctor who served as Minister of Health from July 2020 to his removal from the Communist Party of Vietnam in June 2022 for involvement in the Việt Á corruption scandal. During his term as Minister of Health, he was in acting capacity from July to November 2020. He has been noted for being one of the chief strategists of the response of the Vietnamese government to the COVID-19 pandemic. In January 2024, he was sentenced to 18 years in prison for taking bribes worth USD 2.25 million.

Võ Thị Ánh Xuân is a Vietnamese politician and former educator who serves as the 17th vice president of Vietnam since 2021. She briefly served as acting president of Vietnam in 2023 and 2024.

During the Nguyễn dynasty period (1802–1945) of Vietnamese history its Ministry of Education was reformed a number of times, in its first iteration it was called the Học Bộ, which was established during the reign of the Duy Tân Emperor (1907–1916) and took over a number of functions of the Lễ Bộ, one of the Lục Bộ. The Governor-General of French Indochina wished to introduce more education reforms, the Nguyễn court in Huế sent Cao Xuân Dục and Huỳnh Côn, the Thượng thư of the Hộ Bộ, to French Cochinchina to discuss these reforms with the French authorities. After their return the Học Bộ was established in the year Duy Tân 1 (1907) with Cao Xuân Dục being appointed to be its first Thượng thư (minister). Despite nominally being a Nguyễn dynasty institution, actual control over the ministry fell in the hands of the French Council for the Improvement of Indigenous Education in Annam.
References
- ↑ Nguyen, Nam H. (2018-03-18). Essential 25000 English-Polish Law Dictionary (in Polish). Nam H Nguyen.
- ↑ Agrawal, Chandresh; books, nandini (2024-05-14). SEBI Exam PDF- Officer Grade A- Assistant Manager (Legal) Stream Exam: Law Objective Questions From Various Competitive Exams. Chandresh Agrawal.
- ↑ Parnes, Joseph (2020-03-26). Short Selling for the Long Term: How a Combination of Short and Long Positions Leads to Investing Success. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-119-52778-7.