Related Research Articles
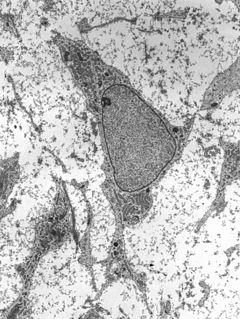
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type.
Transdifferentiation, also known as lineage reprogramming, is an artificial process in which one mature somatic cell is transformed into another mature somatic cell without undergoing an intermediate pluripotent state or progenitor cell type. It is a type of metaplasia, which includes all cell fate switches, including the interconversion of stem cells. Current uses of transdifferentiation include disease modeling and drug discovery and in the future may include gene therapy and regenerative medicine. The term 'transdifferentiation' was originally coined by Selman and Kafatos in 1974 to describe a change in cell properties as cuticle producing cells became salt-secreting cells in silk moths undergoing metamorphosis.
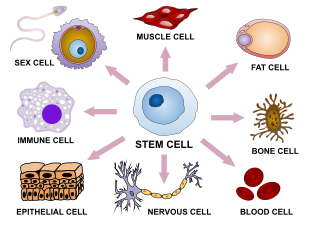
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a cell changes from one cell type to another. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Although metabolic composition does get altered quite dramatically where stem cells are characterized by abundant metabolites with highly unsaturated structures whose levels decrease upon differentiation. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.
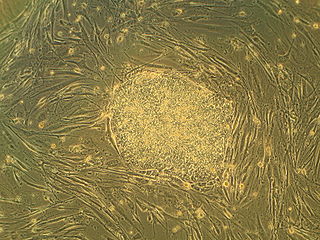
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent stem cells derived from the inner cell mass of a blastocyst, an early-stage pre-implantation embryo. Human embryos reach the blastocyst stage 4–5 days post fertilization, at which time they consist of 50–150 cells. Isolating the embryoblast, or inner cell mass (ICM) results in destruction of the blastocyst, a process which raises ethical issues, including whether or not embryos at the pre-implantation stage have the same moral considerations as embryos in the post-implantation stage of development.

Oct-4, also known as POU5F1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU5F1 gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. It is critically involved in the self-renewal of undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. As such, it is frequently used as a marker for undifferentiated cells. Oct-4 expression must be closely regulated; too much or too little will cause differentiation of the cells.

Jun dimerization protein 2 (JUNDM2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JDP2 gene. The Jun dimerization protein is a member of the AP-1 family of transcription factors.

Induced pluripotent stem cells are a type of pluripotent stem cell that can be generated directly from a somatic cell. The iPSC technology was pioneered by Shinya Yamanaka’s lab in Kyoto, Japan, who showed in 2006 that the introduction of four specific genes, collectively known as Yamanaka factors, encoding transcription factors could convert somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells. He was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize along with Sir John Gurdon "for the discovery that mature cells can be reprogrammed to become pluripotent."

Telomerase reverse transcriptase is a catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase, which, together with the telomerase RNA component (TERC), comprises the most important unit of the telomerase complex.

Kruppel-like factor 4 is a member of the KLF family of zinc finger transcription factors, which belongs to the relatively large family of SP1-like transcription factors. KLF4 is involved in the regulation of proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and somatic cell reprogramming. Evidence also suggests that KLF4 is a tumor suppressor in certain cancers, including colorectal cancer. It has three C2H2-zinc fingers at its carboxyl terminus that are closely related to another KLF, KLF2. It has two nuclear localization sequences that signals it to localize to the nucleus. In embryonic stem cells (ESCs), KLF4 has been demonstrated to be a good indicator of stem-like capacity. It is suggested that the same is true in mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs).

SRY -box 2, also known as SOX2, is a transcription factor that is essential for maintaining self-renewal, or pluripotency, of undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Sox2 has a critical role in maintenance of embryonic and neural stem cells.

Shinya Yamanaka is a Japanese stem cell researcher, winner of the Nobel Prize. He serves as the director of Center for iPS Cell Research and Application and a professor at the Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences at Kyoto University; as a senior investigator at the UCSF-affiliated Gladstone Institutes in San Francisco, California; and as a professor of anatomy at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). Yamanaka is also a past president of the International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR).
A mesenchymal–epithelial transition (MET) is a reversible biological process that involves the transition from motile, multipolar or spindle-shaped mesenchymal cells to planar arrays of polarized cells called epithelia. MET is the reverse process of epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and it has been shown to occur in normal development, induced pluripotent stem cell reprogramming, cancer metastasis and wound healing.

Cell potential, based on the 2007 works of Hans R. Schöler "The Potential of Stem Cells: An Inventory", is a cell's ability to differentiate into other cell types. The more cell types a cell can differentiate into, the greater its potency. Potency is also described as the gene activation potential within a cell, which like a continuum, begins with totipotency to designate a cell with the most differentiation potential, pluripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, and finally unipotency.
A list of examples of transdifferentiation:
Induced stem cells (iSC) are stem cells derived from somatic, reproductive, pluripotent or other cell types by deliberate epigenetic reprogramming. They are classified as either totipotent (iTC), pluripotent (iPSC) or progenitor or unipotent – (iUSC) according to their developmental potential and degree of dedifferentiation. Progenitors are obtained by so-called direct reprogramming or directed differentiation and are also called induced somatic stem cells.

Glis1 is gene encoding a Krüppel-like protein of the same name whose locus is found on Chromosome 1p32.3. The gene is enriched in unfertilised eggs and embryos at the one cell stage and it can be used to promote direct reprogramming of somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells, also known as iPS cells. Glis1 is a highly promiscuous transcription factor, regulating the expression of numerous genes, either positively or negatively. In organisms, Glis1 does not appear to have any directly important functions. Mice whose Glis1 gene has been removed have no noticeable change to their phenotype.
A Muse cell is an endogenous non-cancerous pluripotent stem cell. They reside in the connective tissue of nearly every organ including the umbilical cord, bone marrow and peripheral blood. They are collectable from commercially obtainable mesenchymal cells such as human fibroblasts, bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived stem cells. Muse cells are able to generate cells representative of all three germ layers from a single cell both spontaneously and under cytokine induction. Expression of pluripotency genes and triploblastic differentiation are self-renewable over generations. Muse cells do not undergo teratoma formation when transplanted into a host environment in vivo. This can be explained in part by their intrinsically low telomerase activity, eradicating the risk of tumorigenesis through unbridled cell proliferation. They were discovered in 2010 by Mari Dezawa and her research group. Clinical trials for acute myocardial infarction, stroke, epidermolysis bullosa, spinal cord injury, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) related to novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection, are conducted by Life Science Institute, Inc., a group company of Mitsubishi Chemical Holdings company. Physician-led clinical trial for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy was also started. The summary results of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial in patients with stroke was announced.
After the blastocyst stage, once an embryo implanted in endometrium, the inner cell mass (ICM) of a fertilized embryo segregates into two layers: hypoblast and epiblast. The epiblast cells are the functional progenitors of soma and germ cells which later differentiate into three layers: definitive endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. Stem cells derived from epiblast are pluripotent. These cells are called epiblast-derived stem cells (EpiSC) and have several different cellular and molecular characteristics with Embryonic Stem Cells (ESC). Pluripotency in EpiSC is essentially different from that of embryonic stem cells. The pluripotency of EpiSC is primed pluripotency: primed to differentiate into specific cell lineages. Naïve pluripotent stem cells and primed pluripotent stem cells not only sustain the ability to self-renew but also maintain the capacity to differentiate. Since the cell status is primed to differentiate in EpiSC, however, one copy of the X chromosome in XX cells in EpiSC is silenced (XaXi). EpiSC is unable to colonize and is not available to be used to produce chimeras. Conversely, XX cells in ESC are both active and can produce chimera when inserted into a blastocyst. Both ESC and EpiSC induce teratoma when injected in the test animals which proves pluripotency. EpiSC display several distinctive characteristics distinct from ESC. The cellular status of human ESC (hESC) is similar to primed state mouse stem cells rather than Naïve state.

F-box protein 15 also known as Fbx15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FBXO15 gene.
Transflamation describes the process by which innate immune response mechanisms affect the epigenetic plasticity of a cell during nuclear reprogramming. This phenomenon is essential in dedifferentiating a somatic cell to a pluripotent cell and also in transdifferentiating a terminally differentiated cell to another terminally differentiated cell.
References
- ↑ Pournasr, B.; Khaloughi, K.; Salekdeh, G. H.; Totonchi, M.; Shahbazi, E.; Baharvand, H. (2011). "Concise Review: Alchemy of Biology: Generating Desired Cell Types from Abundant and Accessible Cells". Stem Cells. 29 (12): 1933–1941. doi: 10.1002/stem.760 . PMID 21997905.
- ↑ Szabo, E.; Rampalli, S.; Risueño, R. M.; Schnerch, A.; Mitchell, R.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.; Levadoux-Martin, M.; Bhatia, M. (2010). "Direct conversion of human fibroblasts to multilineage blood progenitors". Nature. 468 (7323): 521–526. doi:10.1038/nature09591. PMID 21057492. S2CID 205223078.
- ↑ Hiramatsu, K.; Sasagawa, S.; Outani, H.; Nakagawa, K.; Yoshikawa, H.; Tsumaki, N. (2011). "Generation of hyaline cartilaginous tissue from mouse adult dermal fibroblast culture by defined factors". Journal of Clinical Investigation. 121 (2): 640–657. doi:10.1172/JCI44605. PMC 3026734 . PMID 21293062.
- ↑ Efe, J. A.; Hilcove, S.; Kim, J.; Zhou, H.; Ouyang, K.; Wang, G.; Chen, J.; Ding, S. (2011). "Conversion of mouse fibroblasts into cardiomyocytes using a direct reprogramming strategy". Nature Cell Biology. 13 (3): 215–222. doi:10.1038/ncb2164. PMID 21278734. S2CID 5310172.
- ↑ Kim, J.; Efe, J. A.; Zhu, S.; Talantova, M.; Yuan, X.; Wang, S.; Lipton, S. A.; Zhang, K.; Ding, S. (2011). "Direct reprogramming of mouse fibroblasts to neural progenitors". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 108 (19): 7838–7843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1103113108 . PMC 3093517 . PMID 21521790.