
The New Zealand Defence Force consists of three services: the Royal New Zealand Navy, the New Zealand Army and the Royal New Zealand Air Force; and is commanded and headed by the chief of Defence Force (CDF).

The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution. The oldest and most senior branch of the U.S. military in order of precedence, the modern U.S. Army has its roots in the Continental Army, which was formed 14 June 1775 to fight the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783)—before the United States was established as a country. After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army. The United States Army considers itself to be a continuation of the Continental Army, and thus considers its institutional inception to be the origin of that armed force in 1775.

The Special Air Service Regiment, officially abbreviated SASR though commonly known as the SAS, is a special forces unit of the Australian Army. Formed in 1957, it was modelled on the British SAS sharing the motto, "Who Dares Wins". The regiment is based at Campbell Barracks, in Swanbourne, a suburb of Perth, Western Australia, and is a direct command unit of the Special Operations Command. It has taken part in operations in Borneo, Vietnam, Somalia, East Timor, Iraq and Afghanistan, as well as many other peacekeeping missions. The SASR also provides a counter-terrorist capability, and has been involved in a number of domestic security operations.

The Indian Army is the land-based branch and the largest component of the Indian Armed Forces. The President of India is the Supreme Commander of the Indian Army, and its professional head is the Chief of Army Staff (COAS), who is a four-star general. Two officers have been conferred with the rank of field marshal, a five-star rank, which is a ceremonial position of great honour. The Indian Army originated from the armies of the East India Company, which eventually became the British Indian Army, and the armies of the princely states, which were merged into the national army after independence. The units and regiments of the Indian Army have diverse histories and have participated in several battles and campaigns around the world, earning many battle and theatre honours before and after Independence.

The 1st New Zealand Special Air Service Regiment, abbreviated as 1 NZSAS Regt, was formed on 7 July 1955 and is the special forces unit of the New Zealand Army, closely modelled on the British Special Air Service (SAS). It traces its origins to the Second World War and the famous Long Range Desert Group that New Zealanders served with.

The Five Power Defence Arrangements (FPDA), is a series of bilateral defence relationships established by a series of multi-lateral agreements between Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Singapore, and the United Kingdom – all Commonwealth members, with the first four once belonging to the British Empire.

The New Zealand Cadet Forces is a voluntary military-style training organisation for New Zealand youth between the ages of 13 and 21. Run in partnership with the New Zealand Defence Force (NZDF) and local community organisations. Through its three branches, the New Zealand Cadet Forces provide young adults with a four-year training curriculum, while a number of local, area, and national camps and courses provide further experience and qualifications. It is jointly funded by the Ministry of Defence, the Royal New Zealand Returned Services' Association, local communities, and the Associated charities belonging to each branch (CCANZ,SCANZ,ATCANZ). Overall it is directed by Air Marshal Kevin Short, Chief of Defence Force. Cadets are not under any obligation to join the New Zealand Defence Force, however many choose to do so upon turning 18 years old.

As of 18 May 2020, there have been 3,502 coalition deaths in Afghanistan as part of ongoing coalition operations since the invasion in 2001. In this total, the American figure is for deaths "In and Around Afghanistan" which, as defined by the United States Department of Defense, includes some deaths in Pakistan and Uzbekistan and the deaths of 18 CIA operatives.

The New Zealand Army is the land component of the New Zealand Defence Force and comprises around 9,500 Regular Force personnel, 2,900 Reserve Force personnel and 3000 civilians. Formerly the New Zealand Military Forces, the current name was adopted by the New Zealand Army Act 1950. The New Zealand Army traces its history from settler militia raised in 1845.

The Royal New Zealand Army Logistic Regiment , is the New Zealand Army's main military Logistics and combat service support (CSS) element. It is the largest regiment in the NZ Army.
The military history of New Zealand is an aspect of the history of New Zealand that spans several hundred years. When first settled by Māori almost a millennium ago, there was much land and resources, but war began to break out as the country's carrying capacity was approached. Initially being fought with close range weapons of wood and stone, this continued on and off until Europeans arrived, bringing with them new weapons such as muskets. Colonisation by Britain led to the New Zealand Wars in the 19th century in which settler and imperial troops and their Māori allies fought against other Māori and a handful of Pākehā. In the first half of the 20th century, New Zealanders of all races fought alongside Britain in the Boer War and both World Wars. In the second half of the century and into this century the New Zealand Defence Force has provided token assistance to the United States in several conflicts. New Zealand has also contributed troops extensively to multilateral peacekeeping operations.
Trentham Military Camp is a New Zealand Defence Force (NZDF) facility located in Trentham, Upper Hutt, near Wellington. Originally a New Zealand Army installation, it is now run by Defence and accommodates all three services. It also hosts Joint NZDF facilities including:

Exercise Bright Star is a series of combined and joint training exercises led by United States and Egyptian forces in Egypt held every two years. These exercises began in 1980, rooted in the 1977 Camp David Accords. After its signing, the Egyptian Armed Forces and the United States agreed to conduct training together in Egypt.

Exercise Talisman Sabre is a biennial, multinational military exercise led by Australia and the United States. Talisman Sabre involves joint exercises performed by the Australian Defence Force and the United States Military across six locations in northern and central Australia, the Coral Sea, and in Honolulu, Denver, and Suffolk, Va., though the bulk of the exercises are concentrated at the Shoalwater Bay Military Training Area and other locations in northern and central Australia and Australia's territorial sea and exclusive economic zone.

According to the U.S. State Department, relations between New Zealand and the United States as of August 2011 are "the best they have been in decades." New Zealand is a major non-NATO ally of the United States.

Waiouru Military Camp is a camp of the New Zealand Army in the central North Island of New Zealand near Waiouru.
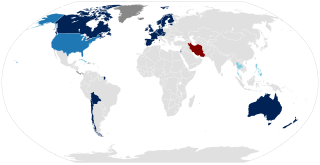
Not all armed forces have policies explicitly permitting LGBT personnel. Generally speaking, Western European militaries show a greater tendency toward inclusion of LGBT individuals. As of January 2021, 21 countries allow transgender military personnel to serve openly: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Israel, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Spain, Sweden, and the United Kingdom. Cuba and Thailand reportedly allowed transgender service in a limited capacity. In 1974, the Netherlands was the first country to allow transgender military personnel. The United States has allowed Transgender personnel to serve in the military under varying conditions since Joe Biden's signing of an executive order.
Operation Burnham was a joint military operation undertaken by the New Zealand Special Air Service and elements of the Afghan Crisis Response Unit and International Security Assistance Force in Afghanistan's Tirgiran Valley on 21–22 October 2010. Operation Burnham became the subject of the investigative journalists Nicky Hager and Jon Stephenson's book Hit & Run: The New Zealand SAS in Afghanistan and the meaning of honour, which alleged that New Zealand forces had committed war crimes against civilians in the Naik and Khak Khudday Dad villages.
















