
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle designed for front-line combat, with heavy firepower, strong armour, tracks and a powerful engine providing good battlefield manoeuvrability. They are a mainstay of modern ground forces and a key part of combined arms combat. Modern tanks are versatile mobile land weapon system platforms, mounting a large-calibre cannon in a rotating gun turret, supplemented by mounted machine guns or other weapons, such as ATGMs, or rockets. They combine this with heavy vehicle armour which provides protection for the crew, the vehicle's weapons, and its propulsion systems, and operational mobility, due to its use of tracks rather than wheels, which allows the tank to move over rugged terrain and adverse conditions such as mud, and be positioned on the battlefield in advantageous locations. These features enable the tank to perform well in a variety of intense combat situations, simultaneously both offensively with fire from their powerful tank gun, and defensively due to their near invulnerability to common firearms and good resistance to heavier weapons, all while maintaining the mobility needed to exploit changing tactical situations. Fully integrating tanks into modern military forces spawned a new era of combat, armoured warfare.

A compressed air car is a compressed air vehicle that uses a motor powered by compressed air. The car can be powered solely by air, or combined with gasoline, diesel, ethanol, or an electric plant with regenerative braking.

A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass or plastic through which domestic wastewater (sewage) flows for basic treatment. Settling and anaerobic processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment efficiency is only moderate. Septic tank systems are a type of simple onsite sewage facility (OSSF). They can be used in areas that are not connected to a sewerage system, such as rural areas. The treated liquid effluent is commonly disposed in a septic drain field which provides further treatment. However, groundwater pollution may occur and can be a problem.

An air compressor is a device that converts power into potential energy stored in pressurized air. By one of several methods, an air compressor forces more and more air into a storage tank, increasing the pressure. When tank pressure reaches its engineered upper limit, the air compressor shuts off. The compressed air, then, is held in the tank until called into use. The energy contained in the compressed air can be used for a variety of applications, utilizing the kinetic energy of the air as it is released and the tank depressurizes. When tank pressure reaches its lower limit, the air compressor turns on again and re-pressurizes the tank.
An air compressor must be differentiated from a pump because it works for any gas/air, while pumps work on a liquid.

A rocket engine uses stored rocket propellant mass for forming its high-speed propulsive jet. Rocket engines are reaction engines, obtaining thrust in accordance with Newton's third law. Most rocket engines use combustion, although non-combusting forms also exist. Vehicles propelled by rocket engines are commonly called rockets. Since they need no external material to form their jet, rocket engines can perform in a vacuum and thus can be used to propel spacecraft and ballistic missiles.

Compressed air energy storage (CAES) is a way to store energy generated at one time for use at another time using compressed air. At utility scale, energy generated during periods of low energy demand (off-peak) can be released to meet higher demand periods. This is especially important in an age where intermittent renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power is becoming more prominent energy sources. CAES systems can have a vital impact in making sure the electricity demands can be met at peak hours.
Small scale systems have long been used in such applications as propulsion of mine locomotives. Large scale applications must conserve the heat energy associated with compressing air; dissipating heat lowers the energy efficiency of the storage system.

A liquid-propellant rocket or liquid rocket is a rocket engine that uses liquid propellants. Liquids are desirable because their reasonably high density allows the volume of the propellant tanks to be relatively low, and it is possible to use lightweight centrifugal turbopumps to pump the propellant from the tanks into the combustion chamber, which means that the propellants can be kept under low pressure. This permits the use of low-mass propellant tanks, resulting in a high mass ratio for the rocket.

The Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-25, otherwise known as the Space Shuttle main engine (SSME), is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine that was used on NASA's Space Shuttle and is planned to be used on its successor, the Space Launch System (SLS).

A boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion is an explosion caused by the rupture of a vessel containing a pressurized liquid that has reached temperatures above its boiling point.

The J-2 was a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine used on NASA's Saturn IB and Saturn V launch vehicles. Built in the U.S. by Rocketdyne, the J-2 burned cryogenic liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, with each engine producing 1,033.1 kN (232,250 lbf) of thrust in vacuum. The engine's preliminary design dates back to recommendations of the 1959 Silverstein Committee. Rocketdyne won approval to develop the J-2 in June 1960 and the first flight, AS-201, occurred on 26 February 1966. The J-2 underwent several minor upgrades over its operational history to improve the engine's performance, with two major upgrade programs, the de Laval nozzle-type J-2S and aerospike-type J-2T, which were cancelled after the conclusion of the Apollo program.

The pressure-fed engine is a class of rocket engine designs. A separate gas supply, usually helium, pressurizes the propellant tanks to force fuel and oxidizer to the combustion chamber. To maintain adequate flow, the tank pressures must exceed the combustion chamber pressure.
In dairy farming a bulk milk cooling tank is a large storage tank for cooling and holding milk at a cold temperature until it can be picked up by a milk hauler.
The bulk milk cooling tank is an important piece of dairy farm equipment. It is usually made of stainless steel and used every day to store the raw milk on the farm in good condition. It must be cleaned after each milk collection.
The milk cooling tank can be the property of the farmer or be rented from a dairy plant.
Paintball is an equipment intensive sport and in order to safely conduct a game, every player requires a marker with propellant to fire the paint, a mask to protect the eyes and face, paintballs, and a loader to hold them. To ensure safety off the playing field, a barrel sock or plug for the marker is also compulsory.

A head gasket is a gasket that sits between the engine block and cylinder head(s) in an internal combustion engine.

The McKinley Climatic Laboratory is both an active laboratory and a historic site located in Building 440 on Eglin Air Force Base, Florida. The laboratory is part of the 96th Test Wing. In addition to Air Force testing, it can be used by other US government agencies and private industry.
The term six-stroke engine has been applied to a number of alternative internal combustion engine designs that attempt to improve on traditional two-stroke and four-stroke engines. Claimed advantages may include increased fuel efficiency, reduced mechanical complexity and/or reduced emissions. These engines can be divided into two groups based on the number of pistons that contribute to the six strokes.

An expansion tank or expansion vessel is a small tank used to protect closed water heating systems and domestic hot water systems from excessive pressure. The tank is partially filled with air, whose compressibility cushions shock caused by water hammer and absorbs excess water pressure caused by thermal expansion.
The High-Low system, also referred to as the "High-Low Pressure system", the "High-Low Propulsion System", and the "High-Low projection system", is a design of cannon and antitank launcher using a smaller high-pressure chamber for storing the propellant. It enables a much larger projectile to be launched without the heavy equipment typically required for large caliber weapons.
When the propellant is ignited, the higher pressure gases are bled out through vents at reduced pressure to a much larger low pressure chamber to push the projectile forward. With the High-Low System a weapon can be designed with reduced or negligible recoil. The High-Low System also allows the weight of the weapon and its ammunition to be significantly reduced. Manufacturing cost and production time are drastically lower than for standard cannon or other small-arm weapon systems firing a projectile of the same size and weight. It has a far more efficient use of the propellant, unlike earlier recoilless weapons, where most of the propellant is expended to the rear of the weapon to counter the recoil of the projectile being fired.

A flushometer is a metal water-diverter that uses an inline handle to flush tankless toilets or urinals. It was invented by William Elvis Sloan and is a product of the Sloan Valve Company.
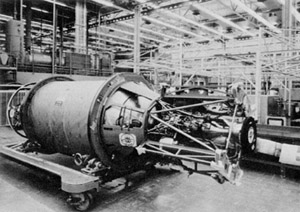
The Bell Aerosystems Company XLR81 was an American liquid-propellant rocket engine, which was used on the Agena upper stage. It burned UDMH and RFNA fed by a turbopump in a fuel rich gas generator cycle. The turbopump had a single turbine with a gearbox to transmit power to the oxidizer and fuel pumps. The thrust chamber was all-aluminum, and regeneratively cooled by oxidizer flowing through gun-drilled passages in the combustion chamber and throat walls. The nozzle was a titanium radiatively cooled extension. The engine was mounted on an hydraulic actuated gimbal which enabled thrust vectoring to control pitch and yaw. Engine thrust and mixture ratio were controlled by cavitating flow venturis on the gas generator flow circuit. Engine start was achieved by solid propellant start cartridge.

















