
Earl Wilbur Sutherland Jr. was an American pharmacologist and biochemist born in Burlingame, Kansas. Sutherland won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1971 "for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones", especially epinephrine, via second messengers, namely cyclic adenosine monophosphate, or cyclic AMP.

Bruce Nathan Ames was an American biochemist who was a professor of biochemistry and Molecular Biology Emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley, and was a senior scientist at Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute (CHORI). Ames made contributions to understanding the mechanisms of mutagenesis and DNA repair. He invented the Ames test, a widely used assay for easily and cheaply evaluating the mutagenicity of compounds. The test revolutionized the field of toxicology and has played a crucial role in identifying numerous environmental and industrial carcinogens.
William Cumming Rose was an American biochemist and nutritionist. He discovered the amino acid threonine, and his research determined the necessity for essential amino acids in diet and the minimum daily requirements of all amino acids for optimal growth.

Joseph Leonard Goldstein ForMemRS is an American biochemist. He received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1985, along with fellow University of Texas Southwestern researcher, Michael Brown, for their studies regarding cholesterol. They discovered that human cells have low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptors that remove cholesterol from the blood and that when LDL receptors are not present in sufficient numbers, individuals develop hypercholesterolemia and become at risk for cholesterol related diseases, notably coronary heart disease. Their studies led to the development of statin drugs.
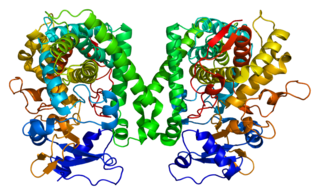
Cytochrome P4502C8 (CYP2C8) is a member of the cytochrome P450 mixed-function oxidase system involved in the metabolism of xenobiotics in the body. Cytochrome P4502C8 also possesses epoxygenase activity, i.e. it metabolizes long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids, e.g. arachidonic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and linoleic acid to their biologically active epoxides.

Lubert Stryer was an American academic who was the Emeritus Mrs. George A. Winzer Professor of Cell Biology, at Stanford University School of Medicine. His research over more than four decades had been centered on the interplay of light and life. In 2007 he received the National Medal of Science from President Bush at a ceremony at the White House for elucidating the biochemical basis of signal amplification in vision, pioneering the development of high density microarrays for genetic analysis, and authoring the standard undergraduate biochemistry textbook, Biochemistry. It is now in its tenth edition and also edited by Jeremy Berg, Justin Hines, John L. Tymoczko and Gregory J. Gatto, Jr.

Robert Joseph Lefkowitz is an American physician and biochemist. He is best known for his discoveries that reveal the inner workings of an important family of G protein-coupled receptors, for which he was awarded the 2012 Nobel Prize for Chemistry with Brian Kobilka. He is currently an Investigator with the Howard Hughes Medical Institute as well as a James B. Duke Professor of Medicine and Professor of Biochemistry and Chemistry at Duke University.

The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (ASBMB) is a learned society that was founded on December 26, 1906, at a meeting organized by John Jacob Abel. The roots of the society were in the American Physiological Society, which had been formed some 20 years earlier. ASBMB is the US member of the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.

Vanderbilt University School of Medicine (VUSM) is the graduate medical school of Vanderbilt University, a private research university located in Nashville, Tennessee. The School of Medicine is primarily housed within the Eskind Biomedical Library which sits at the intersection of the Vanderbilt University and Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) campuses and claims several Nobel laureates in the field of medicine. Through the Vanderbilt Health Affiliated Network, VUSM is affiliated with over 60 hospitals and 5,000 clinicians across Tennessee and five neighboring states which manage more than 2 million patient visits each year. As the home hospital of the medical school, VUMC is considered one of the largest academic medical centers in the United States and is the primary resource for specialty and primary care in hundreds of adult and pediatric specialties for patients throughout the Mid-South.

The College of Natural Science (NatSci) at Michigan State University is home to 27 departments and programs in the biological, physical and mathematical sciences.
The William C. Rose Award given by the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology recognizes outstanding contributions to biochemical and molecular biological research and a demonstrated commitment to the training of younger scientists, as epitomized by the late American nutritionist William Cumming Rose. The nominations are filed by the Society members, but the nominees need not be ASBMB members.

Lynne Elizabeth Maquat is an American biochemist and molecular biologist whose research focuses on the cellular mechanisms of human disease. She is known for her work in describing the process of nonsense-mediated decay. She is an elected member of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, the National Academy of Sciences and the National Academy of Medicine. She currently holds the J. Lowell Orbison Endowed Chair and is a professor of biochemistry and biophysics, pediatrics and oncology at the University of Rochester Medical Center.
Susan Wente is an American cell biologist and academic administrator currently serving as the 14th President of Wake Forest University. From 2014 to 2021 she was Provost and Vice Chancellor for Academic Affairs at Vanderbilt University. Between August 15, 2019 and June 30, 2020, she served as interim Chancellor at Vanderbilt.

Ari Helenius is a Finnish emeritus professor of biochemistry who is known for his research in virology.

Robyn Leigh Tanguay is an American researcher, academic and educator. She is a distinguished professor in the department of environmental and molecular toxicology at Oregon State University. She is the director of Superfund Research Program, the director of Pacific Northwest Center for Translational Environmental Health Research and the director of Sinnhuber Aquatic Research Laboratory at OSU.
Celia White Tabor was an American biochemist and physician-scientist who was an expert on the biosynthesis of polyamines. She was a researcher at the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases from 1952 until her retirement in 2005.

Carlos Federico López Restrepo is a Colombian-American scientist who researches network-driven biological processes using computational tools. Until March 2022, López was an Associate Professor of Biochemistry & Pharmacology & Biomedical Informatics & Mechanical Engineering at Vanderbilt University. He is currently a Principal Scientist and Lead, Multiscale Modeling at Altos Labs.
Lee Limbird is a pharmacologist, Dean of the School of Natural Science, Mathematics and Business & Professor in the Department of Life and Physical Sciences at Fisk University, Nashville, Tennessee.
Jorge H. Capdevila is an American biochemist and professor emeritus of medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical School. He was named fellow of the American Heart Association in 2002 and received the 2004 American Heart Association's "Novartis Excellence Award for Hypertension Research" for his contributions to our understanding of the molecular basis of hypertension. Capdevila's identification of roles for Cytochrome P450 (P450) in the metabolism of arachidonic acid (AA) and of the physiological and pathophysiological importance of these enzymes and their products were recognized in a special section honoring him at the 14th International Winter Eicosanoid Conference (2012). Capdevila received an "Outstanding Achievement Award" from the Eicosanoid Research Foundation at their 15th International Bioactive Lipid Conference (2017).












