Related Research Articles

Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and mathematics principles with materials science, to design, analyze, manufacture, and maintain mechanical systems. It is one of the oldest and broadest of the engineering branches.

Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to organs, cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of biophysics.
In physics and materials science, elasticity is the ability of a body to resist a distorting influence and to return to its original size and shape when that influence or force is removed. Solid objects will deform when adequate loads are applied to them; if the material is elastic, the object will return to its initial shape and size after removal. This is in contrast to plasticity, in which the object fails to do so and instead remains in its deformed state.
Structural analysis is a branch of solid mechanics which uses simplified models for solids like bars, beams and shells for engineering decision making. Its main objective is to determine the effect of loads on the physical structures and their components. In contrast to theory of elasticity, the models used in structure analysis are often differential equations in one spatial variable. Structures subject to this type of analysis include all that must withstand loads, such as buildings, bridges, aircraft and ships. Structural analysis uses ideas from applied mechanics, materials science and applied mathematics to compute a structure's deformations, internal forces, stresses, support reactions, velocity, accelerations, and stability. The results of the analysis are used to verify a structure's fitness for use, often precluding physical tests. Structural analysis is thus a key part of the engineering design of structures.
Solid mechanics is the branch of continuum mechanics that studies the behavior of solid materials, especially their motion and deformation under the action of forces, temperature changes, phase changes, and other external or internal agents.

LS-DYNA is an advanced general-purpose multiphysics simulation software package developed by the former Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), which was acquired by Ansys in 2019. While the package continues to contain more and more possibilities for the calculation of many complex, real world problems, its origins and core-competency lie in highly nonlinear transient dynamic finite element analysis (FEA) using explicit time integration. LS-DYNA is used by the automobile, aerospace, construction and civil engineering, military, manufacturing, and bioengineering industries.
The boundary element method (BEM) is a numerical computational method of solving linear partial differential equations which have been formulated as integral equations, including fluid mechanics, acoustics, electromagnetics, fracture mechanics, and contact mechanics.
Applied mechanics is the branch of science concerned with the motion of any substance that can be experienced or perceived by humans without the help of instruments. In short, when mechanics concepts surpass being theoretical and are applied and executed, general mechanics becomes applied mechanics. It is this stark difference that makes applied mechanics an essential understanding for practical everyday life. It has numerous applications in a wide variety of fields and disciplines, including but not limited to structural engineering, astronomy, oceanography, meteorology, hydraulics, mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, nanotechnology, structural design, earthquake engineering, fluid dynamics, planetary sciences, and other life sciences. Connecting research between numerous disciplines, applied mechanics plays an important role in both science and engineering.
Abaqus FEA is a software suite for finite element analysis and computer-aided engineering, originally released in 1978. The name and logo of this software are based on the abacus calculation tool. The Abaqus product suite consists of five core software products:
- Abaqus/CAE, or "Complete Abaqus Environment". It is a software application used for both the modeling and analysis of mechanical components and assemblies (pre-processing) and visualizing the finite element analysis result. A subset of Abaqus/CAE including only the post-processing module can be launched independently in the Abaqus/Viewer product.
- Abaqus/Standard, a general-purpose Finite-Element analyzer that employs implicit integration scheme (traditional).
- Abaqus/Explicit, a special-purpose Finite-Element analyzer that employs explicit integration scheme to solve highly nonlinear systems with many complex contacts under transient loads.
- Abaqus/CFD, a Computational Fluid Dynamics software application which provides advanced computational fluid dynamics capabilities with extensive support for preprocessing and postprocessing provided in Abaqus/CAE - discontinued in Abaqus 2017 and further releases.
- Abaqus/Electromagnetic, a Computational electromagnetics software application which solves advanced computational electromagnetic problems.
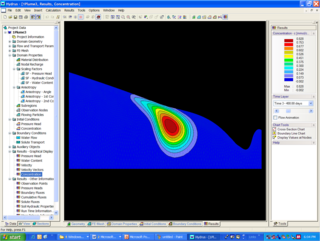
Hydrus is a suite of Windows-based modeling software that can be used for analysis of water flow, heat and solute transport in variably saturated porous media. HYDRUS suite of software is supported by an interactive graphics-based interface for data-preprocessing, discretization of the soil profile, and graphic presentation of the results. While HYDRUS-1D simulates water flow, solute and heat transport in one-dimension, and is a public domain software, HYDRUS 2D/3D extends the simulation capabilities to the second and third dimensions, and is distributed commercially.
Z88 is a software package for the finite element method (FEM) and topology optimization. A team led by Frank Rieg at the University of Bayreuth started development in 1985 and now the software is used by several universities, as well as small and medium-sized enterprises. Z88 is capable of calculating two and three dimensional element types with a linear approach. The software package contains several solvers and two post-processors and is available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Unix/Linux computers in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. Benchmark tests conducted in 2007 showed a performance on par with commercial software.

Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.
ADINA is a commercial engineering simulation software program that is developed and distributed worldwide by ADINA R & D, Inc. The company was founded in 1986 by Dr. Klaus-Jürgen Bathe, and is headquartered in Watertown, Massachusetts, United States. On April 7, 2022, Bentley Systems acquired ADINA R&D, Inc.
Smoothed finite element methods (S-FEM) are a particular class of numerical simulation algorithms for the simulation of physical phenomena. It was developed by combining meshfree methods with the finite element method. S-FEM are applicable to solid mechanics as well as fluid dynamics problems, although so far they have mainly been applied to the former.

VisualFEA is a finite element analysis software program for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. It is developed and distributed by Intuition Software, Inc. of South Korea, and used chiefly for structural and geotechnical analysis. Its strongest point is its intuitive, user-friendly design based on graphical pre- and postprocessing capabilities. It has educational features for teaching and learning structural mechanics, and finite element analysis through graphical simulation. It is widely used in college-level courses related to structural mechanics and finite element methods.
MOOSE is an object-oriented C++ finite element framework for the development of tightly coupled multiphysics solvers from Idaho National Laboratory. MOOSE makes use of the PETSc non-linear solver package and libmesh to provide the finite element discretization.
Goma is an open-source, parallel, and scalable multiphysics software package for modeling and simulation of real-life physical processes, with a basis in computational fluid dynamics for problems with evolving geometry. It solves problems in all branches of mechanics, including fluids, solids, and thermal analysis. Goma uses advanced numerical methods, focusing on the low-speed flow regime with coupled phenomena for manufacturing and performance applications. It also provides a flexible software development environment for specialty physics.
CONSELF is a computer-aided engineering (CAE) platform used by engineers for design purposes. The platform, which highly relies on cloud computing, is developed by CONSELF SRL since its first release in October 2015. In March 2016 a new release of the platform defined guided workflows for the users with focus on turbomachinery, fire scenarios and flows with dispersed solid particles. Through the platform it is possible to run both Computational Fluid Dynamics and Finite Element Analysis. Among the solvers and libraries used by CONSELF platform, a number of open-source technologies are included, such as:
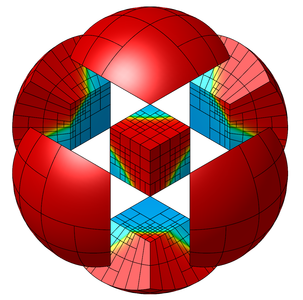
MFEM is an open-source C++ library for solving partial differential equations using the finite element method, developed and maintained by researchers at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory and the MFEM open-source community on GitHub. MFEM is free software released under a BSD license.
The Lattice Boltzmann methods for solids (LBMS) are a set of methods for solving partial differential equations (PDE) in solid mechanics. The methods use a discretization of the Boltzmann equation(BM), and their use is known as the lattice Boltzmann methods for solids.
References
- ↑ Maas, SA; Ellis BJ; Ateshian GA; Weiss JA (2012). "FEBio: Finite elements for biomechanics". Journal of Biomechanical Engineering. 134 (1): 011005. doi:10.1115/1.4005694. PMC 3705975 . PMID 22482660.
- ↑ Maas, Steve A.; Ateshian, Gerard A.; Weiss, Jeffrey A. (2017-06-20). "FEBio: History and Advances". Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering. 19 (1): 279–299. doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516-044738. ISSN 1523-9829. PMC 6141040 . PMID 28633565.
- ↑ Bonet, Javier; Wood, Richard (2008). Nonlinear Continuum Mechanics for Finite Element Analysis. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-83870-2.