Related Research Articles
Multi-disciplinary design optimization (MDO) is a field of engineering that uses optimization methods to solve design problems incorporating a number of disciplines. It is also known as multidisciplinary system design optimization (MSDO), and multidisciplinary design analysis and optimization (MDAO).

LS-DYNA is an advanced general-purpose multiphysics simulation software package developed by the former Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), which was acquired by Ansys in 2019. While the package continues to contain more and more possibilities for the calculation of many complex, real world problems, its origins and core-competency lie in highly nonlinear transient dynamic finite element analysis (FEA) using explicit time integration. LS-DYNA is used by the automobile, aerospace, construction and civil engineering, military, manufacturing, and bioengineering industries.
NASTRAN is a finite element analysis (FEA) program that was originally developed for NASA in the late 1960s under United States government funding for the aerospace industry. The MacNeal-Schwendler Corporation (MSC) was one of the principal and original developers of the publicly available NASTRAN code. NASTRAN source code is integrated in a number of different software packages, which are distributed by a range of companies.

Ansys, Inc. is an American multinational company with its headquarters based in Canonsburg, Pennsylvania. It develops and markets CAE/multiphysics engineering simulation software for product design, testing and operation and offers its products and services to customers worldwide.

NEi Nastran was an engineering analysis and simulation software product of NEi Software. Based on NASA's Structural Analysis program NASTRAN, the software is a finite element analysis (FEA) solver used to generate solutions for linear and nonlinear stress, dynamics, and heat transfer characteristics of structures and mechanical components. NEi Nastran software is used with all major industry pre- and post-processors, including Femap, a product of Siemens PLM Software, and the in-house brands NEi Nastran in-CAD, NEi Fusion, and NEi Works for SolidWorks. This software was acquired by Autodesk in May 2014.
Mercedes Reaves is a Puerto Rican research engineer and scientist. She is responsible for the design of a viable full-scale solar sail and the development and testing of a scale model solar sail at NASA Langley Research Center in Virginia.
Femap is an engineering analysis program sold by Siemens Digital Industries Software that is used to build finite element models of complex engineering problems ("pre-processing") and view solution results ("post-processing"). It runs on Microsoft Windows and provides CAD import, modeling and meshing tools to create a finite element model, as well as postprocessing functionality that allows mechanical engineers to interpret analysis results. The finite element method allows engineers to virtually model components, assemblies, or systems to determine behavior under a given set of boundary conditions, and is typically used in the design process to reduce costly prototyping and testing, evaluate differing designs and materials, and for structural optimization to reduce weight.
Zemax is a software program used for designing and simulating optical systems. It is widely used in the field of optics and photonics for designing and analyzing the performance of lenses, cameras, telescopes, microscopes, and other optical systems. With the software, the behavior of light interacting with various optical components can be modelled, and optical designs can be optimized for desired performance.
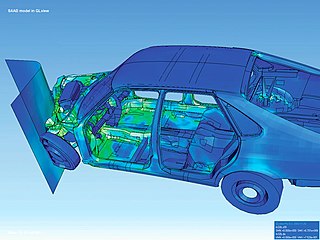
The finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat transfer, fluid flow, mass transport, and electromagnetic potential.
Z88 is a software package for the finite element method (FEM) and topology optimization. A team led by Frank Rieg at the University of Bayreuth started development in 1985 and now the software is used by several universities, as well as small and medium-sized enterprises. Z88 is capable of calculating two and three dimensional element types with a linear approach. The software package contains several solvers and two post-processors and is available for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Unix/Linux computers in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. Benchmark tests conducted in 2007 showed a performance on par with commercial software.

NEi Fusion is a finite element analysis program sold by NEi Software that is used by engineers to build and analyze 3D models of parts and assemblies of various products. NEi Fusion digital-simulation software virtually applies forces, pressures, vibration, acceleration loads, or thermal conditions to 3D models of parts, structures, and assemblies. It obtains results of various engineering parameters, such as deformation, stresses, strains, temperature distributions, and modal shapes the design would experience if implemented. The results, which range from tables of data to contour plots and animations, provide engineering insight. For example, result visualizations like color-coded, contour plots can help deepen understanding of physical phenomena in complex geometry. NEi Fusion consists of a 3D parametric CAD modeler powered by SolidWorks with NEi Nastran finite element analysis solvers. NEi Fusion runs on Microsoft Windows and provides CAD modeling, import and meshing tools.

Synopsys Simpleware ScanIP is a 3D image processing and model generation software program developed by Synopsys Inc. to visualise, analyse, quantify, segment and export 3D image data from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), computed tomography (CT), microtomography and other modalities for computer-aided design (CAD), finite element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), and 3D printing. The software is used in the life sciences, materials science, nondestructive testing, reverse engineering and petrophysics.
ADINA is a commercial engineering simulation software program that is developed and distributed worldwide by ADINA R & D, Inc. The company was founded in 1986 by Dr. Klaus-Jürgen Bathe, and is headquartered in Watertown, Massachusetts, United States. On April 7, 2022, Bentley Systems acquired ADINA R&D, Inc.
MEDINA is a universal pre-/postprocessor for finite element analysis. The development of MEDINA started in the early 1990s at Daimler-Benz AG and was proceeded at debis Systemhaus. Since 2001 the support and the development of MEDINA takes place by T-Systems International GmbH. The current release is MEDINA Rel. 9.0.1.2

VisualFEA is a finite element analysis software program for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. It is developed and distributed by Intuition Software, Inc. of South Korea, and used chiefly for structural and geotechnical analysis. Its strongest point is its intuitive, user-friendly design based on graphical pre- and postprocessing capabilities. It has educational features for teaching and learning structural mechanics, and finite element analysis through graphical simulation. It is widely used in college-level courses related to structural mechanics and finite element methods.
SmartDO is a multidisciplinary design optimization software, based on the Direct Global Search technology developed and marketed by FEA-Opt Technology. SmartDO specialized in the CAE-Based optimization, such as CAE, FEA, CAD, CFD and automatic control, with application on various physics phenomena. It is both GUI and scripting driven, allowed to be integrated with almost any kind of CAD/CAE and in-house codes.
ACTRAN is a finite element-based computer aided engineering software modeling the acoustic behavior of mechanical systems and parts. Actran is being developed by Free Field Technologies, a Belgian software company founded in 1998 by Jean-Pierre Coyette and Jean-Louis Migeot. Free Field Technologies is a wholly owned subsidiary of the MSC Software Corporation since 2011. Free Field Technologies and MSC Software are part of Hexagon AB since 2017.
References
- ↑ "References to technical papers on the official site".
- ↑ "Hong Kong to Monitor Stonecutters Bridge With FEMtools". Archived from the original on 2010-01-04. Retrieved 2010-09-19.
- ↑ Wenzel, H. (2009). Health Monitoring of Bridges. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. p. 212-225. ISBN 9780470031735.
- ↑ "Model updating of a 'clamped'-free beam system using FEMtools" (PDF).
- ↑ "Updating of the Analytical Models of Two Footbridges Based on Modal Testing of Full-Scale Structures" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-09-01.