An allele is a variant form of a given gene. Sometimes, the presence of different alleles of the same gene can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this trait of color variation is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of "pure line" traits which could be used as a control for future experiments. However, most genetic variations result in little or no observable variation.

Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a genetic disorder. Symptoms often include mild to moderate intellectual disability. The average IQ in males is under 55. Physical features may include a long and narrow face, large ears, flexible fingers, and large testicles. About a third of those affected have features of autism such as problems with social interactions and delayed speech. Hyperactivity is common and seizures occur in about 10%. Males are usually more affected than females.

Azacitidine is a chemical analog of cytidine, a nucleoside in DNA and RNA. Azacitidine and its deoxy derivative, decitabine, are used in the treatment of myelodysplastic syndrome. Both drugs were first synthesized in Czechoslovakia as potential chemotherapeutic agents for cancer.

A chromosomal fragile site is a specific heritable point on a chromosome that tends to form a gap or constriction and may tend to break when the cell is exposed to partial replication stress. Based on their frequency, fragile sites are classified as "common" or "rare". To date, more than 120 fragile sites have been identified in the human genome.

Chromosome 1 is the designation for the largest human chromosome. Humans have two copies of chromosome 1, as they do with all of the autosomes, which are the non-sex chromosomes. Chromosome 1 spans about 249 million nucleotide base pairs, which are the basic units of information for DNA. It represents about 8% of the total DNA in human cells.
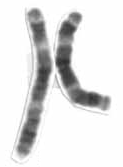
Chromosome 3 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 3 spans almost 200 million base pairs and represents about 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cells.
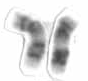
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.

Collagen, type I, alpha 1, also known as alpha-1 type I collagen, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL1A1 gene. COL1A1 encodes the major component of type I collagen, the fibrillar collagen found in most connective tissues, including cartilage.
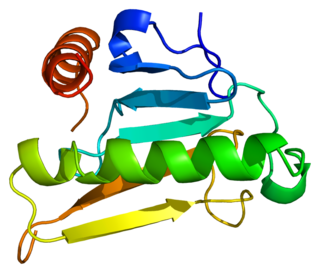
Bis(5'-adenosyl)-triphosphatase also known as fragile histidine triad protein (FHIT) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FHIT gene.

WW domain-containing oxidoreductase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the WWOX gene.

Fos-related antigen 1 (FRA1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOSL1 gene.

Plakophilin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PKP1 gene.

Homeobox protein Hox-D12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXD12 gene.

5-azacytidine-induced protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AZI1 gene.

Caveolin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAV2 gene.

5-azacytidine-induced protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AZI2 gene.

FRA10AC1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FRA10AC1 gene.
Fragile site, aphidicolin type, common, fra(3)(p24.2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FRA3A gene.
Fragile site, folic acid type, rare, fra(2)(q13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FRA2B gene.
FRAXD or FRAXD gene is a gene symbol for fragile site, aphidicolin type, common, fra(X)(q27.2) D. The locus of the gene is located on fragile site of the q arm of chromosome X at position 27.2. It is used for gene testing in Homo sapiens.

















