
Vicia faba, commonly known as the broad bean, fava bean, or faba bean, is a species of vetch, a flowering plant in the pea and bean family Fabaceae. It is widely cultivated as a crop for human consumption, and also as a cover crop. Varieties with smaller, harder seeds that are fed to horses or other animals are called field bean, tic bean or tick bean. Horse bean, Vicia faba var. equinaPers., is a variety recognized as an accepted name. This legume is very common in Southern European, Northern European, East Asian, Latin American and North African cuisines.

Legumes are plants in the family Fabaceae, or the fruit or seeds of such plants. When used as a dry grain for human consumption, the seeds are also called pulses. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, but also as livestock forage and silage, and as soil-enhancing green manure. Well-known legumes include beans, chickpeas, peanuts, lentils, lupins, mesquite, carob, tamarind, alfalfa, and clover. Legumes produce a botanically unique type of fruit – a simple dry fruit that develops from a simple carpel and usually dehisces on two sides.

Phaseolus vulgaris, the common bean, is a herbaceous annual plant grown worldwide for its edible dry seeds or green, unripe pods. Its leaf is also occasionally used as a vegetable and the straw as fodder. Its botanical classification, along with other Phaseolus species, is as a member of the legume family Fabaceae. Like most members of this family, common beans acquire the nitrogen they require through an association with rhizobia, which are nitrogen-fixing bacteria.

Vicia is a genus of over 240 species of flowering plants that are part of the legume family (Fabaceae), and which are commonly known as vetches. Member species are native to Europe, North America, South America, Asia and Africa. Some other genera of their subfamily Faboideae also have names containing "vetch", for example the vetchlings (Lathyrus) or the milk-vetches (Astragalus). The lentils are included in genus Vicia, and were formerly classified in genus Lens. The broad bean is sometimes separated in a monotypic genus Faba; although not often used today, it is of historical importance in plant taxonomy as the namesake of the order Fabales, the Fabaceae and the Faboideae. The tribe Vicieae in which the vetches are placed is named after the genus' current name. The true peas (Pisum) are among the closest living relatives of vetches.
Field bean is a general term for several plants found growing within fields or shrubbery and may refer to:
Favomancy is a form of divination that involves throwing beans on the ground and interpreting the patterns into which the beans fall; it is therefore a type of cleromancy. Various forms of favomancy are present across the world's cultures. The term comes from the Vicia faba meaning Fava bean, and by way of cult etymology, from the Latin faba for "bean" and formed by analogy with the names of similar divination methods such as alectromancy.

Vicine is an alkaloid glycoside found mainly in fava beans, which are also called broad beans. Vicine is toxic in individuals who have a hereditary loss of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. It causes haemolytic anaemia, called favism. The formation of vicine in Vicia faba has been studied, but this natural formation has not yet been found.

Procyanidins are members of the proanthocyanidin class of flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. They yield cyanidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

Bidens mottle virus (BiMoV) is a pathogenic plant virus in the plant virus family Potyviridae. BiMoV is a flexuous filamentous particle, 720 nm long, and belongs to the Potyviridae genus Potyvirus. Like other viruses in this genus, Bidens mottle virus is transmitted both mechanically by sap and by aphids in a stylet-borne fashion.
Clover yellow mosaic virus (ClYMV) is a plant pathogenic virus in the genus Potexvirus and the virus family Alphaflexiviridae. Its flexuous rod-shaped particles measure about 539 nm in length.
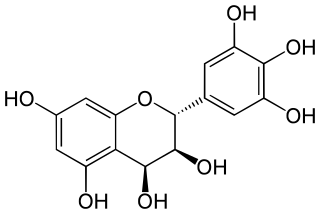
Leucodelphinidin is a colorless chemical compound related to leucoanthocyanidins. It can be found in Acacia auriculiformis, in the bark of Karada and in the kino (gum) from Eucalyptus pilularis.

Aproaerema anthyllidella is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in most of Europe, Kyrgyzstan, Iran and North America.

Vicia orobus is a species of leguminous plant in the genus Vicia, known as wood bitter-vetch. It is found in Atlantic areas of Europe, especially in the rocky edges of seasonally-grazed fields. It grows up to 60 cm (24 in) tall, and has no tendrils at the ends of its pinnate leaves. Its flowers are white with purple veins, and are borne in groups of 6 or more.
Broad bean true mosaic virus is a virus first described in 1953 that affects legumes, commonly found in crops of broad bean in both Europe and Northwest Africa. There are no known vectors, although it has been known to transverse long distances between crops. Infection via seed is common, though the virus is also present in sap.
Amalgaviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Member viruses infect plants and are transmitted vertically via seeds. The name derives from amalgam which refers to amalgaviruses possessing characteristics of both partitiviruses and totiviruses. There are ten species in the family.

Bruchus rufimanus, commonly known as the broadbean weevil, broadbean beetle, or broadbean seed beetle is a leaf beetle which inhabits crops and fields, as well as some homes. It is a pest of faba beans. The adult beetles feed on pollen, while their larvae tunnel in seeds destroying crops and moving on to new ones once they dry out. The adult beetle, being one of the biggest of its genus, ranges from 3 to 5 mm in length.

Vicia bithynica known as Bithynian vetch, is a species of flowering plant in the bean family Fabaceae. It was described by Carl Linnaeus, initially as Lathyrus bithynicus but later moved to the genus Vicia (vetches). The specific name is derived from Bithynia, an ancient kingdom situated on the north coast of Anatolia, in modern day Turkey.
Faba bean necrotic yellows virus (FBNYV) is a Nanovirus disease of legumes.










