The maxilla in vertebrates is the upper fixed bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible, which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw.

The lacrimal bone is a small and fragile bone of the facial skeleton; it is roughly the size of the little fingernail. It is situated at the front part of the medial wall of the orbit. It has two surfaces and four borders. Several bony landmarks of the lacrimal bone function in the process of lacrimation or crying. Specifically, the lacrimal bone helps form the nasolacrimal canal necessary for tear translocation. A depression on the anterior inferior portion of the bone, the lacrimal fossa, houses the membranous lacrimal sac. Tears or lacrimal fluid, from the lacrimal glands, collect in this sac during excessive lacrimation. The fluid then flows through the nasolacrimal duct and into the nasopharynx. This drainage results in what is commonly referred to a runny nose during excessive crying or tear production. Injury or fracture of the lacrimal bone can result in posttraumatic obstruction of the lacrimal pathways.

A snake skeleton consists primarily of the skull, vertebrae, and ribs, with only vestigial remnants of the limbs.

The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located mesial to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication (chewing). There is typically a single cusp on each tooth, called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Formation of these teeth begins at 14 weeks in utero for the deciduous (baby) set and 3–4 months of age for the permanent set.

An articulator is a mechanical hinged device used in dentistry to which plaster casts of the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) jaw are fixed, reproducing some or all the movements of the mandible in relation to the maxilla. The human maxilla is fixed and the scope of movement of the mandible is dictated by the position and movements of the bilateral temperomandibular joints, which sit in the glenoid fossae in the base of the skull. The temperomandibular joints are not a simple hinge but rotate and translate forward when the mouth is opened.

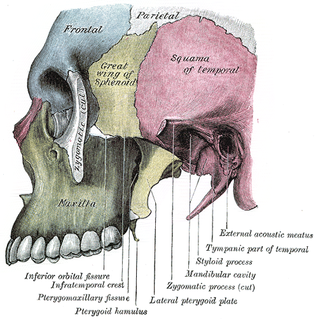
The zygomatic processes are three processes (protrusions) from other bones of the skull which each articulate with the zygomatic bone. The three processes are:
Dental anatomy is a field of anatomy dedicated to the study of human tooth structures. The development, appearance, and classification of teeth fall within its purview. Tooth formation begins before birth, and the teeth's eventual morphology is dictated during this time. Dental anatomy is also a taxonomical science: it is concerned with the naming of teeth and the structures of which they are made, this information serving a practical purpose in dental treatment.
Occlusion, in a dental context, means simply the contact between teeth. More technically, it is the relationship between the maxillary (upper) and mandibular (lower) teeth when they approach each other, as occurs during chewing or at rest.
In dentistry, centric relation is the mandibular jaw position in which the head of the condyle is situated as far anterior and superior as it possibly can within the mandibular fossa/glenoid fossa.
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body.
In dentistry, a mutually protected occlusion is an occlusal scheme in which the anterior teeth protect the posterior teeth, and vice versa.
Cephalometric analysis is the clinical application of cephalometry. It is analysis of the dental and skeletal relationships of a human skull. It is frequently used by dentists, orthodontists, and oral and maxillofacial surgeons as a treatment planning tool. Two of the more popular methods of analysis used in orthodontology are the Steiner analysis and the Downs analysis. There are other methods as well which are listed below.
A jaw abnormality is a disorder in the formation, shape and/or size of the jaw. In general abnormalities arise within the jaw when there is a disturbance or fault in the fusion of the mandibular processes. The mandible in particular has the most differential typical growth anomalies than any other bone in the human skeleton. This is due to variants in the complex symmetrical growth pattern which formulates the mandible.

Overbite medically refers to the extent of vertical (superior-inferior) overlap of the maxillary central incisors over the mandibular central incisors, measured relative to the incisal ridges.
Activator Appliance is an Orthodontics appliance that was developed by Viggo Andresen in 1908. This was one of the first functional appliances that was developed to correct functional jaw in the early 1900s. Activator appliance became the universal appliance that was used widely throughout Europe in the earlier part of the 20th century.
Open bite is a type of orthodontic malocclusion which has been estimated to occur in 0.6% of the people in the United States. This type of malocclusion has no vertical overlap or contact between the anterior incisors. The prevalence varies between different populations, for instance, occurring with 16% in Black people and 4% in white people. The term "open bite" was coined by Carevelli in 1842.
A complete denture is a removable appliance used when all teeth within a jaw have been lost and need to be prosthetically replaced. In contrast to a partial denture, a complete denture is constructed when there are no more teeth left in an arch, hence it is an exclusively tissue-supported prosthesis. A complete denture can be opposed by natural dentition, a partial or complete denture, fixed appliances or, sometimes, soft tissues.

Posselt's envelope of motion or Posselt's envelope of movement refers to the range of motion of the lower jaw bone, or mandible.
Occlusion according to The Glossary of Prosthodontic Terms Ninth Edition is defined as 'the static relationship between the incising or masticating surfaces of the maxillary or mandibular teeth or tooth analogues'.








