
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classical world. It became the capital city of the civilisation of Ancient Carthage and later Roman Carthage.

Maktar or Makthar, also known by other names during antiquity, is a town and archaeological site in Siliana Governorate, Tunisia.

The Punic religion, Carthaginian religion, or Western Phoenician religion in the western Mediterranean was a direct continuation of the Phoenician variety of the polytheistic ancient Canaanite religion. However, significant local differences developed over the centuries following the foundation of Carthage and other Punic communities elsewhere in North Africa, southern Spain, Sardinia, western Sicily, and Malta from the ninth century BC onward. After the conquest of these regions by the Roman Republic in the third and second centuries BC, Punic religious practices continued, surviving until the fourth century AD in some cases. As with most cultures of the ancient Mediterranean, Punic religion suffused their society and there was no stark distinction between religious and secular spheres. Sources on Punic religion are poor. There are no surviving literary sources and Punic religion is primarily reconstructed from inscriptions and archaeological evidence. An important sacred space in Punic religion appears to have been the large open air sanctuaries known as tophets in modern scholarship, in which urns containing the cremated bones of infants and animals were buried. There is a long-running scholarly debate about whether child sacrifice occurred at these locations, as suggested by Greco-Roman and biblical sources.

Madauros was a Roman-Berber city and a former diocese of the Catholic Church in the old state of Numidia, in present-day Algeria.

Pupput, also spelled "Putput", "Pudput", "Pulpud" and "Pulpite" in Latin, sometimes located in Souk el-Obiod ou Souk el-Abiod, is a Colonia in the Roman province of Africa which has been equated with an archaeological site in modern Tunisia. It is situated on the coast near the town of Hammamet, between the two wadis of Temad to the north and Moussa to the south. Much of the Pupput is buried under modern holiday developments which have been built over the major part of the site.
Kanaanäische und Aramäische Inschriften, or KAI, is the standard source for the original text of Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions not contained in the Hebrew Bible.

The Cisterns of La Malga or Cisterns of La Mâalga are a group of cisterns, which are among the most visible features of the archaeological site of Carthage near Tunis, Tunisia. They are some of the best preserved Roman cisterns.

Christian Tuxen Falbe was a Danish naval officer, archaeologist, explorer, cartographer and diplomat.
Liliane Ennabli is a Franco-Tunisian historian, archaeologist and epigrapher, a specialist in the history of the Christian period of the archaeological site of Carthage.

The Corpus Inscriptionum Semiticarum is a collection of ancient inscriptions in Semitic languages produced since the end of 2nd millennium BC until the rise of Islam. It was published in Latin. In a note recovered after his death, Ernest Renan stated that: "Of all I have done, it is the Corpus I like the most."

The Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions, also known as Northwest Semitic inscriptions, are the primary extra-Biblical source for understanding of the society and history of the ancient Phoenicians, Hebrews and Arameans. Semitic inscriptions may occur on stone slabs, pottery ostraca, ornaments, and range from simple names to full texts. The older inscriptions form a Canaanite–Aramaic dialect continuum, exemplified by writings which scholars have struggled to fit into either category, such as the Stele of Zakkur and the Deir Alla Inscription.

The Marseille Tariff is a Punic language inscription from the third century BCE, found on two fragments of a stone in June 1845 at Marseille in Southern France. It is thought to have originally come from the temple of Baal-Saphon in Carthage. It is one of the earliest published inscriptions written in the Phoenician alphabet, and one of the longest ever found.
Carthaginian tombstones are Punic language-inscribed tombstones excavated from the city of Carthage over the last 200 years. The first such discoveries were published by Jean Emile Humbert in 1817, Hendrik Arent Hamaker in 1828 and Christian Tuxen Falbe in 1833.

The Cirta steles are almost 1,000 Punic funerary and votive steles found in Cirta in a cemetery located on a hill immediately south of the Salah Bey Viaduct.

The Carthage Administration Inscription is an inscription in the Punic language, using the Phoenician alphabet, discovered on the archaeological site of Carthage in the 1960s and preserved in the National Museum of Carthage. It is known as KAI 303.

The Pricot de Sainte-Marie steles are more than 2,000 Punic funerary steles found in Carthage near the ancient forum by French diplomat Jean-Baptiste Evariste Charles Pricot de Sainte-Marie in the 1870s. The find was dramatic both in the scale—the largest single discovery of Canaanite and Aramaic inscriptions—and also due to the finds almost being lost in the sinking of the French ironclad Magenta at Toulon.

The Sibbolet funeral inscription is a Punic language inscription found in 1902 at Carthage. It measures 20 by 7 cm and is currently held at the Carthage National Museum. It is known as KAI 92, CIS I 5948, or R 768.

The Persephone Punic stele is a marble bas-relief stele of the Greek deity Persephone above a short punic inscription.
The Khaznadar inscriptions are approximately 120 Punic inscriptions, found in Carthage by Muhammad Khaznadar in the 1860s in Husainid Tunisia.
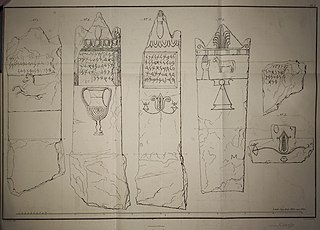
The Humbert Punic inscriptions are three Punic inscriptions, found in Carthage by Jean Emile Humbert in 1817 in Husainid Tunisia.

















