Functions of FOA
The functions of the FOA as laid down in the Act are as follows:-
- To boost, encourage and endeavour economic and social progress of farmers’ organisations
- To register, control and supervise Farmers’ Organisations and making provision for related matters. If a declaration was made through announcement under section 10, to design and implement any agricultural development in Farmers' Organization of those area and
- To control and co-ordinate the implementation of the activities
FOA implements all these activities that can be collated within three main functions as follow :
- functions as Registrar
- functions as Management Agent and
- functions as Development Agent.
Registrar’s Function
Director General of FOA is Registrar of Farmers’ Organisation (FO) and agriculture-based cooperatives and is responsible for registering, supervising and controlling including auditing of account of all Area Farmers' Organization (AFO) and agriculture-based cooperatives. The power and tasks of the agency and registrar are related to :
- As Registrar of FO and agriculture-based cooperatives
- To supervise and control all activities of FO and agriculture-based cooperatives.
- To audit and control the account.
- To revoke registrations including abolishment of any organisation: and
- To give education and training to members
The Registrar has appointed the Chief Executives for related agencies as its representatives to facilitate operation and effectiveness of tasks and responsibilities of registrar in MADA, KADA and Sarawak. Director of state AFO were also appointed. However, the power to form, register, suspend, abolish and others are still under the jurisdiction of the Registrar.
Management Functions
FOA gives management service to FO to facilitate operations and implements projects efficiently. The services given include staff administration, management services, training of staff of FO and consultancy services.
Development Functions
The main thrust of FOA is to explore the economic and social development of FO and implements in an efficient and integrated manner to increase the income of FO to benefit members. Under the Ninth Malaysia Plan (2006–2010), the Federal Government has allocated RM291 million for specific economic and social development of FO.

The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) is an independent agency of the U.S. federal government that is primarily responsible for administering civilian foreign aid and development assistance. With a budget of over $27 billion, USAID is one of the largest official aid agencies in the world and accounts for more than half of all U.S. foreign assistance—the highest in the world in absolute dollar terms.
Innovation, Science and Economic Development Canada is a department of the Government of Canada. ISED is responsible for a number of the federal government's functions in regulating industry and commerce, promoting science and innovation, and supporting economic development. The department was known as Industry Canada (IC) prior to 2015.
Agribusiness is the industry, enterprises, and the field of study of value chains in agriculture and in the bio-economy, in which case it is also called bio-business or bio-enterprise. The primary goal of agribusiness is to maximize profit while satisfying the needs of consumers for products related to natural resources such as biotechnology, farms, food, forestry, fisheries, fuel, and fiber.
The social economy is formed by a rich diversity of enterprises and organisations, such as cooperatives, mutuals, associations, foundations, social enterprises and paritarian institutions, sharing common values and features:

An agricultural cooperative, also known as a farmers' co-op, is a producer cooperative in which farmers pool their resources in certain areas of activity.

The Philippine Statistics Authority is the central statistical authority of the Philippine government that collects, compiles, analyzes and publishes statistical information on economic, social, demographic, political affairs and general affairs of the people of the Philippines and enforces the civil registration functions in the country.
The Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH, often simply shortened to GIZ, is the main German development agency. It is headquartered in Bonn and Eschborn and provides services in the field of international development cooperation and international education work. The organization's self-declared goal is to deliver effective solutions that offer people better prospects and sustainably improve their living conditions.

The Korea Forest Service is a central administrative agency under the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFR), responsible for protecting and nurturing forests, increasing forest resources, developing forest products, conducting research on forest management and improvement, and is located in Daejeon Government Complex. In the past, during the national forestation campaign from 1973 to 1986, it was temporarily under the Ministry of Home Affairs, but returned to the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries in 1987. However, as the agency's work was focused solely on maintaining and managing successful national forestation policies, questions were raised about its necessity for a period of time. Currently, the agency has transformed its identity into one that strives to generate continuous income through forest resources.

The Second Malaysia Plan was an economic development plan introduced by the government of Malaysia with the goal of implementing the Malaysian New Economic Policy (NEP). It lasted from 1971 to 1975 and aimed to "restructure" the society of Malaysia and reduce Malaysian Chinese and foreign dominance in the economy of Malaysia so as to improve the economic position of the Malays. It was the successor to the First Malaysia Plan, which was also intended to specifically tackle the problem of poverty among the Malays. However, the First Malaysia Plan had limited success, which may have been a factor in the 13 May Incident in 1969 when race riots broke out in Kuala Lumpur. The Second Malaysia Plan had been regarded as excessive in its zeal to increase Malay participation in the economy, and the government accordingly scaled back the emphasis on restructuring the economy when the plan ended.
The agrarian reforms in Cuba sought to break up large landholdings and redistribute land to those peasants who worked it, to cooperatives, and the state. Laws relating to land reform were implemented in a series of laws passed between 1959 and 1963 after the Cuban Revolution. The Institutio Nacional de Reforma Agraria (INRA)—an agency of the Cuban government responsible to implement the first and second Agrarian Reforms. The agency adapted the Soviet model of organisation—small collectives and large(er) state farms.
National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is an apex regulatory body for overall regulation of regional rural banks and apex cooperative banks in India. It is under the jurisdiction of Ministry of Finance, Government of India. The bank has been entrusted with "matters concerning policy, planning, and operations in the field of credit for agriculture and other economic activities in rural areas in India". NABARD is active in developing and implementing financial inclusion.
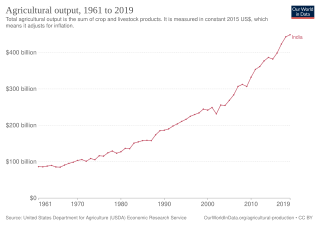
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2018, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 17–18% to the country's GDP.

The Ministry of Commerce (MOC) is the Burmese government agency plays a vital role in the transformation process of the implementation of a market-oriented economic system. Its headquarters is located at Building 3 and 52, Nay Pyi Taw, in Myanmar.

The Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises is the ministry in the Government of India. It is the apex executive body for the formulation and administration of rules, regulations and laws relating to micro, small and medium enterprises in India. The Minister of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises is Narayan Rane.

The South Korean National Agricultural Cooperative Federation was established in 1961 to enhance the social and economic status of its membership and to promote a balanced development of the national economy. Its role is divided into three areas: marketing and supply, banking and insurance, and extension services.

Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member-owners jointly engage in farming activities as a collective, and state farms, which are owned and directly run by a centralized government. The process by which farmland is aggregated is called collectivization. In some countries, there have been both state-run and cooperative-run variants. For example, the Soviet Union had both kolkhozy and sovkhozy.

The Ministry of Agrarian Policy and Food is the central executive authority of Ukraine in charge of country's agro-development. It is one of the oldest government agencies of Ukraine. On 29 August 2019 the ministry's function were taken over by the Ministry of Economic Development, Trade and Agriculture. On 17 December 2020 the ministry was resurrected.
Agrarian socialism is a political ideology that promotes social ownership of agrarian and agricultural production as opposed to private ownership. Agrarian socialism involves equally distributing agricultural land among collectivized peasant villages. Many agrarian socialist movements have tended to be rural, locally focused, and traditional. Governments and political parties seeking agrarian socialist policies have existed throughout the world, in regions including Europe, Asia, North America, Latin America, and Africa.

The Ministry of Agriculture and Food Security, abbreviated MAFS, is a ministry of the Government of Malaysia that is responsible for agriculture, agro-based industry, agritourism, livestock, veterinary services, fisheries, quarantine, inspection, agricultural research, agricultural development, agricultural marketing, pineapple industry, agribusiness, botanical garden, food security, food sovereignty.
The Finnish Competition and Consumer Authority is the Competition regulator in Finland. It is the regulatory authority of Politics of Finland which works in the field of competition and consumer rights protection. The purpose of the Finnish Competition and Consumer Authority is to create healthy and effective markets in which companies and other operators act responsibly and in keeping with consumers' interests.











