Related Research Articles

Mohamed Al-Fayed was an Egyptian billionaire businessman, whose residence and primary business interests were in the United Kingdom from the mid-1960s. His business interests included ownership of the Hôtel Ritz Paris, and Harrods department store and Fulham Football Club, both in London. At the time of his death in 2023, Fayed's wealth was estimated at US$2 billion by Forbes.
A flange is a protruded ridge, lip or rim, either external or internal, that serves to increase strength ; for easy attachment/transfer of contact force with another object ; or for stabilizing and guiding the movements of a machine or its parts. Flanges are often attached using bolts in the pattern of a bolt circle.

Emad El-Din Mohamed Abdel Mena'em Fayed, commonly known as Dodi Fayed, was an Egyptian film producer and the eldest child of the businessman Mohamed Al-Fayed. He was romantically involved with Diana, Princess of Wales, when they both died in a car crash in Paris on 31 August 1997.

A bicycle wheel is a wheel, most commonly a wire wheel, designed for a bicycle. A pair is often called a wheelset, especially in the context of ready built "off the shelf" performance-oriented wheels.

A gasket is a mechanical seal which fills the space between two or more mating surfaces, generally to prevent leakage from or into the joined objects while under compression. It is a deformable material that is used to create a static seal and maintain that seal under various operating conditions in a mechanical assembly.

Standard diving dress, also known as hard-hat or copper hat equipment, deep sea diving suit or heavy gear, is a type of diving suit that was formerly used for all relatively deep underwater work that required more than breath-hold duration, which included marine salvage, civil engineering, pearl shell diving and other commercial diving work, and similar naval diving applications. Standard diving dress has largely been superseded by lighter and more comfortable equipment.

The Apollo spacecraft was composed of three parts designed to accomplish the American Apollo program's goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by the end of the 1960s and returning them safely to Earth. The expendable (single-use) spacecraft consisted of a combined command and service module (CSM) and an Apollo Lunar Module (LM). Two additional components complemented the spacecraft stack for space vehicle assembly: a spacecraft–LM adapter (SLA) designed to shield the LM from the aerodynamic stress of launch and to connect the CSM to the Saturn launch vehicle and a launch escape system (LES) to carry the crew in the command module safely away from the launch vehicle in the event of a launch emergency.

Alexander L. Kielland was a Norwegian semi-submersible drilling rig that, on 27 March 1980, capsized in the Ekofisk oil field in the North Sea, killing 123 people. The capsize was the worst disaster in Norwegian waters since the Second World War. The rig, located approximately 320 km east of Dundee, Scotland, was owned by the Stavanger Drilling Company of Norway and was on hire to the U.S. company Phillips Petroleum at the time of the disaster.

In rail transport, a derailment is a type of train wreck that occurs when a rail vehicle such as a train comes off its rails. Although many derailments are minor, all result in temporary disruption of the proper operation of the railway system and they are a potentially serious hazard.

A machine taper is a system for securing cutting tools or toolholders in the spindle of a machine tool or power tool. A male member of conical form fits into the female socket, which has a matching taper of equal angle.

An I-beam is any of various structural members with an I- or H-shaped cross-section. Technical terms for similar items include H-beam, I-profile, universal column (UC), w-beam, universal beam (UB), rolled steel joist (RSJ), or double-T. I-beams are typically made of structural steel and serve a wide variety of construction uses.

A girder bridge is a bridge that uses girders as the means of supporting its deck. The two most common types of modern steel girder bridges are plate and box.

A fitting or adapter is used in pipe systems to connect sections of pipe or tube, adapt to different sizes or shapes, and for other purposes such as regulating fluid flow. These fittings are used in plumbing to manipulate the conveyance of fluids such as water for potatory, irrigational, sanitary, and refrigerative purposes, gas, petroleum, liquid waste, or any other liquid or gaseous substances required in domestic or commercial environments, within a system of pipes or tubes, connected by various methods, as dictated by the material of which these are made, the material being conveyed, and the particular environmental context in which they will be used, such as soldering, mortaring, caulking, plastic welding, welding, friction fittings, threaded fittings, and compression fittings.

The rail profile is the cross sectional shape of a railway rail, perpendicular to its length.

A flange nut is a nut that has a wide flange at one end that acts as an integrated washer. This serves to distribute the pressure of the nut over the part being secured, reducing the chance of damage to the part and making it less likely to loosen as a result of an uneven fastening surface. These nuts are mostly hexagonal in shape and are made up of hardened steel and often coated with zinc.

Dissorophus (DI-soh-ROH-fus) is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian that lived during the Early Permian Period about 273 million years ago. Its fossils have been found in Texas and in Oklahoma in North America. Its heavy armor and robust build indicate Dissorophus was active on land, similar to other members of the clade Dissorophidae that are known from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Permian periods. Dissorphus is distinguished by its small body size, disproportionately large head and short trunk.
A railway or railroad is a track where the vehicle travels over two parallel steel bars, called rails. The rails support and guide the wheels of the vehicles, which are traditionally either trains or trams. Modern light rail is a relatively new innovation which combines aspects of those two modes of transport. However fundamental differences in the track and wheel design are important, especially where trams or light railways and trains have to share a section of track, as sometimes happens in congested areas.

The Parflange F37 system is a technology from the hydraulic area of Parker-Hannifin, which allows a non welded flange connection of hydraulic tubes and pipes.
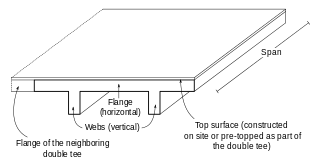
A double tee or double-T beam is a load-bearing structure that resembles two T-beams connected to each other side by side. The strong bond of the flange and the two webs creates a structure that is capable of withstanding high loads while having a long span. The typical sizes of double tees are up to 15 feet (4.6 m) for flange width, up to 5 feet (1.5 m) for web depth, and up to 80 feet (24 m) or more for span length. Double tees are pre-manufactured from prestressed concrete which allows construction time to be shortened.
The Waage Drill II diving accident occurred in the North Sea off Scotland on 9 September 1975, when two divers died of heatstroke after the chamber they were in was inadvertently pressurised with helium gas.
References
- ↑ "Faying surface". Webster's Revised Unabridged Dictionary. S.v. Retrieved 7 November 2013.
- ↑ "Faying Surface definition in Wiktionary" . Retrieved 8 November 2013.
http://www.eaa1000.av.org/technicl/corrosion/faysurf.htm Archived 2016-11-02 at the Wayback Machine