Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. For example, a person's income in an economic sense may be different from their income as defined by law.

In economics, an indifference curve connects points on a graph representing different quantities of two goods, points between which a consumer is indifferent. That is, any combinations of two products indicated by the curve will provide the consumer with equal levels of utility, and the consumer has no preference for one combination or bundle of goods over a different combination on the same curve. One can also refer to each point on the indifference curve as rendering the same level of utility (satisfaction) for the consumer. In other words, an indifference curve is the locus of various points showing different combinations of two goods providing equal utility to the consumer. Utility is then a device to represent preferences rather than something from which preferences come. The main use of indifference curves is in the representation of potentially observable demand patterns for individual consumers over commodity bundles.
In economics, elasticity measures the percentage change of one economic variable in response to a change in another. If a good's price elasticity of demand is -2, a 10% increase in price causes the quantity demanded to fall 20%.
The theory of consumer choice is the branch of microeconomics that relates preferences to consumption expenditures and to consumer demand curves. It analyzes how consumers maximize the desirability of their consumption as measured by their preferences subject to limitations on their expenditures, by maximizing utility subject to a consumer budget constraint.
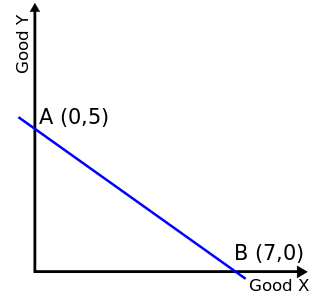
In economics, a budget constraint represents all the combinations of goods and services that a consumer may purchase given current prices within his or her given income. Consumer theory uses the concepts of a budget constraint and a preference map as tools to examine the parameters of consumer choices. Both concepts have a ready graphical representation in the two-good case. The consumer can only purchase as much as their income will allow, hence they are constrained by their budget. The equation of a budget constraint is where P_x is the price of good X, and P_y is the price of good Y, and m = income.
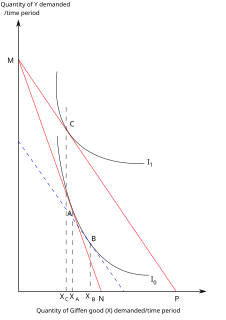
In economics and consumer theory, a Giffen good is a product that people consume more of as the price rises and vice versa—violating the basic law of demand in microeconomics. For any other sort of good, as the price of the good rises, the substitution effect makes consumers purchase less of it, and more of substitute goods; for most goods, the income effect reinforces this decline in demand for the good. But a Giffen good is so strongly an inferior good in the minds of consumers that this contrary income effect more than offsets the substitution effect, and the net effect of the good's price rise is to increase demand for it. This phenomenon is known as the Giffen paradox. A Giffen good is considered to be the opposite of an ordinary good.

In macroeconomics, aggregate demand (AD) or domestic final demand (DFD) is the total demand for final goods and services in an economy at a given time. It is often called effective demand, though at other times this term is distinguished. This is the demand for the gross domestic product of a country. It specifies the amount of goods and services that will be purchased at all possible price levels. Consumer spending, investment, corporate and government expenditure, and net exports make up the aggregate demand.
In microeconomics, two goods are substitutes if the products could be used for the same purpose by the consumers. That is, a consumer perceives both goods as similar or comparable, so that having more of one good causes the consumer to desire less of the other good. Contrary to complementary goods and independent goods, substitute goods may replace each other in use due to changing economic conditions. An example of substitute goods is Coca-Cola and Pepsi; the interchangeable aspect of these goods is due to the similarity of the purpose they serve, i.e fulfilling customers' desire for a soft drink. These types of substitutes can be referred to as close substitutes.
In economics and particularly in consumer choice theory, the income-consumption curve is a curve in a graph in which the quantities of two goods are plotted on the two axes; the curve is the locus of points showing the consumption bundles chosen at each of various levels of income.

Consumption is the act of using resources to satisfy current needs and wants. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of future income. Consumption a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences.

In microeconomics, the law of demand is a fundamental principle which states that there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded. In other words, "conditional on all else being equal, as the price of a good increases (↑), quantity demanded will decrease (↓); conversely, as the price of a good decreases (↓), quantity demanded will increase (↑)". Alfred Marshall worded this as: "When then we say that a person's demand for anything increases, we mean that he will buy more of it than he would before at the same price, and that he will buy as much of it as before at a higher price". The law of demand, however, only makes a qualitative statement in the sense that it describes the direction of change in the amount of quantity demanded but not the magnitude of change.
Output in economics is the "quantity of goods or services produced in a given time period, by a firm, industry, or country", whether consumed or used for further production. The concept of national output is essential in the field of macroeconomics. It is national output that makes a country rich, not large amounts of money.

In economics, a demand curve is a graph depicting the relationship between the price of a certain commodity and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price. Demand curves can be used either for the price-quantity relationship for an individual consumer, or for all consumers in a particular market.
Utility maximization was first developed by utilitarian philosophers Jeremy Bentham and John Stewart Mill. In microeconomics, the utility maximization problem is the problem consumers face: "How should I spend my money in order to maximize my utility?" It is a type of optimal decision problem. It consists of choosing how much of each available good or service to consume, taking into account a constraint on total spending (income), the prices of the goods and their preferences.

In economics, a country's national saving is the sum of private and public saving. It equals a nation's income minus consumption and the government spending.
There are two fundamental theorems of welfare economics. The first states that in economic equilibrium, a set of complete markets, with complete information, and in perfect competition, will be Pareto optimal. The requirements for perfect competition are these:
- There are no externalities and each actor has perfect information.
- Firms and consumers take prices as given.
Revealed preference theory, pioneered by economist Paul Anthony Samuelson in 1938, is a method of analyzing choices made by individuals, mostly used for comparing the influence of policies on consumer behavior. Revealed preference models assume that the preferences of consumers can be revealed by their purchasing habits.

The property of local nonsatiation of consumer preferences states that for any bundle of goods there is always another bundle of goods arbitrarily close that is preferred to it.
In economics and consumer theory, quasilinear utility functions are linear in one argument, generally the numeraire. Quasilinear preferences can be represented by the utility function where is strictly concave. A useful property of the quasilinear utility function is that the Marshallian/Walrasian demand for does not depend on wealth and is thus not subject to a wealth effect; The absence of a wealth effect simplifies analysis and makes quasilinear utility functions a common choice for modelling. Furthermore, when utility is quasilinear, compensating variation (CV), equivalent variation (EV), and consumer surplus are algebraically equivalent. In mechanism design, quasilinear utility ensures that agents can compensate each other with side payments.
In economics and other social sciences, preference is the order that a person gives to alternatives based on their relative utility, a process which results in an optimal "choice". Preferences are evaluations, they concern matters of value, typically in relation to practical reasoning. Instead of the prices of goods, personal income, or availability of goods, the character of the preferences is determined purely by a person's tastes. However, persons are still expected to act in their best interest. Rationality, in this context, means that when individuals are faced with a choice, they would select the option that maximizes self interest. Further, in every set of alternatives, preferences arise.








