Related Research Articles

Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, or Tarquin the Elder, was the legendary fifth king of Rome and first of its Etruscan dynasty. He reigned thirty-eight years. Tarquinius expanded Roman power through military conquest and grand architectural constructions. His wife was the prophetess Tanaquil.
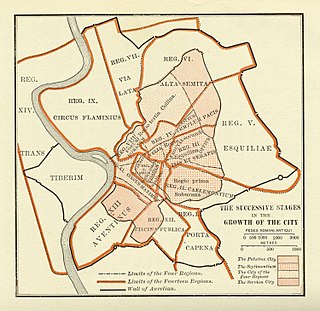
The Roman Kingdom was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began with the city's founding c. 753 BC, with settlements around the Palatine Hill along the river Tiber in central Italy, and ended with the overthrow of the kings and the establishment of the Republic c. 509 BC.

GnaeusMarcius Coriolanus was a Roman general who is said to have lived in the 5th century BC. He received his toponymic cognomen "Coriolanus" because of his exceptional valor in a Roman siege of the Volscian city of Corioli. He was subsequently exiled from Rome, and led troops of Rome's enemy the Volsci to besiege the city.
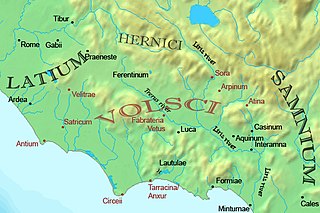
The Volsci were an Italic Osco-Umbrian tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the south, the Hernici on the east, and stretching roughly from Norba and Cora in the north to Antium in the south. Rivals of Rome for several hundred years, their territories were taken over by and assimilated into the growing republic by 300 BCE. Rome's first emperor Augustus was of Volscian descent.

The Aequi were an Italic tribe on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains to the east of Latium in central Italy who appear in the early history of ancient Rome. After a long struggle for independence from Rome, they were defeated and substantial Roman colonies were placed on their soil. Only two inscriptions believed to be in the Aequian language remain. No more can be deduced than that the language was Italic. Otherwise, the inscriptions from the region are those of the Latin-speaking colonists in Latin. The colonial exonym documented in these inscriptions is Aequi and also Aequicoli. The manuscript variants of the classical authors present Equic-, Aequic-, Aequac-. If the form without the -coli is taken as an original, it may well also be the endonym, but to date further evidence is lacking.

Lucius Junius Brutus was the semi-legendary founder of the Roman Republic, and traditionally one of its first consuls in 509 BC. He was reputedly responsible for the expulsion of his uncle the Roman king Tarquinius Superbus after the suicide of Lucretia, which led to the overthrow of the Roman monarchy. He was involved in the abdication of fellow consul Tarquinius Collatinus, and executed two of his sons for plotting the restoration of the Tarquins.

The Battle of Lake Regillus was a legendary Roman victory over the Latin League shortly after the establishment of the Roman Republic and as part of a wider Latin War. The Latins were led by an elderly Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, the seventh and last King of Rome, who had been expelled in 509 BC, and his son-in-law, Octavius Mamilius, the dictator of Tusculum. The battle marked the final attempt of the Tarquins to reclaim their throne. According to legend, Castor and Pollux fought on the side of the Romans.

Lars Porsena was an Etruscan king known for his war against the city of Rome. He ruled over the city of Clusium. There are no established dates for his rule, but Roman sources often place the war at around 508 BC.

Lavinium was a port city of Latium, 6 km (3.7 mi) to the south of Rome, midway between the Tiber river at Ostia and Antium. The coastline then, as now, was a long strip of beach. Lavinium was on a hill at the southernmost edge of the Silva Laurentina, a dense laurel forest, and the northernmost edge of the Pontine Marshes, a vast malarial tract of wetlands. The basis for the port, the only one between Ostia and Antium, was evidently the mouth of the Numicus river.

Publius Valerius Poplicola or Publicola was one of four Roman aristocrats who led the overthrow of the monarchy, and became a Roman consul, the colleague of Lucius Junius Brutus in 509 BC, traditionally considered the first year of the Roman Republic.
The Rutuli or Rutulians were an ancient people in Italy. The Rutuli were located in a territory whose capital was the ancient town of Ardea, located about 35 km southeast of Rome.
Monte Cavo, or less occasionally, "Monte Albano," is the second highest mountain of the complex of the Alban Hills, near Rome, Italy. An old volcano extinguished around 10,000 years ago, it lies about 20 km (12 mi) from the sea, in the territory of the comune of Rocca di Papa. It is the dominant peak of the Alban Hills. The current name comes from Cabum, an Italic settlement existing on this mountain.
The Roman–Etruscan Wars were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome and the Etruscans. Information about many of the wars is limited, particularly those in the early parts of Rome's history, and in large part is known from ancient texts alone. The conquest of Etruria was completed in 265–264 BC.
Octavius Mamilius was princeps of Tusculum, an ancient city of Latium. He was the son-in-law of Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, the seventh and last king of Rome. According to tradition, the gens Mamilia was descended from Mamilia, reputedly a granddaughter of Ulysses (Odysseus) and Circe. Titus Livius described Octavius as head of one of the most distinguished families of Latium, and thus an important ally of Tarquinius.
Turnus Herdonius was a leading citizen and statesman of ancient Aricia in Latium who spoke out against the last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, and was killed as a result.
The Roman–Latin wars were a series of wars fought between ancient Rome and the Latins, from the earliest stages of the history of Rome until the final subjugation of the Latins to Rome in the aftermath of the Latin War.
The Roman–Sabine wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their northern neighbours, the Sabines. It is commonly accepted that the events pre-dating the Roman Republic in 509 BC are semi-legendary in nature.
The Roman-Aequian wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their eastern neighbours, the Aequi.
Attius Tullius was a well-respected and influential political and military leader of the Volsci in the early fifth century BC: according to Plutarch, who calls him Tullus Aufidius, his home town was Antium. Tullius sheltered the exiled Roman hero Gaius Marcius Coriolanus, then incited a war with Rome, in which he and Coriolanus led the Volscian forces. He appears in William Shakespeare's tragedy Coriolanus under the name of Tullus Aufidius.
Pedum was an ancient town of Latium in central Italy, located between Tibur and Praeneste, near modern Gallicano nel Lazio. The town was a member of the Latin League.
References
- ↑ Livy Ab urbe condita 1.50-52
- ↑ Livy, Ab urbe condita , 2:37